Featured This month
-
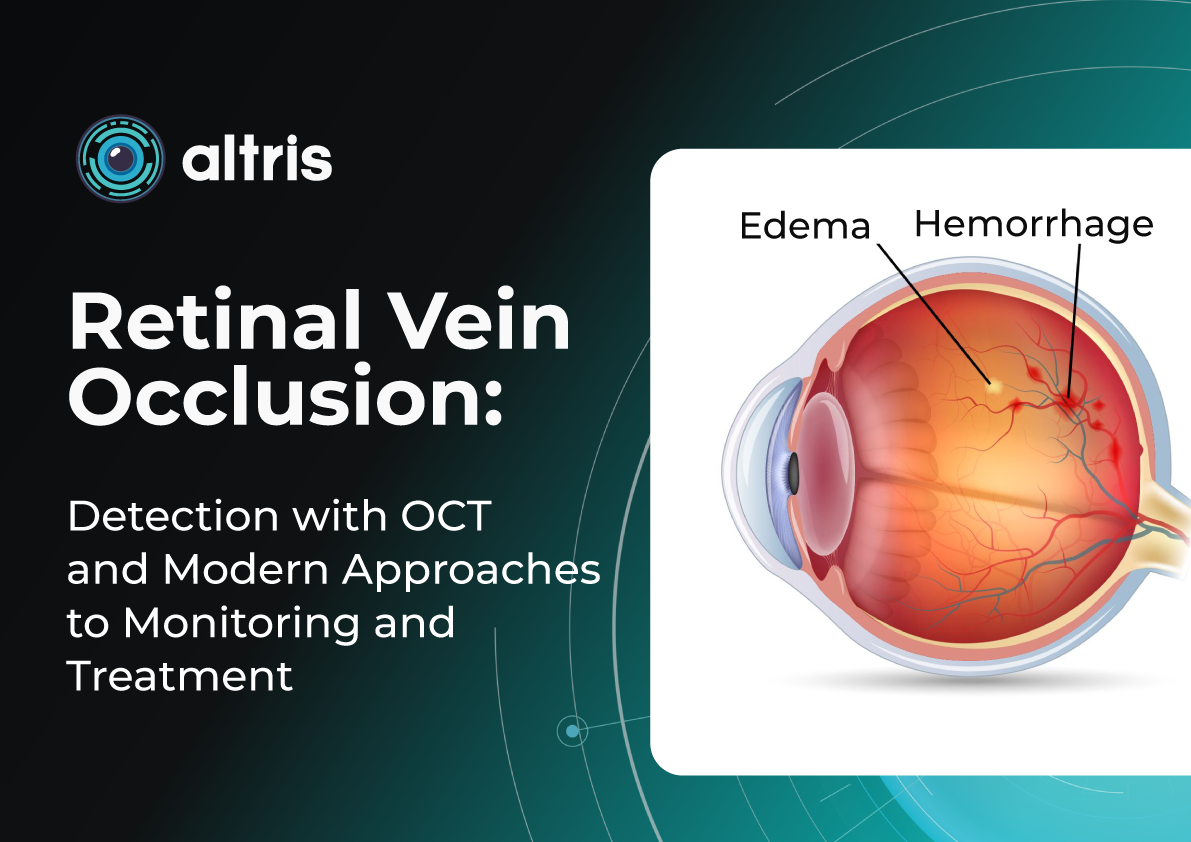
Retinal Vein Occlusion: Detection with OCT and Modern Approaches to Monitoring and Treatment
 Maria Znamenska
3 min.
Maria Znamenska
3 min.Introduction
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is one of the most common and clinically significant vascular disorders affecting the eye, often resulting in substantial visual impairment. This condition ranks second among causes of vision loss due to vascular disease, after diabetic retinopathy, placing a considerable burden on both healthcare systems and patients’ quality of life. Epidemiological studies show that the prevalence of RVO increases with age, and in populations with concomitant cardiovascular disease, the risk of developing occlusion rises severalfold.
Despite a long history of study, it is the breakthroughs in instrumental diagnostics over the past decade that have fundamentally changed our approach to recognizing and managing RVO. Previously, assessment of the macula and retinal vasculature relied primarily on ophthalmoscopy. While still an important tool, it has inherent limitations.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has revolutionized diagnostic standards. With its high resolution and ability to capture subtle structural changes within the retinal layers, OCT has become indispensable for determining disease severity, monitoring treatment efficacy, and conducting long-term follow-up. It allows for the detection of minimal early signs of edema, subclinical structural damage, and initial manifestations of ischemia—changes that were practically inaccessible for dynamic assessment 10–15 years ago.
This level of precision is particularly critical for patients at increased risk of RVO. The most vulnerable groups include individuals with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, coagulation disorders, as well as older adults, in whom the vascular walls may already have undergone degenerative or sclerotic changes.
Importantly, modern RVO treatments require objective dynamic monitoring. OCT enables precise evaluation of structural changes, tracking of therapeutic response, and individualization of treatment strategies, helping to avoid both overtreatment and undertreatment.
Thus, the role of OCT today goes far beyond simple visualization: it is a key tool for prognostic assessment, patient stratification, optimization of therapeutic decisions, and timely detection of complications.
1. What RVO Is and Why It Occurs?
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is a disruption of venous blood outflow in the retina due to partial or complete vein occlusion. As a result, the following occur:
- Blood stasis
- Increased venous pressure
- Impaired capillary perfusion
- Retinal edema, especially in the macular area
- Risk of neovascularization
Early detection is critical, as prompt treatment—particularly for macular edema—significantly increases the chances of preserving or restoring vision. Delayed diagnosis can lead to progression of ischemia, neovascularization, neovascular glaucoma, and persistent macular dysfunction.
RVO also has important systemic implications: patients with a history of RVO have a higher risk of acute cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure) compared with the general population. This emphasizes the need for comprehensive management, involving not only ophthalmologists but also other specialists, such as cardiologists.
Central vs. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion: Pathogenesis Differences
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) occurs when blockage happens at the level of the lamina cribrosa. Compression, arterial wall thickening, or thrombotic processes disrupt blood outflow from the entire retina. Typical signs include:
- Diffuse hemorrhages
- Marked macular edema
- Increased risk of optic disc and iris neovascularization due to severe ischemia
- Generally worsen prognosis than branch occlusions
- Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) usually occurs at arteriovenous crossings, where a thickened artery compresses a vein, causing localized occlusion. Characteristic features include:
- Localized edema and hemorrhages
- Clear segmental distribution
- Prognosis is generally better than that of CRVO, though macular edema may persist
Key Risk Factors for RVO
Modern studies and guidelines identify the following as the main risk factors:- Arterial hypertension
- Atherosclerosis and age-related vascular changes
- Diabetes mellitus (even without diabetic retinopathy)
- Glaucoma and elevated IOP
- Hypercoagulable states, thrombophilia
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Age >50 years
Rare cases of RVO associated with thromboembolic complications after COVID‑19 infection or vaccination have also been reported, highlighting the ongoing relevance of thrombotic mechanisms.
Impact on Microcirculation and Vision
RVO leads to:- Impaired normal venous outflow
- Sharp elevation of hydrostatic venous pressure
- Damage to the blood-retinal barrier
- Leakage of plasma and cellular elements into the retinal interstitium, causing macular edema
- Development of ischemic zones
- Over time, thinning of inner retinal layers, neuroepithelial atrophy, and damage to the photoreceptor layer
These changes are best assessed with OCT, which enables precise patient stratification and treatment planning. Timely diagnosis, proper monitoring, and early therapy are essential.
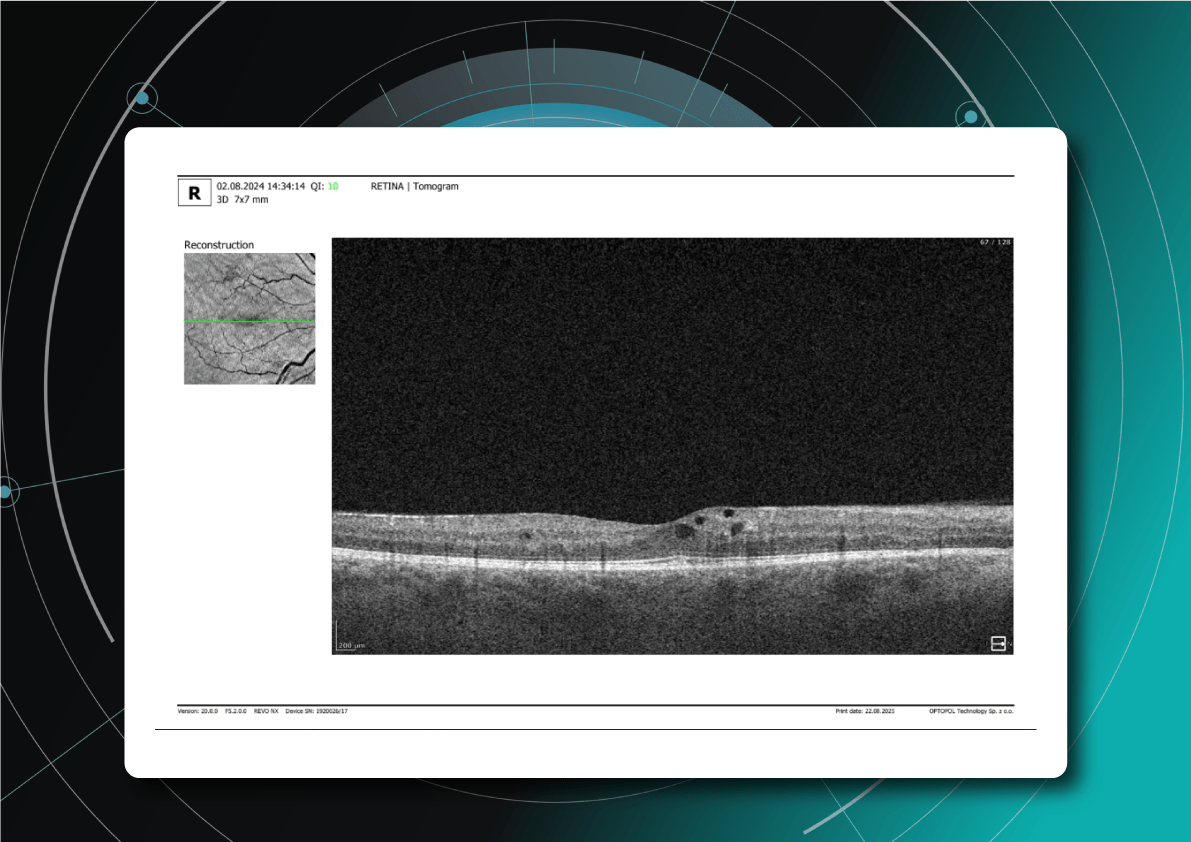
2. OCT Signs of Retinal Vein Occlusion: Detecting Subtle Changes
With the advent of OCT, detection of structural retinal changes in RVO has significantly improved—even at early stages without obvious clinical signs.
Acute Stage Changes (first weeks after occlusion)
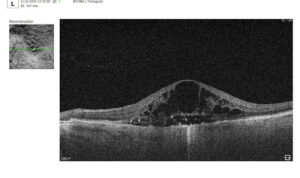
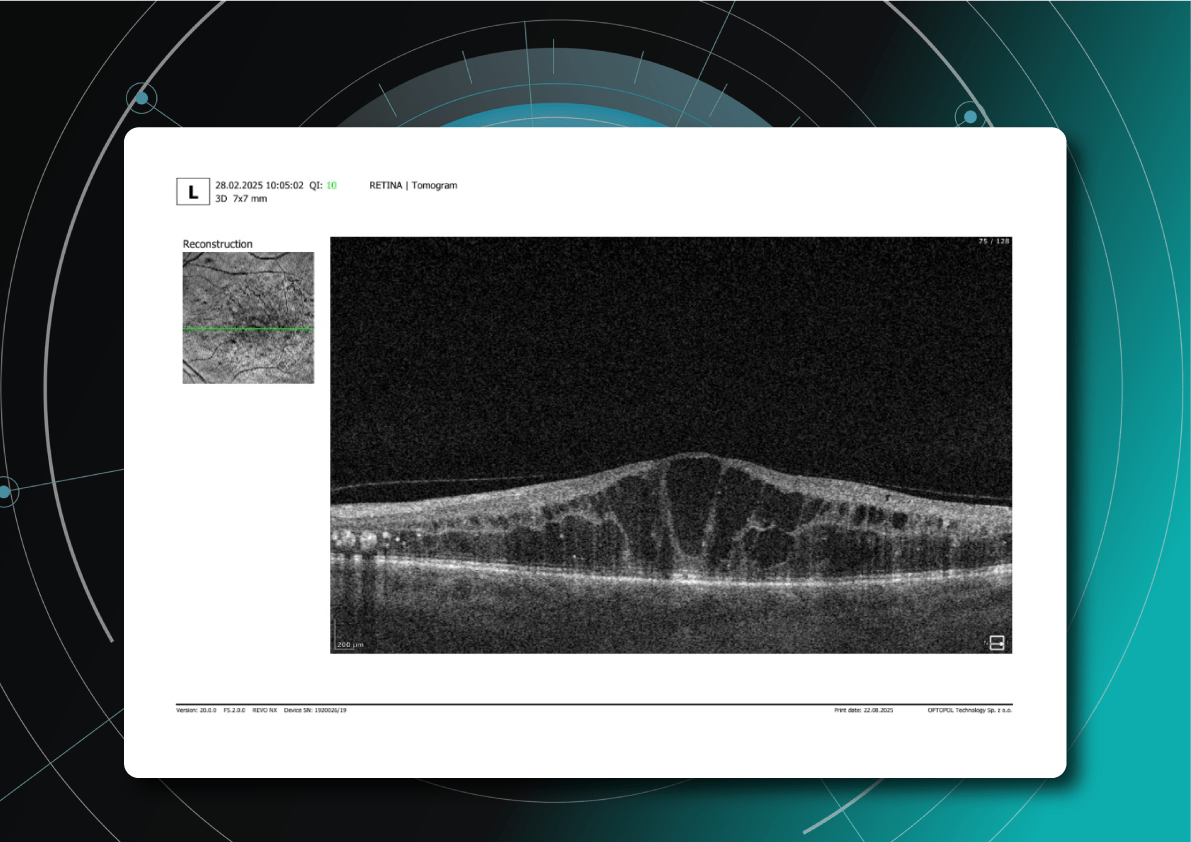
- Macular edema:
- Cystic spaces in inner retinal layers (INL, OPL)
- Increased central retinal thickness
- Subretinal fluid (serous neurosensory detachment)
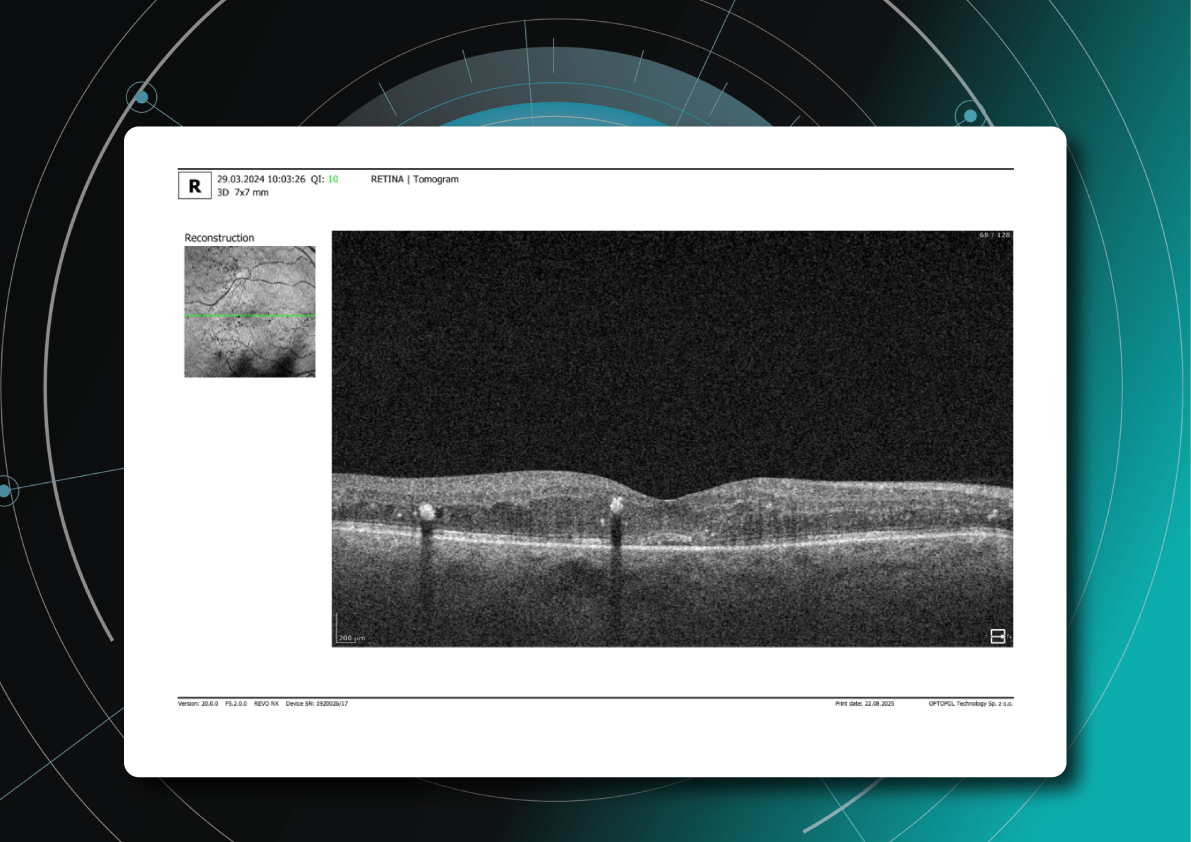
- Intraretinal hemorrhages: appear on OCT as hyperreflective areas with shadowing of underlying layers
- Ischemia indicators:
- Hyperreflectivity of neuroepithelium
- Cotton-wool spots
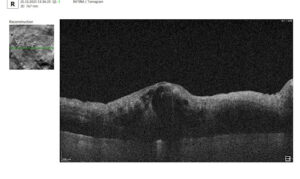
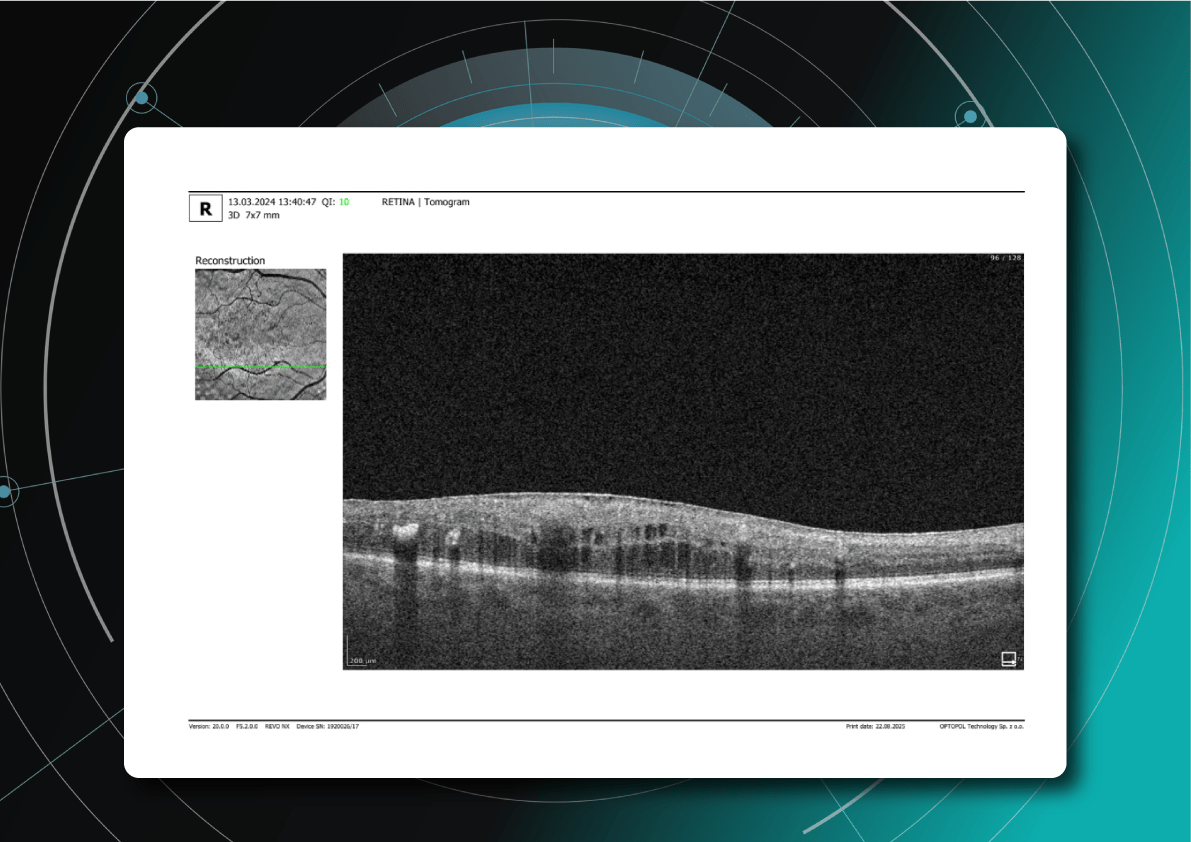
Chronic Stage Changes (months later)
- Chronic ischemic and atrophic changes (thinning of inner retinal layers)
- Disruption of photoreceptor layer (ELM and EZ)
- Disorganization of inner retinal layers (DRIL)
- Persistent edema (>6 months) indicates chronic RVO requiring therapeutic adjustment
AI for OCT thus allows both acute diagnosis and long-term monitoring of ischemic progression or tissue remodeling.




3. Assessment of Macular Changes in RVO Using OCT
OCT is now considered the gold standard for diagnosing, monitoring, and assessing treatment response in macular edema, including that associated with RVO.
OCT is highly sensitive for:
- Quantitative and qualitative analysis (central retinal thickness [CRT], macular volume [MV], size and number of cystic spaces, DRIL, photoreceptor layer integrity)
- Evaluating treatment response
- Detecting minimal residual cysts
- Predicting visual acuity outcomes
Typical OCT Findings in RVO:
- Diffuse retinal thickening
- Cystoid macular edema (localized cysts deforming normal retinal architecture)
- Serous neurosensory detachment (indicative of blood-retinal barrier breakdown)
- Disruption of EZ and ELM (photoreceptor involvement, critical for final visual acuity)
These capabilities make OCT an integral part of modern RVO monitoring.



4. Top 3 Challenges in RVO OCT Analysis
Despite its power, OCT assessment of RVO has significant limitations:
- Need for normative comparison
Interpretation requires comparison with the patient’s contralateral eye or established normal values. Systemic vascular anomalies can affect both eyes, limiting standardization. - Complexity with comorbidities
Many RVO patients have systemic (hypertension, diabetes) or ophthalmic comorbidities (diabetic retinopathy, AMD, glaucoma, epiretinal membrane), complicating interpretation. It can be difficult to distinguish RVO-related changes from combined pathology. - Requirement to consider clinical context
OCT provides only part of the clinical picture. Accurate interpretation requires integration of symptoms, medical history, systemic factors, fundoscopic findings, and other diagnostic tests. Anatomical variations, comorbidities (glaucoma, cataract), and individual treatment response also necessitate a personalized approach.
5. Treatment of RVO: Modern Approaches
Currently, no treatment restores normal retinal venous circulation. Therefore, therapy focuses on controlling complications, primarily macular edema and preventing neovascularization (retinal, iris/optic disc, neovascular glaucoma, hemorrhages, and tractional changes).
All RVO patients should receive systemic management, ideally in collaboration between an ophthalmologist and a cardiologist or internist. Monitoring of blood pressure, lipids, glucose, and coagulation factors is essential, as RVO often signals systemic vascular risk.
Treatment decisions must be individualized, considering:
- RVO subtype (CRVO vs. BRVO)
- Edema severity
- Clinical and OCT findings
- Risk of adverse effects
- Patient status (comorbidities, ability for regular follow-up)
Anti-VEGF Therapy as First-Line Treatment
Intravitreal anti-VEGF injections are the first-line therapy for macular edema associated with RVO. These drugs reduce vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, lowering vascular permeability, fluid leakage, edema, and inhibiting pathological neovascularization.
Commonly used agents:
- Ranibizumab, Aflibercept, Faricimab: proven safe and effective for CRVO and BRVO-related macular edema; studies show significant improvements in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and central macular thickness (CMT).
- Bevacizumab: used off-label for macular edema and neovascularization.
Long-term studies indicate anti-VEGF therapy provides sustained visual improvement for many patients, with injection frequency often decreasing over time.
Advantages:
- High efficacy for macular edema
- Good tolerability and safety (systemic complications are rare)
- Personalized treatment possible
Limitations / Challenges:
- Some patients respond insufficiently
- Requires frequent injections (clinic visits, financial burden, potential complications, patient discomfort)
- Chronic or refractory edema may require alternative or combination approaches
Steroid Implants and Injections: Second-Line Therapy
Dexamethasone intravitreal implant (OZURDEX) is approved for RVO-related macular edema, particularly when:
- Anti-VEGF therapy is insufficient
- Frequent injections are impractical (distance, transportation, cost)
Steroids reduce inflammation, vascular permeability, and fluid accumulation, useful in chronic or resistant edema.
Risks / Limitations:
- Cataract (especially with repeated or long-term use)
- Increased intraocular pressure (IOP), potential steroid-induced glaucoma
Laser Therapy
- Panretinal photocoagulation is effective for neovascularization.
- Its use has declined with anti-VEGF availability, which offers strong anatomical and functional results.
Surgical Approaches
- Vitrectomy may be considered in selected cases.
- Surgery carries risks and is reserved for situations where other treatments fail or are inappropriate.
Combination Strategies
- In practice, clinicians often combine anti-VEGF therapy with steroid implants or laser treatment, depending on disease course.
- This can reduce total injection burden, minimize side effects, and improve outcomes in chronic or recurrent edema.
Monitoring Frequency
- Active macular edema or ongoing treatment requires regular OCT follow-up to evaluate therapeutic response and adjust injection intervals.
- OCT schedule:
- Monthly at treatment initiation
- Individualized intervals using Treat-and-Extend protocols
- Structural monitoring to prevent atrophic changes
- Ischemic RVO patients have the highest neovascularization risk within the first 90 days; monthly monitoring during the first 6 months is critical.
Conclusions and Recommendations
RVO is a complex, multifactorial vascular disorder that can cause sudden and severe vision loss, particularly in patients with systemic risk factors. Modern management aims not only to address acute complications but also to control long-term structural retinal changes.
OCT has transformed RVO care by providing:
- Early detection of edema, subclinical ischemia, and architectural changes
- Dynamic monitoring of treatment response, allowing timely adjustments and optimization
- Improved long-term prognostication through evaluation of macular thickness, outer retinal layers, and fluid volume
OCT helps identify edema type and secondary changes—atrophy, photoreceptor damage, inner retinal thinning—allowing a more accurate visual prognosis, especially in ischemic RVO.
When combined with modern anti-VEGF agents, long-acting steroid implants, and personalized dosing regimens, OCT enables:
- Reduction of unnecessary injections via interval optimization
- Maximized treatment efficacy based on morphological findings
- Prevention of recurrence and progression through early detection of edema
Thus, OCT is not merely a visualization tool but a core element of clinical decision-making, improving patient management, preventing complications, and enabling more complete and stable visual recovery.
Clinical Recommendation: Integrate regular OCT assessments into RVO management, with attention to macular thickness dynamics and outer retinal layer integrity for precise disease control and optimized therapeutic outcomes.
References:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38714470/
- https://www.rcophth.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Retinal-Vein-Occlusion-Guidelines-Executive-Summary-2022.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/14/4/1183
- https://www.auctoresonline.org/article/clinical-therapeutic-orientation-in-retinal-venous-obstruction
- https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/10/3/405
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10801953
- https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/13/19/3100
- https://karger.com/oph/article-abstract/242/1/8/255831/Microvascular-Retinal-and-Choroidal-Changes-in?redirectedFrom=fulltext
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-024-01077-9
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39717563/
- https://provider-rvo.vision-relief.com/introduction/management/
-
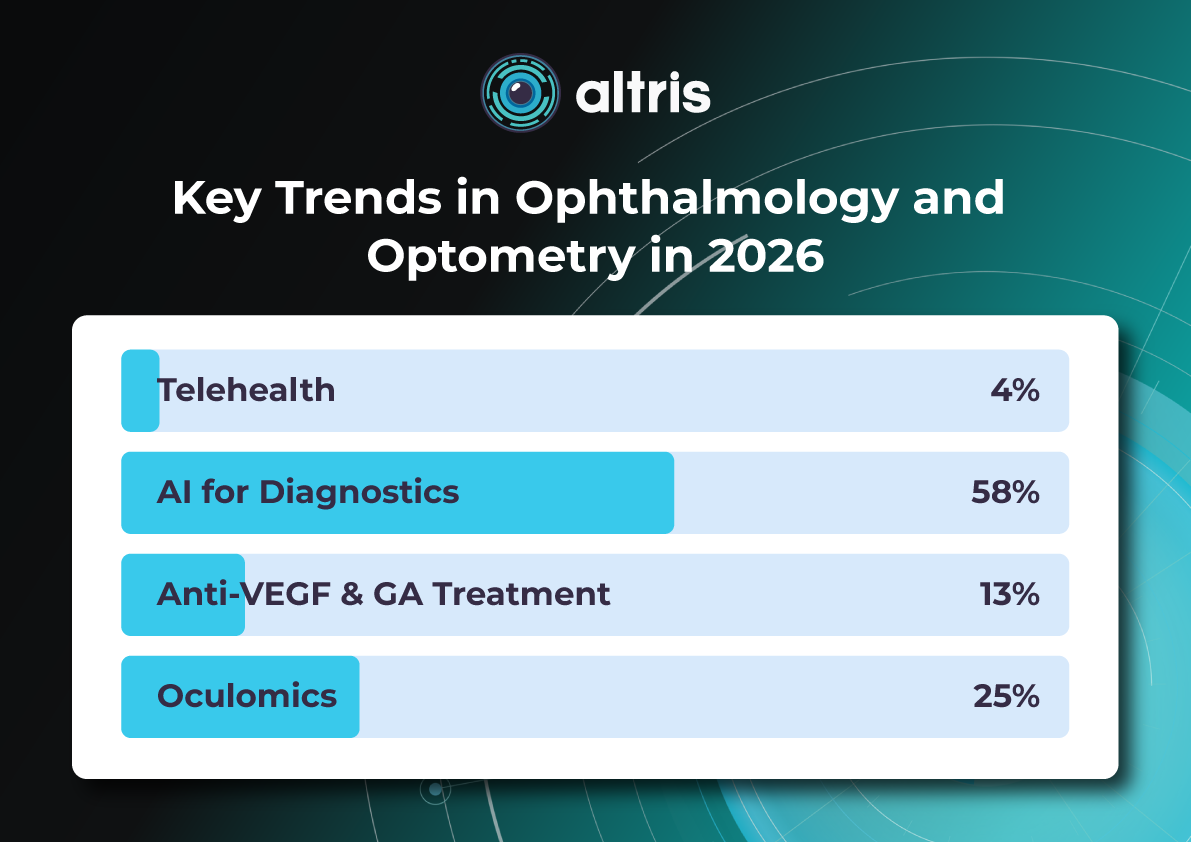
Key Trends in Ophthalmology and Optometry in 2026

 Maria Znamenska
3 min.
Maria Znamenska
3 min.Introduction
The year 2026 in ophthalmology will not be defined by a single “major breakthrough,” but rather by the maturation of several directions whose discoveries and innovations are now transitioning into everyday clinical practice. While just a few years ago innovations were often perceived as isolated technologies far removed from real-world care (a new drug, device, or piece of equipment), today entire ecosystems are being formed: from early detection to long-term monitoring, from the ophthalmologist’s office to optometric screening, from a single consultation to a longitudinal patient journey supported by digital tools.
The core logic of 2026 is a shift from reactive to proactive ophthalmology. Increasingly, the goal is to prevent disease at the stage of risk-factor modification, intervene in the earliest pathological changes, and track preclinical markers. This shift is visible across several dimensions: the growing role of telemedicine and portable diagnostics; autonomous AI becoming a public health tool; and oculomics, which enables ocular image analysis to serve as a source of early biomarkers for systemic conditions. At the same time, the treatment paradigm is evolving: where repeated procedures once dominated (for example, frequent intravitreal injections), 2026 brings a move toward extended-duration regimens, implant-based drug delivery platforms, and disease control with fewer clinic visits.
Another important axis is the alignment of patient expectations. Some new approaches (for example, in the management of dry AMD and geographic atrophy) do not promise to “restore vision,” but rather to buy time—slowing structural retinal damage and functional vision loss. As a result, in 2026, risk–benefit communication and shared decision-making become almost as important as the choice of molecule or device itself.
Below, we outline the key eye care trends of 2026: what is changing, why it matters, and how it will shape ophthalmic and optometric practice.

1. New Approaches to Treatment
1.1. Geographic Atrophy (GA): The Introduction of Active Treatment in eye care trends 2026
1.1.1. Injectable Therapies as Ophthalmology Trends 2026
Following the development of injectable therapies for geographic atrophy, clinical practice is entering a “second wave” phase—where the main questions are no longer whether therapy is possible for a disease historically considered untreatable, but how that therapy should be practically implemented. In 2026, the focus will be on patient selection, treatment initiation, dosing frequency and duration, as well as monitoring.
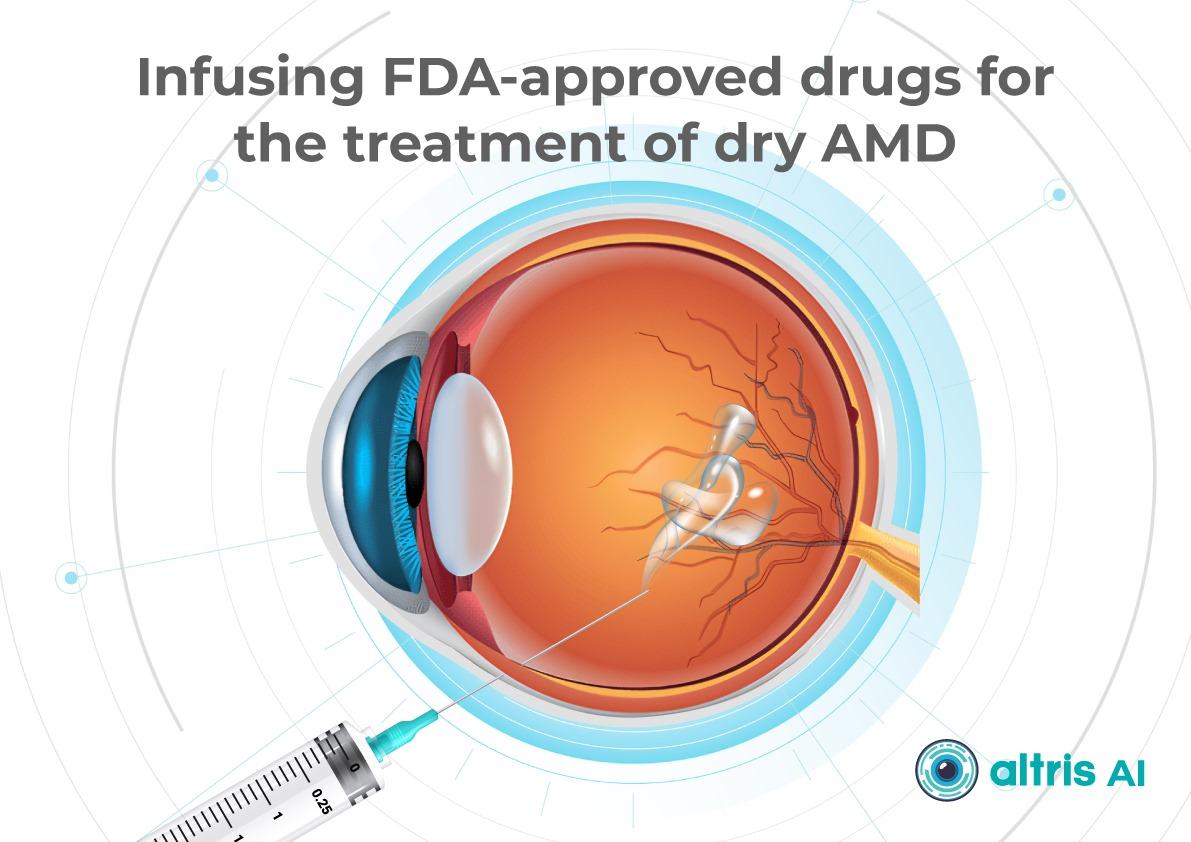
Currently, the FDA has approved the following injectable therapies for GA:
- Izervay (avacincaptad pegol) — a C5 complement inhibitor.
- Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) — a C3 complement inhibitor.
Their mechanism of action involves reducing chronic inflammation and cellular damage in the retina and—most importantly—slowing the rate of GA lesion expansion.
Because most available data focus on slowing atrophy progression (an anatomical endpoint) rather than guaranteed improvements in visual acuity, properly managing patient expectations becomes particularly critical in 2026. Clear discussions about therapeutic goals and limitations are emphasized in review publications addressing the first approved GA treatments.

1.1.2. Multiwavelength Photobiomodulation
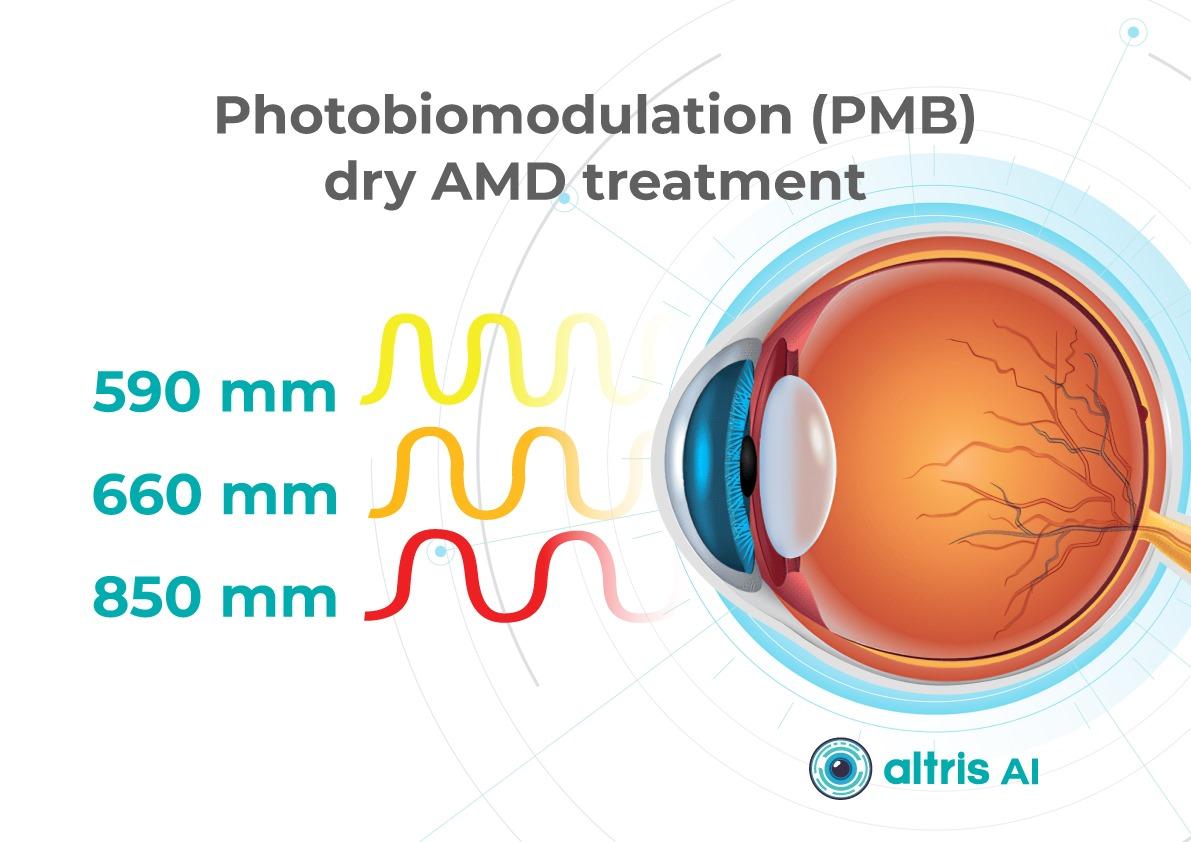
Multiwavelength photobiomodulation is one of the most promising emerging approaches aimed at halting or slowing the progression of dry AMD through modulation of mitochondrial activity. The use of specific wavelengths (red and near-infrared light, approximately 590–850 nm) may reduce oxidative stress in retinal cells, inflammation, and apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelium cells.
Its appeal is clear: a non-invasive procedure with significantly better acceptability for some patients compared with regular injections.
Until recently, its effectiveness remained debated, with studies showing only temporary functional improvement and reduction in drusen volume. At ARVO 2025, updated results from the LIGHTSITE III study demonstrated that photobiomodulation can significantly slow visual acuity decline and reduce the rate of GA expansion.
In 2025, the FDA approved photobiomodulation for AMD, creating strong prospects for broader clinical adoption in 2026.
The 2026 trend is correct positioning and stratification:
- Use of photobiomodulation based on clear indications for specific dry AMD stages and patient profiles.
- Transparent communication of expectations, with goals focused on functional support and slowing GA progression rather than guaranteed vision restoration.

1.2. Extended Anti-VEGF Treatment Regimens
Another major trend is the shift toward regimens with reduced injection frequency. This is not merely about comfort, but primarily about preventing missed visits: patients with AMD and diabetic retinopathy with DME often fall out of treatment due to visit burden. Thus, 2026 reinforces the principle that treatment must be effective in real-world conditions, not only under ideal adherence.
The ranibizumab port delivery system (Susvimo, Port Delivery System) has become emblematic of this trend. In 2025, the FDA also approved Susvimo for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
1.3. Gene Therapy for Macular Telangiectasia Type 2 (MacTel 2)
MacTel 2 is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative retinal disease that previously lacked active treatment.
In 2025, the first implantation of ENCELTO (revakinagene taroretcel)—the first and currently only FDA-approved gene therapy for MacTel 2—was performed in the United States. ENCELTO enables a shift from observation to active intervention, with the potential to preserve visual function in early-stage patients.
The device is based on encapsulated cell therapy technology: a capsule containing genetically modified cells that continuously secrete recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), acting as a neuroprotective agent that slows photoreceptor degeneration.
In 2026, the focus will move from “innovation storytelling” to routine clinical implementation, including defining early selection criteria, monitoring protocols (OCT biomarkers, functional testing), and accumulating real-world long-term data on photoreceptor preservation and visual function.
1.4. Gene Therapy for Neovascular AMD: Closest to Real Transformation
For neovascular AMD, gene therapy remains one of the most anticipated eye care trends 2026 directions, as it has the potential to fundamentally change treatment logic—from repeated injections to a single vector administration enabling long-term therapeutic protein expression. Reviews published in 2025 highlight active programs such as RGX-314, ADVM-022 (Ixo-vec), 4D-150, and others.
In 2026, the key questions shift from “does it work?” to “how does it work across different patient groups?” including:
- Stability and duration of expression;
- Inflammatory and immune response profiles;
- Need for supplemental anti-VEGF therapy;
- Patient selection criteria;
Injection centers and post-procedure monitoring standards.
2. Oculomics: The Eye as a “Window to the Body” and a Source of Digital Biomarkers
Oculomics is one of the most compelling trends of 2026, as it reshapes ophthalmology’s role within medicine as a whole. The concept is simple: the eye is the only structure where microvasculature, neurons, and signs of metabolic and inflammatory processes can be visualized non-invasively at high resolution. As a result, fundus and OCT/OCTA data may serve as biomarkers for systemic conditions—from cardiovascular risk to neurodegenerative diseases.

In contemporary research, oculomics is described as an approach that uses retinal images to assess systemic risks and conditions, with potential scalability for screening. In 2026, this “scale” becomes critical: data may originate not only from ophthalmology clinics, but also from optometric practices, mobile screening programs, and telemedicine.
What truly changes in 2026:
- A transition from “interesting correlations” to clinical utility, with models expected to demonstrate actionable impact on patient management.
- Data verification and management of false-positive risk, including the communication of systemic risk to patients.
- Integration with AI, as multidimensional patterns often exceed human interpretive capacity.
A major risk in 2026 is over-marketing, reinforcing the need for externally validated models with clear clinical context that do not generate unnecessary “medical noise.”
3. AI Technologies: From Decision Support to Autonomous Screening and Managed Patient Pathways

3.1. Autonomous Diabetic Retinopathy Screening as a Scalable Standard
In 2026, diabetic retinopathy remains the most studied use case for autonomous AI. In the United States, three FDA-approved autonomous DR screening systems are already described (LumineticsCore/IDx-DR, EyeArt, AEYE-DS). This positions AI as a practical tool capable of influencing large-scale screening programs, particularly in primary care, endocrinology clinics, and mobile settings.
The FDA approval of AEYE-DS as a fully autonomous solution (portable camera plus algorithm) underscores that in 2026, AI increasingly “works where the patient is,” not only where an ophthalmologist is present.
3.2. 2026 as the Year of Integration
Successful projects in 2026 will be distinguished by:
- Image quality standards and quality control;
- Clear referral rules and urgency levels;
- Mechanisms to ensure patient follow-through (scheduling, reminders, visit tracking);
- Transparent documentation for clinicians, patients, and audit purposes.
3.3. AI as “Invisible Infrastructure”
In 2026, AI increasingly functions as invisible infrastructure: highlighting high-risk cases, prioritizing queues, generating structured reports, and standardizing interpretation. The impact is reduced variability, faster routing, and fewer missed cases.
4. Telemedicine: From Video Calls to Retinal Screening and Remote Management
By 2026, telemedicine in ophthalmology is no longer synonymous with video consultations. Its foundation is tele-imaging: transmission and assessment of retinal images (fundus photos, sometimes OCT) with structured referral protocols.
At the same time, limitations become more openly discussed. Certain conditions and components of assessment may be less accurately captured remotely, requiring clear protocols to define which patients can be managed remotely and which require in-person examination.
The 2026 trend is a shift from “tool” to “pathway”:
- Tele-screening as the first step;
- Automated or semi-automated reporting;
- Referral and follow-up control;
Remote reassessment for ongoing risk monitoring.
5. New Devices and Portable Diagnostics: Closer, Faster, More Scalable Care

5.1. Portable Diagnostics as the Foundation of Coverage
Portable fundus cameras and compact diagnostic systems represent one of the most practical changes of 2026. Their value lies not only in technology, but in enabling large-scale screening in locations without full ophthalmic infrastructure.
Synergy with autonomous AI (such as AEYE-DS) is especially strong here, supporting new partnership models:
- Endocrinology and primary care clinics;
- Optical stores and optometric practices;
- Mobile programs for workplaces or regions.
5.2. Devices Deliver Value Only with Quality Protocols
Success depends not just on acquiring devices, but on defined protocols:
- Staff training in image acquisition;
- Minimum quality criteria;
- Retake rules;
- Handling ungradable cases.
In 2026, image quality becomes decisive, as AI and telemedicine depend on it.
5.3. Home and Remote Monitoring for Extended Treatment Regimens as eye care trends 2026
As treatment intervals lengthen, the risk of between-visit deterioration increases. Thus, 2026 strengthens the role of:
- Home functional monitoring;
- Digital questionnaires and symptom trackers;
Remote checkpoints signaling the need for earlier recall.
6. 2026 as the Year of Standardized Myopia Control and Greater Risk Awareness
By 2026, myopia control is no longer debated but formalized, grounded in consensus documents and systematic reviews. Myopia is increasingly recognized as a chronic disease with stages, phenotypes, and potentially blinding complications.
Implications for practice:
- Focus on preventing progression to high myopia.
- Combined strategies integrating behavioral, optical, and pharmacologic interventions with monitoring.
- A shared language between optometrists and ophthalmologists, with coordinated patient pathways.
- Support from AI and telemedicine for risk detection and personalized care.
Myopia control in 2026 becomes a structured, long-term risk-reduction process.
7. Optogenetics: Expanding the Evidence Horizon in Inherited Retinal Degenerations
In 2026, optogenetics moves beyond concept into longer-term observation. Publications from 2025 highlight functional stabilization or improvement in retinitis pigmentosa, emphasizing pragmatic success criteria.
For patients with severe vision loss, meaningful outcomes extend beyond visual acuity charts to spatial orientation, object recognition, and contrast sensitivity. In 2026, discussions increasingly focus on realistic endpoints and honest communication of limitations.
8. Less Invasive Interventions and Patient Comfort as Components of Clinical Effectiveness
Another key eye care trends 2026 is less traumatic technology that preserves efficacy while improving patient experience. A notable example is the FDA approval of Epioxa (epi-on) for keratoconus in 2025, preserving corneal epithelium and potentially reducing pain and recovery time.
This trend spans refractive surgery, ocular surface disease, and chronic condition management, reinforcing that patient experience is integral to adherence and clinical outcomes.

Conclusion
The ophthalmology trends 2026 clearly demonstrate that ophthalmology and optometry are entering a phase of mature transformation, where success is driven not by isolated innovations but by their integration into coherent clinical pathways. The focus is shifting from treating consequences to early detection, slowing progression, and long-term management of chronic eye disease.
Active treatment of geographic atrophy, photobiomodulation, extended anti-VEGF regimens, and the emergence of gene therapies for MacTel 2 and neovascular AMD fundamentally reshape patient management—from observation or frequent procedures to strategies aimed at preserving retinal structure and function with minimal procedural burden. These approaches require careful patient stratification and responsible expectation management, as the goal increasingly becomes slowing neurodegeneration rather than restoring vision.
At the diagnostic level, 2026 reinforces decentralization: portable devices, telemedicine, and autonomous AI bring screening closer to patients and enable coverage of much broader populations. Oculomics and AI transform ocular images into sources of digital biomarkers that may influence not only ophthalmic but also general clinical management. At the same time, it becomes clear that technological value is defined not by algorithms or devices, but by data quality, model validation, and clearly structured patient pathways—from screening to treatment.
popular Posted
-
Retinal Vein Occlusion: Detection with OCT and Modern Approaches to Monitoring and Treatment

 Maria Znamenska
3 min.
Maria Znamenska
3 min.Introduction
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is one of the most common and clinically significant vascular disorders affecting the eye, often resulting in substantial visual impairment. This condition ranks second among causes of vision loss due to vascular disease, after diabetic retinopathy, placing a considerable burden on both healthcare systems and patients’ quality of life. Epidemiological studies show that the prevalence of RVO increases with age, and in populations with concomitant cardiovascular disease, the risk of developing occlusion rises severalfold.
Despite a long history of study, it is the breakthroughs in instrumental diagnostics over the past decade that have fundamentally changed our approach to recognizing and managing RVO. Previously, assessment of the macula and retinal vasculature relied primarily on ophthalmoscopy. While still an important tool, it has inherent limitations.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) has revolutionized diagnostic standards. With its high resolution and ability to capture subtle structural changes within the retinal layers, OCT has become indispensable for determining disease severity, monitoring treatment efficacy, and conducting long-term follow-up. It allows for the detection of minimal early signs of edema, subclinical structural damage, and initial manifestations of ischemia—changes that were practically inaccessible for dynamic assessment 10–15 years ago.
This level of precision is particularly critical for patients at increased risk of RVO. The most vulnerable groups include individuals with arterial hypertension, diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, coagulation disorders, as well as older adults, in whom the vascular walls may already have undergone degenerative or sclerotic changes.
Importantly, modern RVO treatments require objective dynamic monitoring. OCT enables precise evaluation of structural changes, tracking of therapeutic response, and individualization of treatment strategies, helping to avoid both overtreatment and undertreatment.
Thus, the role of OCT today goes far beyond simple visualization: it is a key tool for prognostic assessment, patient stratification, optimization of therapeutic decisions, and timely detection of complications.
1. What RVO Is and Why It Occurs?
Retinal vein occlusion (RVO) is a disruption of venous blood outflow in the retina due to partial or complete vein occlusion. As a result, the following occur:
- Blood stasis
- Increased venous pressure
- Impaired capillary perfusion
- Retinal edema, especially in the macular area
- Risk of neovascularization
Early detection is critical, as prompt treatment—particularly for macular edema—significantly increases the chances of preserving or restoring vision. Delayed diagnosis can lead to progression of ischemia, neovascularization, neovascular glaucoma, and persistent macular dysfunction.
RVO also has important systemic implications: patients with a history of RVO have a higher risk of acute cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure) compared with the general population. This emphasizes the need for comprehensive management, involving not only ophthalmologists but also other specialists, such as cardiologists.
Central vs. Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion: Pathogenesis Differences
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO) occurs when blockage happens at the level of the lamina cribrosa. Compression, arterial wall thickening, or thrombotic processes disrupt blood outflow from the entire retina. Typical signs include:
- Diffuse hemorrhages
- Marked macular edema
- Increased risk of optic disc and iris neovascularization due to severe ischemia
- Generally worsen prognosis than branch occlusions
- Branch Retinal Vein Occlusion (BRVO) usually occurs at arteriovenous crossings, where a thickened artery compresses a vein, causing localized occlusion. Characteristic features include:
- Localized edema and hemorrhages
- Clear segmental distribution
- Prognosis is generally better than that of CRVO, though macular edema may persist
Key Risk Factors for RVO
Modern studies and guidelines identify the following as the main risk factors:- Arterial hypertension
- Atherosclerosis and age-related vascular changes
- Diabetes mellitus (even without diabetic retinopathy)
- Glaucoma and elevated IOP
- Hypercoagulable states, thrombophilia
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Age >50 years
Rare cases of RVO associated with thromboembolic complications after COVID‑19 infection or vaccination have also been reported, highlighting the ongoing relevance of thrombotic mechanisms.
Impact on Microcirculation and Vision
RVO leads to:- Impaired normal venous outflow
- Sharp elevation of hydrostatic venous pressure
- Damage to the blood-retinal barrier
- Leakage of plasma and cellular elements into the retinal interstitium, causing macular edema
- Development of ischemic zones
- Over time, thinning of inner retinal layers, neuroepithelial atrophy, and damage to the photoreceptor layer
These changes are best assessed with OCT, which enables precise patient stratification and treatment planning. Timely diagnosis, proper monitoring, and early therapy are essential.
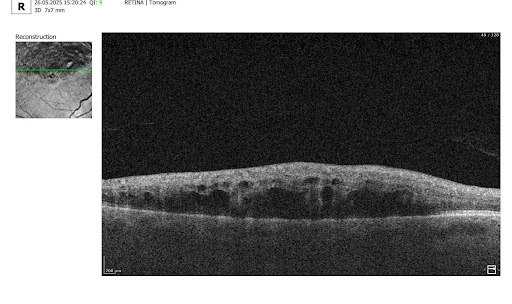
2. OCT Signs of Retinal Vein Occlusion: Detecting Subtle Changes
With the advent of OCT, detection of structural retinal changes in RVO has significantly improved—even at early stages without obvious clinical signs.
Acute Stage Changes (first weeks after occlusion)
- Macular edema:
- Cystic spaces in inner retinal layers (INL, OPL)
- Increased central retinal thickness
- Subretinal fluid (serous neurosensory detachment)
- Intraretinal hemorrhages: appear on OCT as hyperreflective areas with shadowing of underlying layers
- Ischemia indicators:
- Hyperreflectivity of neuroepithelium
- Cotton-wool spots
Chronic Stage Changes (months later)
- Chronic ischemic and atrophic changes (thinning of inner retinal layers)
- Disruption of photoreceptor layer (ELM and EZ)
- Disorganization of inner retinal layers (DRIL)
- Persistent edema (>6 months) indicates chronic RVO requiring therapeutic adjustment
AI for OCT thus allows both acute diagnosis and long-term monitoring of ischemic progression or tissue remodeling.




3. Assessment of Macular Changes in RVO Using OCT
OCT is now considered the gold standard for diagnosing, monitoring, and assessing treatment response in macular edema, including that associated with RVO.
OCT is highly sensitive for:
- Quantitative and qualitative analysis (central retinal thickness [CRT], macular volume [MV], size and number of cystic spaces, DRIL, photoreceptor layer integrity)
- Evaluating treatment response
- Detecting minimal residual cysts
- Predicting visual acuity outcomes
Typical OCT Findings in RVO:
- Diffuse retinal thickening
- Cystoid macular edema (localized cysts deforming normal retinal architecture)
- Serous neurosensory detachment (indicative of blood-retinal barrier breakdown)
- Disruption of EZ and ELM (photoreceptor involvement, critical for final visual acuity)
These capabilities make OCT an integral part of modern RVO monitoring.



4. Top 3 Challenges in RVO OCT Analysis
Despite its power, OCT assessment of RVO has significant limitations:
- Need for normative comparison
Interpretation requires comparison with the patient’s contralateral eye or established normal values. Systemic vascular anomalies can affect both eyes, limiting standardization. - Complexity with comorbidities
Many RVO patients have systemic (hypertension, diabetes) or ophthalmic comorbidities (diabetic retinopathy, AMD, glaucoma, epiretinal membrane), complicating interpretation. It can be difficult to distinguish RVO-related changes from combined pathology. - Requirement to consider clinical context
OCT provides only part of the clinical picture. Accurate interpretation requires integration of symptoms, medical history, systemic factors, fundoscopic findings, and other diagnostic tests. Anatomical variations, comorbidities (glaucoma, cataract), and individual treatment response also necessitate a personalized approach.
5. Treatment of RVO: Modern Approaches
Currently, no treatment restores normal retinal venous circulation. Therefore, therapy focuses on controlling complications, primarily macular edema and preventing neovascularization (retinal, iris/optic disc, neovascular glaucoma, hemorrhages, and tractional changes).
All RVO patients should receive systemic management, ideally in collaboration between an ophthalmologist and a cardiologist or internist. Monitoring of blood pressure, lipids, glucose, and coagulation factors is essential, as RVO often signals systemic vascular risk.
Treatment decisions must be individualized, considering:
- RVO subtype (CRVO vs. BRVO)
- Edema severity
- Clinical and OCT findings
- Risk of adverse effects
- Patient status (comorbidities, ability for regular follow-up)
Anti-VEGF Therapy as First-Line Treatment
Intravitreal anti-VEGF injections are the first-line therapy for macular edema associated with RVO. These drugs reduce vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression, lowering vascular permeability, fluid leakage, edema, and inhibiting pathological neovascularization.
Commonly used agents:
- Ranibizumab, Aflibercept, Faricimab: proven safe and effective for CRVO and BRVO-related macular edema; studies show significant improvements in best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and central macular thickness (CMT).
- Bevacizumab: used off-label for macular edema and neovascularization.
Long-term studies indicate anti-VEGF therapy provides sustained visual improvement for many patients, with injection frequency often decreasing over time.
Advantages:
- High efficacy for macular edema
- Good tolerability and safety (systemic complications are rare)
- Personalized treatment possible
Limitations / Challenges:
- Some patients respond insufficiently
- Requires frequent injections (clinic visits, financial burden, potential complications, patient discomfort)
- Chronic or refractory edema may require alternative or combination approaches
Steroid Implants and Injections: Second-Line Therapy
Dexamethasone intravitreal implant (OZURDEX) is approved for RVO-related macular edema, particularly when:
- Anti-VEGF therapy is insufficient
- Frequent injections are impractical (distance, transportation, cost)
Steroids reduce inflammation, vascular permeability, and fluid accumulation, useful in chronic or resistant edema.
Risks / Limitations:
- Cataract (especially with repeated or long-term use)
- Increased intraocular pressure (IOP), potential steroid-induced glaucoma
Laser Therapy
- Panretinal photocoagulation is effective for neovascularization.
- Its use has declined with anti-VEGF availability, which offers strong anatomical and functional results.
Surgical Approaches
- Vitrectomy may be considered in selected cases.
- Surgery carries risks and is reserved for situations where other treatments fail or are inappropriate.
Combination Strategies
- In practice, clinicians often combine anti-VEGF therapy with steroid implants or laser treatment, depending on disease course.
- This can reduce total injection burden, minimize side effects, and improve outcomes in chronic or recurrent edema.
Monitoring Frequency
- Active macular edema or ongoing treatment requires regular OCT follow-up to evaluate therapeutic response and adjust injection intervals.
- OCT schedule:
- Monthly at treatment initiation
- Individualized intervals using Treat-and-Extend protocols
- Structural monitoring to prevent atrophic changes
- Ischemic RVO patients have the highest neovascularization risk within the first 90 days; monthly monitoring during the first 6 months is critical.
Conclusions and Recommendations
RVO is a complex, multifactorial vascular disorder that can cause sudden and severe vision loss, particularly in patients with systemic risk factors. Modern management aims not only to address acute complications but also to control long-term structural retinal changes.
OCT has transformed RVO care by providing:
- Early detection of edema, subclinical ischemia, and architectural changes
- Dynamic monitoring of treatment response, allowing timely adjustments and optimization
- Improved long-term prognostication through evaluation of macular thickness, outer retinal layers, and fluid volume
OCT helps identify edema type and secondary changes—atrophy, photoreceptor damage, inner retinal thinning—allowing a more accurate visual prognosis, especially in ischemic RVO.
When combined with modern anti-VEGF agents, long-acting steroid implants, and personalized dosing regimens, OCT enables:
- Reduction of unnecessary injections via interval optimization
- Maximized treatment efficacy based on morphological findings
- Prevention of recurrence and progression through early detection of edema
Thus, OCT is not merely a visualization tool but a core element of clinical decision-making, improving patient management, preventing complications, and enabling more complete and stable visual recovery.
Clinical Recommendation: Integrate regular OCT assessments into RVO management, with attention to macular thickness dynamics and outer retinal layer integrity for precise disease control and optimized therapeutic outcomes.
References:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38714470/
- https://www.rcophth.ac.uk/wp-content/uploads/2015/07/Retinal-Vein-Occlusion-Guidelines-Executive-Summary-2022.pdf
- https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/14/4/1183
- https://www.auctoresonline.org/article/clinical-therapeutic-orientation-in-retinal-venous-obstruction
- https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/10/3/405
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10801953
- https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/13/19/3100
- https://karger.com/oph/article-abstract/242/1/8/255831/Microvascular-Retinal-and-Choroidal-Changes-in?redirectedFrom=fulltext
- https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40123-024-01077-9
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39717563/
- https://provider-rvo.vision-relief.com/introduction/management/
-
Key Trends in Ophthalmology and Optometry in 2026

 Maria Znamenska
3 min.
Maria Znamenska
3 min.Introduction
The year 2026 in ophthalmology will not be defined by a single “major breakthrough,” but rather by the maturation of several directions whose discoveries and innovations are now transitioning into everyday clinical practice. While just a few years ago innovations were often perceived as isolated technologies far removed from real-world care (a new drug, device, or piece of equipment), today entire ecosystems are being formed: from early detection to long-term monitoring, from the ophthalmologist’s office to optometric screening, from a single consultation to a longitudinal patient journey supported by digital tools.
The core logic of 2026 is a shift from reactive to proactive ophthalmology. Increasingly, the goal is to prevent disease at the stage of risk-factor modification, intervene in the earliest pathological changes, and track preclinical markers. This shift is visible across several dimensions: the growing role of telemedicine and portable diagnostics; autonomous AI becoming a public health tool; and oculomics, which enables ocular image analysis to serve as a source of early biomarkers for systemic conditions. At the same time, the treatment paradigm is evolving: where repeated procedures once dominated (for example, frequent intravitreal injections), 2026 brings a move toward extended-duration regimens, implant-based drug delivery platforms, and disease control with fewer clinic visits.
Another important axis is the alignment of patient expectations. Some new approaches (for example, in the management of dry AMD and geographic atrophy) do not promise to “restore vision,” but rather to buy time—slowing structural retinal damage and functional vision loss. As a result, in 2026, risk–benefit communication and shared decision-making become almost as important as the choice of molecule or device itself.
Below, we outline the key eye care trends of 2026: what is changing, why it matters, and how it will shape ophthalmic and optometric practice.

1. New Approaches to Treatment
1.1. Geographic Atrophy (GA): The Introduction of Active Treatment in eye care trends 2026
1.1.1. Injectable Therapies as Ophthalmology Trends 2026
Following the development of injectable therapies for geographic atrophy, clinical practice is entering a “second wave” phase—where the main questions are no longer whether therapy is possible for a disease historically considered untreatable, but how that therapy should be practically implemented. In 2026, the focus will be on patient selection, treatment initiation, dosing frequency and duration, as well as monitoring.
Currently, the FDA has approved the following injectable therapies for GA:
- Izervay (avacincaptad pegol) — a C5 complement inhibitor.
- Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) — a C3 complement inhibitor.
Their mechanism of action involves reducing chronic inflammation and cellular damage in the retina and—most importantly—slowing the rate of GA lesion expansion.
Because most available data focus on slowing atrophy progression (an anatomical endpoint) rather than guaranteed improvements in visual acuity, properly managing patient expectations becomes particularly critical in 2026. Clear discussions about therapeutic goals and limitations are emphasized in review publications addressing the first approved GA treatments.

1.1.2. Multiwavelength Photobiomodulation
Multiwavelength photobiomodulation is one of the most promising emerging approaches aimed at halting or slowing the progression of dry AMD through modulation of mitochondrial activity. The use of specific wavelengths (red and near-infrared light, approximately 590–850 nm) may reduce oxidative stress in retinal cells, inflammation, and apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelium cells.
Its appeal is clear: a non-invasive procedure with significantly better acceptability for some patients compared with regular injections.
Until recently, its effectiveness remained debated, with studies showing only temporary functional improvement and reduction in drusen volume. At ARVO 2025, updated results from the LIGHTSITE III study demonstrated that photobiomodulation can significantly slow visual acuity decline and reduce the rate of GA expansion.
In 2025, the FDA approved photobiomodulation for AMD, creating strong prospects for broader clinical adoption in 2026.
The 2026 trend is correct positioning and stratification:
- Use of photobiomodulation based on clear indications for specific dry AMD stages and patient profiles.
- Transparent communication of expectations, with goals focused on functional support and slowing GA progression rather than guaranteed vision restoration.

1.2. Extended Anti-VEGF Treatment Regimens
Another major trend is the shift toward regimens with reduced injection frequency. This is not merely about comfort, but primarily about preventing missed visits: patients with AMD and diabetic retinopathy with DME often fall out of treatment due to visit burden. Thus, 2026 reinforces the principle that treatment must be effective in real-world conditions, not only under ideal adherence.
The ranibizumab port delivery system (Susvimo, Port Delivery System) has become emblematic of this trend. In 2025, the FDA also approved Susvimo for the treatment of diabetic retinopathy.
1.3. Gene Therapy for Macular Telangiectasia Type 2 (MacTel 2)
MacTel 2 is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative retinal disease that previously lacked active treatment.
In 2025, the first implantation of ENCELTO (revakinagene taroretcel)—the first and currently only FDA-approved gene therapy for MacTel 2—was performed in the United States. ENCELTO enables a shift from observation to active intervention, with the potential to preserve visual function in early-stage patients.
The device is based on encapsulated cell therapy technology: a capsule containing genetically modified cells that continuously secrete recombinant human ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF), acting as a neuroprotective agent that slows photoreceptor degeneration.
In 2026, the focus will move from “innovation storytelling” to routine clinical implementation, including defining early selection criteria, monitoring protocols (OCT biomarkers, functional testing), and accumulating real-world long-term data on photoreceptor preservation and visual function.
1.4. Gene Therapy for Neovascular AMD: Closest to Real Transformation
For neovascular AMD, gene therapy remains one of the most anticipated eye care trends 2026 directions, as it has the potential to fundamentally change treatment logic—from repeated injections to a single vector administration enabling long-term therapeutic protein expression. Reviews published in 2025 highlight active programs such as RGX-314, ADVM-022 (Ixo-vec), 4D-150, and others.
In 2026, the key questions shift from “does it work?” to “how does it work across different patient groups?” including:
- Stability and duration of expression;
- Inflammatory and immune response profiles;
- Need for supplemental anti-VEGF therapy;
- Patient selection criteria;
Injection centers and post-procedure monitoring standards.
2. Oculomics: The Eye as a “Window to the Body” and a Source of Digital Biomarkers
Oculomics is one of the most compelling trends of 2026, as it reshapes ophthalmology’s role within medicine as a whole. The concept is simple: the eye is the only structure where microvasculature, neurons, and signs of metabolic and inflammatory processes can be visualized non-invasively at high resolution. As a result, fundus and OCT/OCTA data may serve as biomarkers for systemic conditions—from cardiovascular risk to neurodegenerative diseases.

In contemporary research, oculomics is described as an approach that uses retinal images to assess systemic risks and conditions, with potential scalability for screening. In 2026, this “scale” becomes critical: data may originate not only from ophthalmology clinics, but also from optometric practices, mobile screening programs, and telemedicine.
What truly changes in 2026:
- A transition from “interesting correlations” to clinical utility, with models expected to demonstrate actionable impact on patient management.
- Data verification and management of false-positive risk, including the communication of systemic risk to patients.
- Integration with AI, as multidimensional patterns often exceed human interpretive capacity.
A major risk in 2026 is over-marketing, reinforcing the need for externally validated models with clear clinical context that do not generate unnecessary “medical noise.”
3. AI Technologies: From Decision Support to Autonomous Screening and Managed Patient Pathways

3.1. Autonomous Diabetic Retinopathy Screening as a Scalable Standard
In 2026, diabetic retinopathy remains the most studied use case for autonomous AI. In the United States, three FDA-approved autonomous DR screening systems are already described (LumineticsCore/IDx-DR, EyeArt, AEYE-DS). This positions AI as a practical tool capable of influencing large-scale screening programs, particularly in primary care, endocrinology clinics, and mobile settings.
The FDA approval of AEYE-DS as a fully autonomous solution (portable camera plus algorithm) underscores that in 2026, AI increasingly “works where the patient is,” not only where an ophthalmologist is present.
3.2. 2026 as the Year of Integration
Successful projects in 2026 will be distinguished by:
- Image quality standards and quality control;
- Clear referral rules and urgency levels;
- Mechanisms to ensure patient follow-through (scheduling, reminders, visit tracking);
- Transparent documentation for clinicians, patients, and audit purposes.
3.3. AI as “Invisible Infrastructure”
In 2026, AI increasingly functions as invisible infrastructure: highlighting high-risk cases, prioritizing queues, generating structured reports, and standardizing interpretation. The impact is reduced variability, faster routing, and fewer missed cases.
4. Telemedicine: From Video Calls to Retinal Screening and Remote Management
By 2026, telemedicine in ophthalmology is no longer synonymous with video consultations. Its foundation is tele-imaging: transmission and assessment of retinal images (fundus photos, sometimes OCT) with structured referral protocols.
At the same time, limitations become more openly discussed. Certain conditions and components of assessment may be less accurately captured remotely, requiring clear protocols to define which patients can be managed remotely and which require in-person examination.
The 2026 trend is a shift from “tool” to “pathway”:
- Tele-screening as the first step;
- Automated or semi-automated reporting;
- Referral and follow-up control;
Remote reassessment for ongoing risk monitoring.
5. New Devices and Portable Diagnostics: Closer, Faster, More Scalable Care

5.1. Portable Diagnostics as the Foundation of Coverage
Portable fundus cameras and compact diagnostic systems represent one of the most practical changes of 2026. Their value lies not only in technology, but in enabling large-scale screening in locations without full ophthalmic infrastructure.
Synergy with autonomous AI (such as AEYE-DS) is especially strong here, supporting new partnership models:
- Endocrinology and primary care clinics;
- Optical stores and optometric practices;
- Mobile programs for workplaces or regions.
5.2. Devices Deliver Value Only with Quality Protocols
Success depends not just on acquiring devices, but on defined protocols:
- Staff training in image acquisition;
- Minimum quality criteria;
- Retake rules;
- Handling ungradable cases.
In 2026, image quality becomes decisive, as AI and telemedicine depend on it.
5.3. Home and Remote Monitoring for Extended Treatment Regimens as eye care trends 2026
As treatment intervals lengthen, the risk of between-visit deterioration increases. Thus, 2026 strengthens the role of:
- Home functional monitoring;
- Digital questionnaires and symptom trackers;
Remote checkpoints signaling the need for earlier recall.
6. 2026 as the Year of Standardized Myopia Control and Greater Risk Awareness
By 2026, myopia control is no longer debated but formalized, grounded in consensus documents and systematic reviews. Myopia is increasingly recognized as a chronic disease with stages, phenotypes, and potentially blinding complications.
Implications for practice:
- Focus on preventing progression to high myopia.
- Combined strategies integrating behavioral, optical, and pharmacologic interventions with monitoring.
- A shared language between optometrists and ophthalmologists, with coordinated patient pathways.
- Support from AI and telemedicine for risk detection and personalized care.
Myopia control in 2026 becomes a structured, long-term risk-reduction process.
7. Optogenetics: Expanding the Evidence Horizon in Inherited Retinal Degenerations
In 2026, optogenetics moves beyond concept into longer-term observation. Publications from 2025 highlight functional stabilization or improvement in retinitis pigmentosa, emphasizing pragmatic success criteria.
For patients with severe vision loss, meaningful outcomes extend beyond visual acuity charts to spatial orientation, object recognition, and contrast sensitivity. In 2026, discussions increasingly focus on realistic endpoints and honest communication of limitations.
8. Less Invasive Interventions and Patient Comfort as Components of Clinical Effectiveness
Another key eye care trends 2026 is less traumatic technology that preserves efficacy while improving patient experience. A notable example is the FDA approval of Epioxa (epi-on) for keratoconus in 2025, preserving corneal epithelium and potentially reducing pain and recovery time.
This trend spans refractive surgery, ocular surface disease, and chronic condition management, reinforcing that patient experience is integral to adherence and clinical outcomes.

Conclusion
The ophthalmology trends 2026 clearly demonstrate that ophthalmology and optometry are entering a phase of mature transformation, where success is driven not by isolated innovations but by their integration into coherent clinical pathways. The focus is shifting from treating consequences to early detection, slowing progression, and long-term management of chronic eye disease.
Active treatment of geographic atrophy, photobiomodulation, extended anti-VEGF regimens, and the emergence of gene therapies for MacTel 2 and neovascular AMD fundamentally reshape patient management—from observation or frequent procedures to strategies aimed at preserving retinal structure and function with minimal procedural burden. These approaches require careful patient stratification and responsible expectation management, as the goal increasingly becomes slowing neurodegeneration rather than restoring vision.
At the diagnostic level, 2026 reinforces decentralization: portable devices, telemedicine, and autonomous AI bring screening closer to patients and enable coverage of much broader populations. Oculomics and AI transform ocular images into sources of digital biomarkers that may influence not only ophthalmic but also general clinical management. At the same time, it becomes clear that technological value is defined not by algorithms or devices, but by data quality, model validation, and clearly structured patient pathways—from screening to treatment.
-
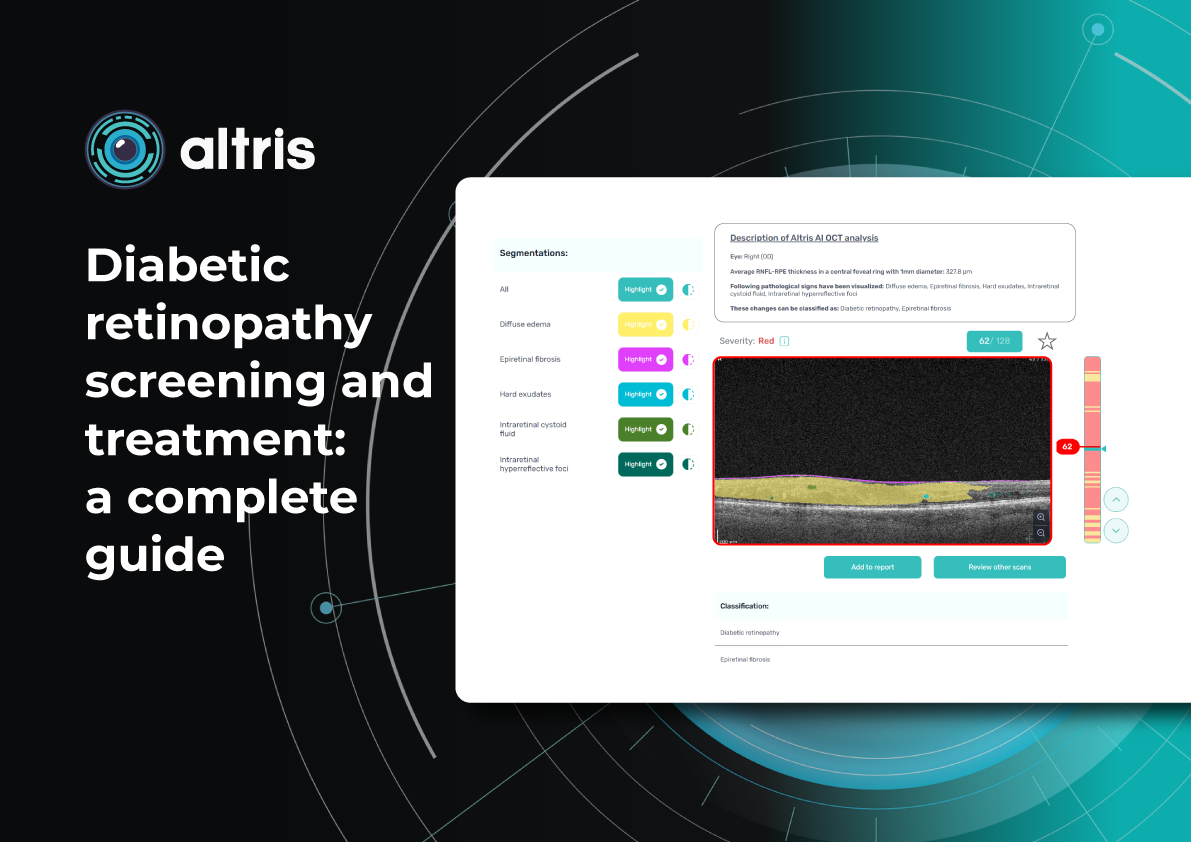
Diabetic Retinopathy Screening and Treatment: a Complete Guide

 Maria Znamenska
5 min
Maria Znamenska
5 minDiabetic retinopathy screening and treatment: a complete guide
Table of Contents
- What are the diabetic retinopathy screening methods?
- Fundus images in DR screening
- Can OCT detect diabetic retinopathy?
- What does diabetic retinopathy look like on OCT?
- What is optimal diabetic retinopathy screening frequency?
- What is the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy?
- Diabetic retinopathy management: key takeaways
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) remains the leading cause of irreversible vision loss among working-age adults worldwide. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), one in three patients with diabetes shows signs of DR, and 10% develop diabetic macular edema (DME). Early diagnosis, systematic screening, and individualized monitoring are essential to prevent vision loss.
What are the diabetic retinopathy screening methods?
Modern methods of DR screening include:
- Telemedicine platforms – enable automated transmission of fundus images
- Mobile fundus cameras – Wi-Fi–enabled devices for field examinations
- Smartphone-based platforms – use specialized lenses for retinal imaging
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT) – used to detect early retinal changes and diabetic macular edema, complementing fundus photography
- AI-based systems – solutions for automated image analysis for fundus and OCT
In practice, these methods are often combined. For example, patients may undergo fundus photography, after which images are sent to telemedicine centres and analysed by AI algorithms. More complex cases are then referred to ophthalmologists.
DR screening is frequently incorporated into annual diabetes check-ups conducted by primary care physicians trained in basic fundus photography. This approach, already successfully implemented in several EU countries, has reduced the incidence of severe DR.
Innovations in DR screening have broadened access for rural residents, older adults, and individuals with limited mobility. Integration into national e-health systems enables automated reminders and electronic medical record linkage, incorporating laboratory data (HbA1c, blood pressure) alongside retinal images.
Fundus images in DR screening
Fundus photography is the optimal primary screening method due to its high diagnostic yield, cost-efficiency, simplicity, and ability to integrate with AI and telemedicine solutions.
It enables detection of microaneurysms, hemorrhages, exudates, and neovascularization, often before symptoms arise. National screening programs rely heavily on digital fundus imaging, which, when combined with AI, provides an efficient platform for mass DR detection.
Advances in fundus imaging for diabetic retinopathy have improved efficiency. Modern non-mydriatic cameras deliver high-quality images without pupil dilation, while automated image analysis supports rapid identification of suspicious cases. Cloud storage and telemedicine platforms facilitate remote evaluation, increasing coverage in regions with limited ophthalmology services.
Next-generation wide-field cameras further enhance detection by capturing peripheral pathology. Some devices also generate automated annotations, reporting lesion type, DR stage, and DME presence, thereby standardizing interpretation and expediting clinical decision-making.

Diabetic retinopathy detection from fundus images Can OCT detect diabetic retinopathy?
Yes. OCT can detect early structural changes in the retina and is increasingly used to complement standard diabetic retinopathy screening.
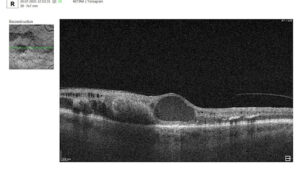
- Role in DR screening – While not a primary screening tool, OCT is now widely applied alongside fundus photography. It is especially valuable for detecting early diabetic macular edema (DME) and subtle morphological changes in the central retina not visible during ophthalmoscopy.
- High-resolution imaging – OCT visualizes changes such as photoreceptor layer disruption, subclinical intraretinal fluid, neurosensory retinal thickening, and foveal edema. These findings often appear before clinically significant macular edema.
- Differential diagnosis – OCT also helps identify other causes of vision loss in diabetic patients, for example, ruling out age-related macular degeneration.
- Clinical evidence – Studies confirm that combining OCT with fundus photography increases diagnostic accuracy for DME. Experts therefore recommend this approach for patients with long-standing diabetes, poor glycemic control, or vision complaints.
What does diabetic retinopathy look like on OCT?
On OCT, diabetic retinopathy (DR) can appear as a combination of retinal structural damage, fluid accumulation, and microvascular changes that may not be visible on fundus photography.
Typical OCT findings in DR include:
- Photoreceptor damage – loss of outer retinal layers, especially the ellipsoid zone
- Intraretinal hyperreflective foci, hard exudates
- Microaneurysms – visible as small, round changes within the retina
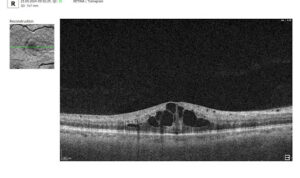
- Retinal thickness changes and neuroepithelial layer atrophy
- Diabetic macular edema – with intraretinal hyporeflective cystoid spaces and neuroepithelial swelling
- Subretinal fluid – resulting from increased vascular permeability
- DRIL – disorganization of inner retinal layers, associated with poor prognosis
- Epiretinal membranes – potential precursors to retinal detachment
Advanced findings
OCT can also reveal proliferative changes and tractional zones, which may progress to tractional retinal detachment.OCTA insights
Beyond structural analysis, OCT angiography (OCTA) allows visualization of retinal microvascular changes without the contrast injection. OCTA helps identify areas of neovascularization, capillary network disruption, and the degree of macular ischemia.
Diabetic retinopathy (hyperreflective foci, moderate destruction of the ellipsoid zone and RPE), diabetic macular edema (neuroepithelium edema, intraretinal cystic cavities), epiretinal membrane What is optimal diabetic retinopathy screening frequency?
The screening frequency for diabetic retinopathy is tailored to diabetes type, disease stage, and risk factors:
Type 1 diabetes
- First screening: 3–5 years after diagnosis (due to onset in children and young adults)
- Then annually, if no DR is detected
- If DR is present, frequency depends on severity
Type 2 diabetes
- Screening at diagnosis, as DR may already be present.
- If no DR, repeat every 1–2 years.
Patients with confirmed DR
- No visible DR, mild non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR), no DME — every 1–2 years
- Moderate NPDR — every 6–12 months.
- Severe NPDR — every 3 months.
- Proliferative DR (PDR) — monthly, with regular OCT monitoring of the macula.
- DME — monthly if center-involving, every 3 months if not.
Pregnant women with type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- Screening before conception or in the first trimester, with follow-up each trimester and postpartum
- Screening is not required for gestational diabetes without pre-existing diabetes
Post-treatment patients (laser or vitrectomy)
- Typically, every 3–6 months during the first year, individualized based on retinal stability

Diabetic retinopathy (hyperreflective foci, microaneurysms, destruction of the ellipsoid zone and RPE), diabetic macular edema (neuroepithelial swelling, intraretinal cystic cavities), epiretinal membrane. Monitoring of diabetic retinopathy progression
Ongoing diabetic retinopathy monitoring is essential to detect early signs of progression and guide treatment decisions. A key focus in monitoring is diabetic macular edema (DME), which represents fluid accumulation in the macula due to leakage from damaged retinal vessels. DME is a common complication of DR and the leading cause of vision loss in diabetic patients. OCT plays a central role in detecting DME and identifying structural changes that indicate disease progression.
OCT biomarkers in DME
OCT enables precise visualization of retinal layers with micron resolution, confirming DME presence and providing prognostic biomarkers for treatment selection and monitoring.
The main OCT biomarkers in DME include:
- Cystoid hyporeflective intraretinal spaces – usually in the inner nuclear layer (INL) or outer plexiform layer (OPL). Their number, size, and location correlate with edema severity. Large or confluent spaces may indicate chronicity and a worse prognosis.
- Subretinal fluid – accumulation between the neurosensory retina and retinal pigment epithelium. Often associated with a better visual prognosis, but requires close monitoring and consideration in anti-VEGF therapy.
- Central macular thickening – a key marker of treatment effectiveness and disease activity.

Diabetic retinopathy (hyperreflective foci, hard exudates), diabetic macular edema (neuroepithelial swelling, intraretinal cystic cavities). OCT red flags in DR progression
Beyond DME, OCT helps identify broader signs of DR worsening that require therapy reassessment:
- Progressive central macular thickening despite treatment
- Increase in intraretinal or subretinal fluid, or enlargement of cystoid spaces
- New hyperreflective foci, reflecting inflammatory activity (these may precede hard exudates or RPE changes)
- Development or progression of disorganization of inner retinal layers (DRIL), an independent predictor of poor prognosis, even when orphological improvement is seen on OCT
- Ellipsoid zone disruption, indicating photoreceptor damage
- Signs of macular ischemia, although better evaluated with OCTA, indirect signs on OCT may include thinning of the inner retinal layers.
- Tractional changes, such as epiretinal membranes, inner retinal stretching, or macular traction

Diabetic retinopathy (hyperreflective foci, hard exudates, destruction of the ellipsoid zone and RPE, disorganisation of the retinal inner layers (DRIL)), Diabetic macular edema (neuroepithelial swelling, intraretinal cystic cavities), subretinal fluid. The appearance of these OCT features should prompt clinicians to reconsider therapy, whether by switching anti-VEGF agents, introducing steroids, using combination therapy, or referring patients for surgical evaluation when traction is present.

Diabetic retinopathy (hyperreflective foci, hard exudates, destruction of the RPE), Diabetic macular edema (neuroepithelial swelling, intraretinal cystic cavities), subretinal fluid. What is the best treatment for diabetic retinopathy?
The treatment of diabetic retinopathy is based on a comprehensive approach that takes into account not only the disease stage, but also individual patient characteristics, OCT findings, comorbidities, and prognostic biomarkers. Modern strategies combine preventive, pharmacological, and surgical methods, as well as personalized medicine tools based on retinal imaging.
Criteria for treatment selection
The choice of therapy is guided by the following parameters:
- DR stage – non-proliferative, proliferative, with or without DME
- Form of macular edema – focal, diffuse, with or without subretinal fluid
- Presence of DRIL, EZ disruption, ischemic changes on OCTA
- Response to previous treatment – anti-VEGF, steroids, laser
- Comorbidities – renal insufficiency, hypertension, poor adherence
For low-risk patients, observation or focal laser may be sufficient. Patients with significant DME usually require anti-VEGF or steroid injections. Those with proliferative DR often undergo panretinal laser photocoagulation or vitrectomy.
Diabetic retinopathy treatment methods
The main treatment options for diabetic retinopathy include pharmacotherapy, laser therapy, surgical intervention, and personalized approaches based on OCT.
1. Pharmacotherapy: anti-VEGF and steroids
Anti-VEGF agents such as aflibercept, ranibizumab, and bevacizumab are the first-line therapy for diabetic macular edema. They are especially effective in patients with pronounced edema and without ischemia.
New drugs with extended duration of effect, including port delivery systems, are becoming available.
Steroids are used when DME is persistent, when patients do not respond to anti-VEGF therapy, or in cases with an inflammatory phenotype.
2. Laser therapy
Injections have largely replaced laser therapy in the treatment of DME. However, panretinal photocoagulation remains the standard treatment for proliferative DR.
Subthreshold micropulse laser is increasingly applied for focal edema, as it minimizes tissue damage.
3. Surgical treatment
Vitrectomy is recommended in cases of tractional macular edema, vitreous hemorrhage, or retinal detachment.
4. Personalization with OCT
Modern treatment protocols use OCT biomarkers to tailor therapy and improve prognosis.
Patient education and multidisciplinary care
DR treatment outcomes strongly depend on adherence. Patients must be informed about the need for regular injections, monitoring, and systemic control. Coordinated care involving ophthalmologists, endocrinologists, and family doctors helps maintain stable glycemic control and slows DR progression.
Diabetic retinopathy management: key takeaways
Diabetic retinopathy is a progressive disease, but modern diagnostics and treatments make it possible to preserve vision and improve outcomes. OCT and OCTA have become essential tools for early detection, risk assessment, and personalized therapy planning. Effective management combines pharmacotherapy, laser treatment, surgery, and patient education. Multidisciplinary care and strong patient adherence remain crucial for long-term success. With timely monitoring and tailored treatment, the progression of diabetic retinopathy can be significantly slowed.
Disclaimer: USA FDA 510(k) Class II; Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS); AI/ML models and components intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
-
Altris Achieves MDSAP Certification, Strengthening Global Presence and Clinical Credibility

 Altris Inc.
22.08.20251 min.
Altris Inc.
22.08.20251 min.22.08.2025
Altris Achieves MDSAP Certification, Strengthening Global Presence and Clinical Credibility
Altris Inc., a leading decision support platform for OCT scan analysis, proudly announces that it has passed the Medical Device Single Audit Program (MDSAP) audit.
Based on the objective evidence reviewed, this audit enables a recommendation for Initial certification to ISO 13485:2016 MDSAP, including the requirements of Australia, Brazil, Canada, the USA, and Japan, and EU 2017/745, and that the scope was reviewed and found to be appropriate for ISO 13485:2016/MDSAP and EU MDR 2017/745.
The results of this audit are suitable for obtaining the EU MDR 2017/745 certificate, which we are currently in the process of pursuing.
ISO 13485:2016/MDSAP enables Altris Inc. to “design, manufacture, and distribute medical software for the analysis and diagnosis of retinal conditions globally.” It is recognized by leading global health regulators and signals trust and credibility to public and private hospitals, eye care networks, and optometry chains worldwide.
MDSAP Certification also opens the door for Altris Inc. to enter new international markets, including Asia-Pacific, Latin America, and additional parts of North America. The MDSAP certification allows a single regulatory audit of Altris AI’s Quality Management System (QMS) to be recognized by multiple major health authorities, including:
- FDA (United States)
- Health Canada
- TGA (Australia)
- ANVISA (Brazil)
- MHLW/PMDA (Japan)
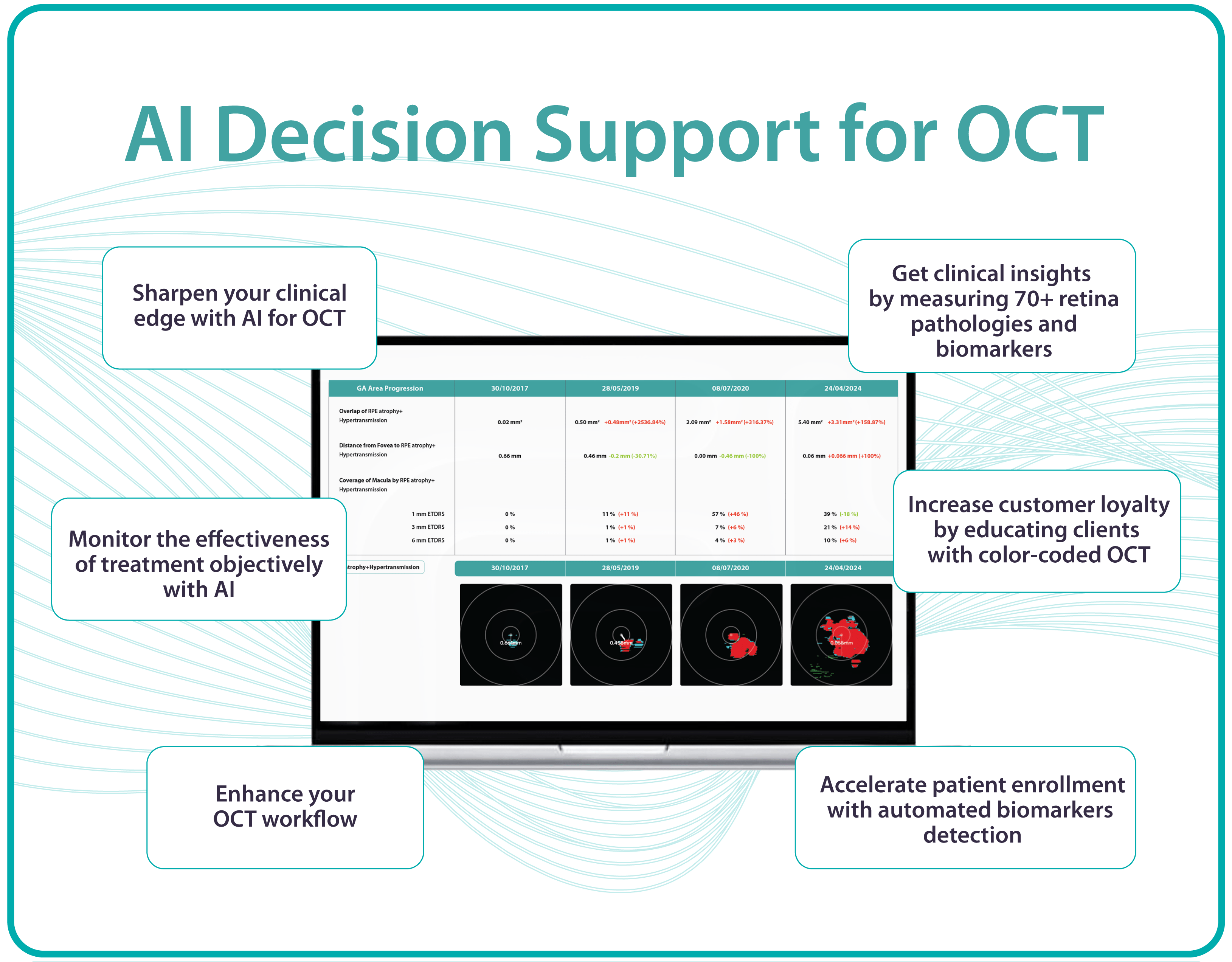
MDSAP enforces that the Quality Management System for developing, testing, and maintaining AI Decision Support for OCT complies with international medical device standards. Altris AI Decision Support for OCT Analysis system that facilitates the detection and monitoring of over 70 retinal pathologies and biomarkers, including early signs of glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, and age-related macular degeneration.
“Achieving ISO 13485:2016 certification under the stringent MDSAP requirements is a significant accomplishment for our team,” said Maria Znamenska, MD, PhD, Chief Medical Officer at Altris AI. “As a practicing ophthalmologist, I understand that the safety of patients is the absolute priority. Especially when implementing such an innovative technology as AI for decision support in OCT analysis. That is why we did everything possible to build quality processes that guarantee the highest level of safety for the patients.
This certification enables Altris AI to expand its presence and offer eye care specialists upgraded functions such as GA progression monitoring, flags for smart patient filtering, or automated drusen count.”
“This is more than a regulatory milestone for our team – it’s a signal to the global eye care community that Altris AI is a trusted clinical partner,” said Andrey Kuropyatnyk, CEO of Altris AI.
About Altris
Founded in 2017, Altris AI is at the forefront of integrating artificial intelligence analysis into ophthalmology and optometry.
The company’s platform is designed to assist eye care professionals in interpreting OCT scans with greater objectivity and make informed treatment decisions. It’s a vendor-neutral platform compatible with OCT devices from 8 major global manufacturers. With a commitment to innovation and compliance, Altris AI continues to develop solutions that set higher standards in the eye care industry and improve patient outcomes.
Disclaimer: USA FDA 510(k) Class II; Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS); AI/ML models and components intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
-
Glaucoma OCT Monitoring Guide: From Detection to Long-Term Care

 Maria Znamenska
5 min
Maria Znamenska
5 minGlaucoma OCT Monitoring Guide: From Detection to Long-Term Care
Table of Contents
- Glaucoma detection: why early diagnosis is critical
- How to detect glaucoma in early stages: key approaches
- Advanced imaging for glaucoma: OCTA
- OCT glaucoma monitoring after diagnosis
- Additional tools for monitoring glaucoma treatment
- Glaucoma OCT: the foundation of long-term glaucoma care
Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) has fundamentally changed glaucoma diagnostics over the past two decades. It enables non-invasive, micron-level imaging of retinal microstructures and provides objective measurements of the retinal nerve fibre layer (RNFL), ganglion cell complex (GCC), and optic nerve head (ONH) parameters. Moreover, the advent of OCT angiography (OCTA) has introduced a new dimension in assessing microcirculation—complementing structural analysis and potentially predicting glaucoma progression.
Today, OCT is the standard for early detection, monitoring, and risk stratification of glaucoma progression, as recognised in international clinical guidelines. When combined with functional tests, tonometry, and anterior chamber angle assessment, OCT becomes the foundation for personalised glaucoma management.
Glaucoma detection: why early diagnosis is critical
Early glaucoma diagnosis is vital, as optic nerve damage caused by the disease is irreversible. Many patients seek care only after significant vision loss has occurred, at which point treatment may slow progression but cannot restore lost function. This is why ophthalmologists emphasise the importance of glaucoma detection at preclinical or pre-perimetric stages.
How does OCT help in early glaucoma detection?
OCT provides high-resolution imaging of the retina and optic nerve head. Unlike subjective functional tests, OCT delivers objective, quantitative data on ganglion cells, nerve fibre layers, and the neuroretinal rim, enabling recognition of even subtle structural changes.
Recent OCT models go further, allowing detailed visualisation of the lamina cribrosa, a structure known to be altered in glaucoma. Today, OCT is recognised as a key diagnostic tool in the guidelines of both the European Glaucoma Society and the American Academy of Ophthalmology.
How to detect glaucoma in early stages: key approaches
Early glaucoma detection relies on evaluating structural and functional parameters of the eye, supported by advanced imaging techniques. The three main parameters assessed with glaucoma OCT are:
- Ganglion Cell Complex (GCC) thickness and asymmetry
- Retinal Nerve Fibre Layer (RNFL) thickness
- Optic nerve head parameters with the DDLS scale
In addition, OCT Angiography (OCTA) provides complementary insights into ocular microvasculature that may indicate early glaucomatous damage.
Glaucoma detection parameter 1: GCC thickness and asymmetry
One of the most sensitive preclinical biomarkers of glaucomatous damage is thinning of the ganglion cell complex (GCC), which includes the ganglion cell layer (GCL), inner plexiform layer (IPL), and macular RNFL (mRNFL). It is assessed through macular OCT scans. Damage in this area is particularly critical, as 50–60% of all ganglion cells are concentrated within the central 6 mm zone.
Assessing asymmetry between the superior and inferior halves of the macula within the GCC is a key diagnostic indicator. Studies show that minimum GCC thickness and FLV/GLV indices (Focal Loss Volume / Global Loss Volume) are predictors of future RNFL thinning or emerging visual field defects. Asymmetry maps significantly ease clinical interpretation.
A newer approach—vector analysis of GCC loss—also allows clinicians to visualise the direction of damage, which often correlates with future visual field defects.

Glaucoma detection parameter 2: RNFL thickness analysis
RNFL analysis is among the most widely used glaucoma diagnostic methods. The RNFL reflects the axons of the ganglion cells and is readily measured in optic nerve scans. Temporal sectors are the most sensitive and often show the earliest changes.
Even when the overall thickness appears normal, localised defects should raise suspicion. Sectoral thinning of ≥5–7 μm is considered statistically significant. Age-related RNFL decline (~0.2–0.5 μm/year) must also be considered.
Glaucoma detection parameter 3: optic nerve head parameters and the DDLS scale
Evaluating the optic nerve head (ONH) is essential. OCT enables automated assessment of optic disc area, cup-to-disc ratio (C/D), cup volume, rim area, and the lamina cribrosa.
The Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS) classifies glaucomatous ONH changes based on the thinnest radial rim width or, if absent, the extent of rim loss. Unlike the C/D ratio, DDLS adjusts for disc size. When combined with OCT, DDLS significantly enhances objective clinical assessment.
In high myopia, automatic ONH segmentation often misclassifies anatomy. Here, newer deep learning–based segmentation models improve accuracy.

Advanced imaging for glaucoma: OCTA
OCT Angiography (OCTA), an advanced glaucoma OCT technique, provides unique insights into ocular circulation. It enables evaluation of:
- Vessel density in the peripapillary region
- Optic nerve and macular vascularisation
- Retinal versus ONH perfusion in both eyes

Studies confirm that reduced vessel density correlates with RNFL loss and visual field deterioration, and often precedes both.
OCT glaucoma monitoring after diagnosis
Glaucoma can progress even with stable intraocular pressure (IOP), making regular structural assessment of the optic nerve and inner retina crucial for therapy adjustment.
Glaucoma OCT is not only a diagnostic tool but also the primary method for monitoring glaucomatous damage. Unlike functional tests, OCT can detect even minimal RNFL or GCL thinning months or even years before visual field loss appears. With serial measurements and built-in analytics, OCT allows clinicians to track glaucoma progression rates and identify high-risk patients.
Methods for glaucoma progression monitoring
There are two main approaches to monitoring glaucoma progression with OCT:
Method 1: event-based analysis
This method compares current scans with a reference baseline, identifying whether RNFL or GCL thinning exceeds expected variability.
? Example: Heidelberg Eye Explorer (HEYEX) highlights suspicious areas in yellow (possible loss) or red (confirmed loss).
Limitations include sensitivity to artifacts, image misalignment, and segmentation quality. A high-quality baseline scan is essential.
Method 2: trend-based analysis
This approach accounts for time. The software plots RNFL/GCL thickness trends over time in selected sectors or globally and calculates the rate of progression.
Examples:
- RNFL thinning >1.0 μm/year is clinically significant.
- Thinning >1.5 μm/year indicates active progression.
It also accounts for age-related changes, helping differentiate physiological vs. pathological decline.
Visual assessment in glaucoma OCT
Qualitative analysis also plays an important role in detecting glaucoma progression. Key aspects include:
- Focal RNFL thinning (localised defects)
- Changes in the neuroretinal rim
- Alterations in ONH cupping
- GCL/GCIPL comparison (superior vs. inferior) on macular maps
- New segmentation artifacts (may mimic progression)

OCT glaucoma findings that indicate true progression
Five OCT findings suggest true glaucomatous progression:
- RNFL thinning >10 μm in one sector or >5 μm in several sectors
- New or worsening GCL asymmetry (yellow to red colour shift)
- Emerging or expanding RNFL defects on colour maps
- Increasing C/D ratio with concurrent rim thinning
- New localised areas of vessel density loss on OCTA
Particular attention should be paid to the inferotemporal and superotemporal RNFL sectors, where 80% of early changes occur.
Frequency of glaucoma OCT monitoring
According to the AAO and EGS, the recommended frequency for OCT glaucoma monitoring is:
- High-risk patients: every 6 months
- Stable patients: once a year
- For trend analysis: at least 6–8 scans over 2 years to ensure statistical reliability
Looking ahead, broader use of AI for glaucoma is expected to support earlier and more accurate detection, while also reducing false positives.
Additional tools for monitoring glaucoma treatment
While glaucoma OCT is essential for detecting structural changes, a comprehensive glaucoma assessment requires a multimodal approach. Additional tools include perimetry, tonometry, optic disc fundus photography, and gonioscopy.
Perimetry (visual field testing)
Functional assessment of the optic nerve remains crucial. Standard Automated Perimetry (SAP), most often performed with Humphrey Visual Field Analyzer protocols (24-2, 30-2, 10-2), is the most widely used method.
Key indices:
- MD (mean deviation): average deviation from normal values
- PSD (pattern standard deviation): highlights localised defects
- VFI (visual field index): summarises global visual function; useful for tracking glaucoma progression
- GHT (glaucoma hemifield test): automated analysis of field asymmetry
? Important: In 30–50% of cases, structural changes such as RNFL thinning on OCT precede visual field defects; in others, functional loss appears first. Best practice relies on integrated OCT and perimetry to correlate damage location and monitor glaucoma progression more precisely.
Combined OCT and perimetry remains the gold standard for progression monitoring.
Tonometry
Intraocular pressure (IOP) is the only clearly modifiable risk factor associated with both glaucoma onset and progression.
- Goldmann applanation tonometry remains the gold standard.
- A single IOP reading is insufficient — diurnal fluctuations are an independent risk factor, particularly in normal-tension glaucoma.
Optic disc fundus photography
Although subjective, fundus imaging remains valuable for documenting glaucomatous changes, especially in borderline cases. Unlike OCT, it does not provide quantitative data but helps visualise morphology over time.
What to assess:
- Progressive disc cupping
- Changes in neuroretinal rim shape or colour
- Disc margin haemorrhages (linked to faster RNFL thinning and visual field loss)
- Inter-eye comparisons
Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy evaluates the anterior chamber angle and helps exclude angle-closure, pigmentary, or pseudoexfoliative glaucoma. It also identifies:
- Neovascularisation
- Trabecular meshwork abnormalities
- Other angle anomalies
Patient education: a key to successful glaucoma management
Accurate glaucoma detection and therapy are not enough; adherence to monitoring and treatment is equally critical.
The challenge:
- Early-stage glaucoma is asymptomatic.
- Many patients underestimate its seriousness, leading to poor compliance, missed follow-ups, and discontinuation of therapy.
The goals of patient education:
- Explain that glaucoma progresses silently but can lead to irreversible blindness if untreated.
- Use real-life examples (before/after OCT scans, visual field comparisons) to illustrate progression.
- Teach patients to recognise warning signs (vision changes, eye pain).
- Visualise disease progression with AI tools showing RNFL loss and future risk.
Educational resources may include:
- Printed brochures in patient-friendly language
- Videos featuring OCT images with explanations
- Doctor–patient in-clinic discussions
- Telemedicine platforms with reminders and follow-up prompts
According to the AAO, patients who understand glaucoma are 2.5 times more likely to adhere to treatment and attend check-ups.
Glaucoma OCT: the foundation of long-term glaucoma care
Glaucoma OCT now plays a central role in both diagnosis and monitoring. Its ability to detect subtle structural changes before measurable functional loss makes early intervention possible and increases the chances of preserving vision.
But technology alone is not enough. Accurate interpretation, combined with strong patient education, is essential. When patients understand their disease and the role of glaucoma OCT in treatment, adherence improves and outcomes are better.
OCT is not just a diagnostic device; it is the cornerstone of an integrated glaucoma management strategy, from initial screening to long-term monitoring and treatment optimisation.
Disclaimer: USA FDA 510(k) Class II; Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS); AI/ML models and components intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
-
Dry AMD Treatment: Modern Ways to Slow Progression

 Maria Znamenska
5 min.
Maria Znamenska
5 min.Dry AMD Treatment: Modern Ways to Slow Progression
Table of Contents
- What are the dry macular degeneration treatment breakthroughs?
- How to monitor dry AMD progression with OCT?
- What are the challenges of dry age-related macular degeneration monitoring?
- How do I organize efficient dry AMD monitoring in my clinic?
- Why are optometrists on the front line of early AMD detection?
- How can OCT insights help support patients emotionally?
- Conclusion
For many years, dry or non-exudative AMD was seen as untreatable. Most research focused on wet AMD and anti-VEGF therapy.
Today, this paradigm is shifting. Around 30% of patients with age-related macular degeneration are affected by the dry form, which makes finding effective therapies critical. Recently, the first FDA-approved drugs for dry macular degeneration injections have appeared, offering hope to patients with geographic atrophy (GA). Alongside, new physiotherapeutic methods, such as multi-wavelength photobiomodulation, are showing promising results.
Geographic atrophy (GA) is an advanced, irreversible form of dry AMD. It occurs when parts of the retina undergo cell death, leading to progressive vision loss. But even the best dry AMD treatment is incomplete without objective measurement. That’s where modern tools for macular degeneration monitoring come in, and optical coherence tomography (OCT) is now at the core of this process.
What are the dry macular degeneration treatment breakthroughs?
The latest dry macular degeneration treatment breakthroughs include:
- Multiwavelength photobiomodulation
- FDA-approved injectable drugs
- AREDS 2-based supplements
In the past, recommendations focused only on reducing risks — quitting smoking, managing blood pressure, and eating a healthy diet.
Now, new approaches to dry AMD treatment combine prevention with active therapies to slow AMD progression and especially the advance of GA.1. Dry AMD treatment using multiwavelength photobiomodulation
Multiwavelength photobiomodulation for AMD is a promising new treatment. It uses specific red and near-infrared light wavelengths (~590–850 nm) and helps reduce oxidative stress, inflammation, and pigment epithelial cell death.
One of the best-known systems is Valeda Light Therapy, which delivers controlled multiwavelength light directly to the retina.
The LIGHTSITE III clinical trial showed that photobiomodulation can slow the decline in visual acuity and reduce the rate of GA expansion.
Limitations:
- Only 3–5 years of long-term data available
- Requires costly equipment and training
- Effectiveness in late-stage GA remains unclear

2. Dry AMD treatment using FDA-approved injectable drugs
AMD injection drugs approved by the FDA include Izervay and Syfovre.
- Izervay (avacincaptad pegol): A C5 complement protein inhibitor that targets the complement cascade involved in chronic retinal inflammation and damage. Izervay, approved for geographic atrophy secondary to dry AMD, has demonstrated a reduced rate of GA progression in clinical trials.
- Syfovre (pegcetacoplan): A C3 complement inhibitor that blocks the central component of the complement system to reduce inflammation. Syfovre is the first FDA-approved treatment for GA that targets complement component C3, showing a clinically meaningful slowing of GA progression.
Both dry macular degeneration injections have shown the ability to slow GA progression compared to placebo. Although they do not restore vision, slowing vision loss is a meaningful clinical outcome.
Key considerations for injections:
- Administered intravitreally, usually monthly or every other month
- Require doctor training and patient education on risks (e.g., endophthalmitis, increased intraocular pressure)
- Cost and access may limit use

3. Dry AMD treatment using AREDS 2-based supplements
AREDS 2 supplements are antioxidant supplements containing lutein, zeaxanthin, vitamins C and E, zinc, and copper. They can reduce the risk of progression to late-stage AMD by around 25% over five years, according to the AREDS 2 study.
Pros:
- Widely available
- Safe, with low side effect risk
- Supported by strong clinical evidence
Cons:
- Do not directly treat GA
- Cannot replace active therapies such as dry macular degeneration injections or photobiomodulation
How to monitor dry AMD progression with OCT
Effective macular degeneration monitoring relies on OCT. It is the gold standard for tracking retinal changes and predicting GA development.
Without OCT, clinicians are essentially “flying blind” when assessing AMD progression.Key monitoring parameters of AMD progression
The key monitoring parameters of AMD progression include GA area, drusen, and distance to fovea.
1. GA area
This is the main metric when using intravitreal eye injections. Modern OCT systems provide GA measurements in mm², allowing doctors to objectively track changes over time.
Even if patients don’t notice symptoms, a growing GA area signals disease progression. In FDA trials for Syfovre and Izervay, the GA area was the primary endpoint.
2. Drusen
Drusen vary in number, size, and shape. A reduction or disappearance of drusen on OCT may seem like an improvement, but could actually indicate a transition to the atrophic stage. Regular monitoring helps detect this early.
3. Distance to fovea
The closer GA is to the fovea, the greater the risk of sudden vision loss.
Early detection enables:
- Referral to an ophthalmologist
- Timely conversations about potential vision loss
OCT outputs for AMD progression monitoring and communication
Useful OCT outputs for AMD progression monitoring and communication are heat maps and progress charts.
1. Heat maps
Modern OCT systems use color-coded heat maps to show pigment epithelium thickness and drusen distribution. This visual format helps in several ways:
- Makes interpretation easier for clinicians
- Helps patients better understand their condition
- Encourages patients to stay engaged with treatment
In clinical practice, it serves as a highly effective communication tool.
2. Progress charts
Most OCT systems can compare results across visits
- For doctors: Helps guide treatment decisions
- For patients: Provides visual proof of stabilization or worsening
The role of objective evidence in patient treatment
Patients may question the value of long-term treatments or costly procedures.
OCT is the gold standard for patient motivation. When patients see actual changes, they’re more likely to agree to treatment.
What are the challenges of macular degeneration monitoring?
Monitoring dry AMD presents technical, organizational, and psychological challenges. Doctors of all levels of experience should be aware of them.
1. Invisible microchanges
Early atrophy or drusen changes may be subtle. Patients may not notice them due to eccentric fixation or slow adaptation.
Without OCT, doctors may miss early GA, delaying treatment.
It is necessary to perform OCT even when there are only minor changes in visual acuity or if the patient reports image distortion (metamorphopsia).
2. Subjective assessment
Ophthalmoscopy reveals only obvious changes. Subtle drusen or early atrophy might be missed.
Relying on patients’ complaints is risky — many don’t notice issues until it’s too late.
That’s why even small optical practices should establish clear referral pathways for OCT exams.
3. Unnecessary referrals
Optometrists or primary care doctors often refer patients to ophthalmologists “just in case,” because they don’t have access to OCT or lack experience interpreting it.
This puts unnecessary strain on specialists. In many cases, nothing new is done after the exam because there are no previous images for comparison.
4. Limitations of OCT devices
Not all OCT devices measure GA or track drusen equally well. Older models may lack automated measurements of atrophy area.
In some cases, referral to a center with advanced OCT is necessary.

How do I organize efficient dry AMD monitoring in my clinic?
Practical tips:
1. Create a baseline chart with OCT images during the first visit.
2. Monitor regularly:
- Every 6–12 months in the early stages
- Every 3–6 months with GA
- Before each intravitreal injection
3. Standardise scanning protocols to minimise variability.
4. Use OCT software tools for image comparison, GA calculation, heat maps.
5. Communicate clearly with patients about drusen, atrophy, and treatment goals.
Why are optometrists on the front line of early AMD detection?
Optometrists play a key role in spotting the early signs of AMD, as they are often the first point of contact in eye care.
They perform initial screenings, provide guidance on lifestyle and supplements, and ensure regular OCT monitoring.
If drusen, pigment epithelial changes, or signs of GA are present, they refer patients to ophthalmologists for confirmation and treatment planning.
How can OCT insights help support patients emotionally?
Patients with dry AMD often ask: “Why bother if it can’t be cured?”
Here, OCT plays an emotional as well as clinical role. Showing OCT scans can:- Prove the value of slowing AMD progression
- Emphasise patients’ role in preserving sight
- Reassure them that long-term care makes a difference
Dry macular degeneration treatment breakthroughs: key takeaways for slowing AMD progression
Modern dry macular degeneration treatment breakthroughs, including FDA-approved injections, photobiomodulation, and AREDS 2 supplements, have changed the outlook for patients.
Yet treatment alone is not enough. Without consistent macular degeneration monitoring using OCT, the benefits of these therapies may be lost.The future of dry AMD treatment lies in a partnership between optometrists, ophthalmologists, and patients. Together, with breakthrough therapies and precise monitoring, we can slow AMD progression and give patients the best chance of preserving vision.
Disclaimer: USA FDA 510(k) Class II; Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS); AI/ML models and components intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
-
AItris for Buchanan Optometrists

 Mark Braddon
3 min.
Mark Braddon
3 min.Disclaimer: In the USA, Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS) has USA FDA 510(k) Class II clearance; AI/ML models and components are intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
Buchanan Optometrists and Audiologists is no ordinary eye-care center.
The Association of Optometrists (AOP) estimates 17,500 registered optometrists working across roughly 6,000 practices in the UK. The UK Optician Awards recognise the best in the UK Optical industry. To even make the top 5 is our equivalent of an Oscar nomination! They are the only practice in the UK to consistently make the top 5 since 2008. Buchanan Optometrists describe themselves as innovators who “continually push boundaries.”
Their list of awards speaks for itself:
- 2012 – National Optician Award for Premium Lens Practice of the Year
- 2013 – Luxury Eyewear Retailer of the Year and Premium Lens Practice of the Year
- 2013 – Winner at the UK Optician Awards
- 2015–2016 – Best UK Independent Practice
- 2017–2018 – Optometrist of the Year, with Alisdair Buchanan named the top optometrist in the UK
- 2023–2024 – Best Independent Optician and Best Technology Practice
And this list is not finished, as Alisdair Buchanan, the Owner and the Director of the center, is investing in their growth continuously.

With a track record like this, it’s no surprise that Buchanan Optometrists was among the first to adopt AI for Decision Support in OCT. AI is rapidly becoming a vital part of modern eye care, and leading centers are already embracing it.
Mark Braddon, Altris AI VP of Clinical Sales, sat down with Alisdair Buchanan, the owner and director of the practice, to talk about his experience with AI and what it means for the future of optometry.
Mark Braddon: You’ve been working with OCT for years. What changed in your practice after bringing in Altris AI Decision Support for OCT?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: As someone already confident in interpreting scans, I didn’t need help understanding OCT—but Altris provides something even more valuable: a kind of second opinion. It supports my clinical decisions and offers an added layer of reassurance, particularly in borderline or complex cases. That’s not just helpful—it’s powerful.
I didn’t think our OCT assessments could improve much—until we started using Altris AI. It’s not just an upgrade; it’s become an indispensable part of delivering modern, high-quality eye care. Altris AI has significantly enhanced the way we interpret OCT scans. What used to require prolonged focus and cross-referencing now takes moments, without sacrificing accuracy or depth. The system analyses images with incredible precision, highlighting subtle pathological changes that are often time-consuming to detect, especially during a busy clinic day.

Mark Braddon: What was the first real benefit you noticed after bringing Altris AI into your day-to-day routine?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: One of the most immediate benefits has been in patient communication. The platform generates clear, colour-coded visuals that make explaining findings effortless. Instead of trying to talk patients through grainy greyscale images, we can now show them precisely what we’re seeing. It’s improved understanding, reduced anxiety, and increased trust in the care we’re providing.
Mark Braddon: Was it easy to fit AI Decision Support into your OCT workflow? How easy did you find integrating Altris AI?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: Integration was seamless—no faff, no friction. It fits naturally into our existing workflow, with scans uploaded and analysed within seconds. It’s helped us work more efficiently, without compromising the thoroughness our patients expect.
In short, Altris AI has sharpened our clinical edge and strengthened the service we offer. It doesn’t replace experience—it enhances it. And that, for me, is the real value.
Mark Braddon: In your experience, where has AI been the most helpful in clinical work?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: The main area where it shines is in picking up early macular changes, particularly dry AMD. Things like drusen or subtle changes in the outer retinal layers, which could easily be missed at a glance, are brought to the surface immediately.

It’s also been handy with diabetic patients. Just having that extra layer of input to flag microstructural changes helps us stay ahead of progression.
We’ve also started using it with glaucoma suspects. While our Heidelberg Spectralis remains our go-to for structural monitoring, having the RNFL analysis from Altris adds a checkpoint. I’d never base a referral purely on it, but it’s nice to have a second opinion—even if it’s an AI one.
Mark Braddon: Has AI Decision Support changed how you handle borderline or difficult-to-call cases?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: I’d say it’s given us more confidence, particularly in the grey areas—those borderline cases where you’re not quite sure if it’s time to refer or just monitor a bit more closely. With AMD, for example, it has helped us catch early signs of progression and refer patients before things become urgent.
And for glaucoma, again, it’s not replacing anything we do—it’s just another tool we can lean on. Sometimes it confirms what we already thought, and other times it nudges us to look again more carefully.
Mark Braddon: How has using AI impacted your conversations with patients during consultations?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: One of the unexpected benefits has been how much it helps with patient conversations. We show the scans on-screen during the consultation, and the colour overlays make things much easier to explain, especially with older patients. They can see what we’re talking about, which makes the whole thing feel more real and less abstract.
They often say, “Ah, now I understand,” or “So that’s what you’re looking at.” It’s not about dazzling them with tech—it just helps make the discussion more transparent and more reassuring.

Mark Braddon: Some professionals worry that AI might replace human judgment. How do you see its role in clinical decision-making?
Alisdair Buchanan, Owner: I don’t see Altris —or any AI—as a threat to what we do. It’s not here to replace us. We still make the decisions, take responsibility, and guide our patients. But it does help.
For me, it’s like having a quiet assistant in the background. It doesn’t get everything right, and I certainly wouldn’t act on it blindly—but it prompts me to pause, double-check, and sometimes spot something I might have missed otherwise. That can only be a good thing.
In short, Altris has sharpened our clinical edge and strengthened the service we offer. It doesn’t replace experience—it enhances it. And that, for me, is the real value.
-
AI for Decision Support with OCT: “Altris Gave Me More Certainty in My Clinical Decisions”

 Maria Martynova
2 minutes
Maria Martynova
2 minutesDisclaimer: In the USA, Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS) has USA FDA 510(k) Class II clearance; AI/ML models and components are intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
AI for Decision Support with OCT: An Interview with Clara Pereira, Optometrist from Franco Oculista
About Franco Oculista Optometry in Portugal.
Franco Oculista is the optometry center with a 70-year-old history: its roots date back to the mid-1950s in Luanda, where it was founded by Gonçalo Viana Franco. Having left behind a career in pharmacy, Gonçalo pursued his entrepreneurial vision by opening an optician’s bearing his name in the heart of the Angolan capital. Driven by a thirst for knowledge and a deep sense of dedication, he turned his dream into reality. With a commitment to professionalism and a forward-thinking approach, he integrated the most innovative technologies available at the time. This blend of passion, expertise, and innovation established Franco Oculista as a benchmark for quality and excellence in the field. In 1970s, the family returned to Portugal and opened the new FRANCO OCULISTA space on Avenida da Liberdade.
How do Franco Oculista describe their mission?
“Through individualized and segmented service, we seek to respond to the needs of each client. We combine our knowledge with the most sophisticated technical equipment and choose quality and reliable brands. We prioritize the evolution of our services and, for this reason, we work daily to satisfy and retain our customers with the utmost professionalism.”

Clara Pereira is one of the optometrists at Franco Oculista and has been an optometrist for nearly two decades. Based in a private clinic in Portugal, she brings years of experience and calm confidence to her consultations. We talked with her to learn how her clinical practice has evolved, particularly since integrating OCT and, more recently, Altris AI – AI for Decision Support with OCT.
Altris AI: Clara, can you tell us a bit about your daily work?
Clara: “Of course. I’ve been working as an optometrist for 19 years now. My practice is quite comprehensive—I assess refractive status, binocular vision, check the anterior segment with a slit lamp, measure intraocular pressure, and always examine the fundus.
Clara: “In Portugal, we face limitations. We’re not allowed to prescribe medication or perform cycloplegia, so imaging becomes crucial. I rely heavily on fundus photography and OCT to guide referrals and detect early pathology.”

Altris AI: How central is OCT diagnostics to your workflow?
Clara: “OCT is substantial. I perform an OCT exam on nearly every patient, on average, eight OCT exams per day. It’s an essential part of how I gather information. With just one scan, I can learn so much about eye health.”Altris AI: What kind of conditions do you encounter most frequently?
Clara: “The most common diagnosis is epiretinal membrane—fibrosis. But I also manage patients with macular degeneration and other retinal pathologies. Having the right tools is key.”Altris AI: And what OCT features do you use the most?
Clara: “I regularly use the Retina, Glaucoma, and Macula maps. But if I had to choose one, the Retina Map gives me the most complete picture. It’s become my go-to.”Altris AI: You’ve recently started using Altris AI. What has that experience been like?
Clara: “At first, I didn’t know much about it. But when Optometron introduced Altris AI to me—a company I trust—I didn’t hesitate. And I’m glad I didn’t. From the beginning, it felt like a natural extension of my clinical reasoning.Clara: “Altris AI gives me an extra layer of certainty. It helps me extract more from the OCT images. I usually interpret the scan myself first, and then I run it through the platform. That way, I validate my thinking while also learning something new.”
Altris AI: Have any standout cases where Altris AI made a difference?
Clara: “Yes. I’ve had a few. One was a case of advanced macular degeneration, in which the AI visualization really helped me explain the condition to the patient. Another was using anterior segment maps for fitting scleral lenses—Altris was incredibly useful there, too. I do a lot of specialty lens fittings, so that was a big advantage.”
Altris AI: Would you recommend Altris AI to your colleagues?
Clara: “I would recommend Altris AI to my colleagues. For me, it’s about more than just the diagnosis. It’s about feeling confident that I’m seeing everything clearly and giving my patients the best care possible. Altris AI helps me do exactly that.”
Why This Matters: Altris AI in Real Practice
Clara’s story reflects the real value of AI in optometry—not as a replacement for clinical judgment, but as a powerful companion. With every OCT scan, she strengthens her expertise, improves diagnostic accuracy, and gives her patients the reassurance they deserve.
Whether identifying early signs of fibrosis, supporting complex scleral lens fittings, or acting as a second opinion, Altris AI seamlessly fits into the modern optometrist’s workflow, making every scan more meaningful.
AI for Decision Support with OCT: Transforming Retinal Diagnostics
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the field of ophthalmology, particularly through its integration with Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). OCT is a non-invasive imaging technique that captures high-resolution cross-sectional images of the retina, enabling early detection and monitoring of various ocular conditions. However, interpreting these scans requires time, expertise, and consistency—factors that AI-based decision support systems are uniquely positioned to enhance.
Altris AI (AI for OCT decision support platform) analyzes thousands of data points across B-scans, automatically detecting retinal pathologies, quantifying biomarkers, and identifying patterns that may be subtle or overlooked by the human eye. By providing objective, standardized assessments, Altris AI reduces diagnostic variability and improves clinical accuracy, especially in busy or high-volume practices.
For optometrists and ophthalmologists, AI acts as a second opinion, flagging early signs of diseases such as age-related macular degeneration (AMD), diabetic retinopathy, and glaucoma. It streamlines workflows by highlighting areas of concern, prioritizing cases that require urgent attention, and offering visual explanations that are easy to communicate to patients.
Moreover, Altris AI enableS longitudinal tracking of pathology progression. By comparing OCT scans over time ( even from various OCT devices), clinicians can monitor subtle changes in drusen volume, retinal thickness, supporting timely clinical decisions and tailored treatment strategies. The integration of AI into OCT interpretation not only enhances diagnostic confidence but also supports evidence-based care, early intervention, and improved patient outcomes. As AI continues to evolve, it will play a vital role in advancing precision medicine in ophthalmology, empowering eye care professionals with tools that are fast, reliable, and scalable.

In essence, AI for OCT decision support is not replacing clinical expertise; it is augmenting it, elevating the standard of care through speed, accuracy, and actionable insights.
-
Future of Ophthalmology: 2025 Top Trends

 Maria Znamenska
13.03.202512 min read
Maria Znamenska
13.03.202512 min readFuture of Ophthalmology: 2025 Top Trends
In a recent survey conducted by our team, we asked eye care specialists to identify the most transformative trends in ophthalmology by 2025. The results highlighted several key areas, with artificial intelligence (AI) emerging as the clear frontrunner, cited by 78% of respondents.

However, the survey also underscored the significant impact of optogenetics, novel AMD/GA therapies, and the continuing evolution of anti-VEGF treatments. This article will explore the practical implications of these advancements, providing an overview of how they are poised to reshape diagnosis, treatment, research, and, ultimately, patient outcomes in ophthalmology.
In this article, we will also discuss Oculomics, a very promising field that is gaining momentum.
Top AI Technology for Detecting Eye-related Health Risks 2025
Building upon the survey’s findings, we begin with the most prevalent trend: top AI technology for detecting eye-related health risks in 2025

AI in Clinical Eye Care Practice
With the increasing prevalence of conditions like diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration, there is a growing need for efficient and accurate screening tools. And AI is already valuable for eye-care screening: algorithms can analyze retinal images and OCT scans to identify signs of these diseases, enabling early detection and timely intervention.

AI-powered screening tools can also help identify rare inherited retinal dystrophies, such as Vitelliform dystrophy and Macular telangiectasia type 2. These conditions can be challenging to diagnose, but AI algorithms can analyze retinal images to detect subtle signs that human observers may miss.
AI also starts to play a crucial role in glaucoma management. Early detection of glaucoma demands exceptional precision, as the early signs are often subtle and difficult to detect. Another significant challenge in glaucoma screening is the high rate of false positive referrals, which can lead to unnecessary appointments in secondary care and cause anxiety for patients, yet delayed or missed detection of glaucoma results in irreversible vision loss for millions of people worldwide. So, automated AI-powered glaucoma analysis can offer transformative potential to improve patient outcomes.
This OD module evaluates optic disc parameters using OCT, providing personalized assessments by accounting for individual disc sizes and angle of rim absence. Such a tailored approach eliminates reliance on normative databases, making evaluations more accurate and patient-specific.
Furthermore, it enables cross-evaluation across different OCT systems, allowing practitioners to analyze macula and optic disc pathology, even when data originates from multiple OCT devices. Key parameters evaluated by Altris AI’s Optic Disc Analysis include disc area, cup area, cup volume, minimal and maximum cup depth, cup/disc area ratio, rim absence angle, and disc damage likelihood scale (DDLS).

AI for Clinical Trials and Research
AI is revolutionizing clinical trials and research in ophthalmology. One such key application of AI is biomarker discovery and analysis. Algorithms can analyze large datasets of medical images, such as OCT scans, to identify and quantify biomarkers for various eye diseases. These biomarkers can be used to assess disease progression, monitor treatment response, and predict clinical outcomes.
AI is also being used to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of clinical trials. By automating the process of identifying eligible patients for clinical trials, AI can help researchers recruit participants more quickly and ensure that trials include appropriate patient populations, accelerating the development of new treatments.

Algorithms can analyze real-world data (RWD) collected from electronic health records and other sources to generate real-world evidence (RWE). RWE provides valuable insights into disease progression, treatment patterns, and long-term outcomes in everyday clinical settings, complementing the findings of traditional randomized controlled trials.
Oculomics
Integrating digitized big data and computational power in multimodal imaging techniques has presented a unique opportunity to characterize macroscopic and microscopic ophthalmic features associated with health and disease, a field known as oculomics. To date, early detection of dementia and prognostic evaluation of cerebrovascular disease based on oculomics has been realized. Exploiting ophthalmic imaging in this way provides insights beyond traditional ocular observations.

For example, the NeurEYE research program, led by the University of Edinburgh, is using AI to analyze millions of anonymized eye scans to identify biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative conditions. This research can potentially revolutionize early detection and intervention for these devastating diseases.
Another effort spearheaded by researchers from Penn Medicine, Penn Engineering is exploring the use of AI to analyze retinal images for biomarkers indicative of cardiovascular risk. AI systems are being trained on fundus photography to detect crucial indicators, such as elevated HbA1c levels, a hallmark of high blood sugar, and a significant risk factor for both diabetes and cardiovascular diseases.

AI analysis of retinal characteristics, such as retinal thinning, vascularity reduction, corneal nerve fiber damage, and eye movement, has shown promise in predicting Neurodegenerative diseases. Specifically, decreases in retinal vascular fractal dimension and vascular density have been identified as potential biomarkers for early cognitive impairment, while reductions in the retinal arteriole-to-venular ratio correlate with later stages.
Moving from AI, we now turn to another significant trend identified in our survey:
Optogenetics
Optogenetics represents a significant leap forward in ophthalmic therapeutics, offering a potential solution for vision restoration in patients with advanced retinal degenerative diseases, where traditional gene therapy often falls short. While gene replacement therapies are constrained by the need for viable target cells and the complexity of multi-gene disorders like retinitis pigmentosa (RP), optogenetics offers a broader approach.

This technique aims to circumvent the loss of photoreceptors by introducing light-sensitive proteins, known as opsins, into the surviving inner retinal cells and optic nerve, restoring visual function through light modulation. This method is particularly advantageous as it is agnostic to the specific genetic cause of retinal degeneration.
By delivering opsin genes to retinal neurons, the technology enables the precise manipulation of cellular activity, essentially transforming these cells into new light-sensing units. This approach can bypass the damaged photoreceptor layer, transmitting visual signals directly to the brain.
Several companies are pioneering advancements in this field. RhyGaze, for example, has secured substantial funding to accelerate the development of its lead clinical candidate, a novel gene therapy designed for optogenetic vision restoration. Their efforts encompass preclinical testing, including pharmacology and toxicology studies, an observational study to define clinical endpoints, and a first-in-human trial to assess safety and efficacy. The success of RhyGaze’s research could pave the way for widespread clinical applications, significantly impacting the treatment of blindness globally.

Nanoscope Therapeutics is also making significant strides with its MCO-010 therapy. This investigational treatment, administered through a single intravitreal injection, delivers the Multi-Characteristic Opsin (MCO) gene, enabling remaining retinal cells to function as new light-sensing cells. Unlike earlier optogenetic therapies that required bulky external devices, MCO-010 eliminates the need for high-tech goggles, simplifying the treatment process and enhancing patient convenience. The ability to restore light sensitivity without external devices represents a major advancement, potentially broadening the applicability of optogenetics to a wider patient population.

Another critical area of innovation highlighted in our survey is the advancement of treatments for AMD and GA.
New AMD/GA Treatment
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and geographic atrophy (GA) represent a significant challenge in ophthalmology, demanding innovative therapeutic strategies beyond the established anti-VEGF paradigm.

Gene Correction
Gene editing is emerging as a powerful tool in the fight against AMD and GA, potentially correcting the underlying genetic errors that contribute to these diseases. Essentially, it allows us to make precise changes to a patient’s DNA.
Traditional gene editing techniques often rely on creating ‘double-strand breaks’ (DSBs) in the DNA at specific target sites, which are like precise cuts in the DNA strand. These cuts are made using specialized enzymes, like CRISPR-Cas9, which act as molecular scissors. While effective, these methods can sometimes introduce unwanted changes at the cut site, such as small insertions or deletions.
After a DSB is made, the cell’s natural repair mechanisms kick in. There are two main pathways:
- Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ): This is the cell’s quick-fix method. It essentially glues the broken ends back together. However, this process can sometimes introduce errors, leading to small insertions or deletions that can disrupt the gene’s function.
- Homology-Directed Repair (HDR): This is a more precise repair method. It uses a ‘donor’ DNA template to guide the repair process, ensuring accuracy. However, HDR is more complex and less efficient, especially in non-dividing cells.
To overcome these limitations of traditional gene editing, researchers have developed more precise techniques:
- Base Editing: This technique allows scientists to change a single ‘letter’ in the DNA code without creating DSBs.
- Prime Editing: This advanced technique builds upon CRISPR-Cas9, allowing for a wider range of precise DNA changes. It can correct most disease-causing mutations with enhanced safety and accuracy.
- CASTs (CRISPR-associated transposases): This method enables larger DNA modifications without creating DSBs, offering a safer approach to genetic correction.
Why does this matter for AMD and GA? These advancements in gene editing are crucial for addressing the genetic roots of these pathologies. We can potentially develop more effective and targeted therapies by precisely correcting the faulty genes that contribute to these diseases. The technologies are still being researched, but they hold great promise for the future of ophthalmology.
Cell Reprogramming
Cell reprogramming offers a novel approach to regenerative medicine, with the potential to replace damaged retinal cells. This technique involves changing a cell’s fate, either in vitro or in vivo. In vitro reprogramming involves extracting cells, reprogramming them in a laboratory, and then transplanting them back into the patient. In vivo reprogramming, which directly reprograms cells within the body, holds particular promise for retinal diseases. This approach has succeeded in preclinical studies, demonstrating the potential to restore vision in conditions like congenital blindness.

Vectors and Delivery Methods
The success of gene therapy relies on efficiently delivering therapeutic genes to target retinal cells. Vectors are essentially delivery vehicles, designed to carry therapeutic genes into cells. These vectors can be broadly classified into two categories: viral and non-viral. Vectors, both viral and non-viral, are crucial for this process.
Viral vectors are modified viruses that have been engineered to remove their harmful components and replace them with therapeutic genes. They are highly efficient at delivering genes into cells, as they have evolved to do just that. Adeno-associated viruses (AAVs) are the most commonly used viral vectors in ocular gene therapy due to their safety profile and cell-specificity. The diversity of AAV serotypes allows for tailored gene delivery to specific retinal cell types.
Non-viral vectors, on the other hand, are synthetic systems that don’t rely on viruses. They can be made from lipids, polymers, or even DNA itself. While they may be less efficient than viral vectors, they offer safety and ease of production advantages.
Advances in vector design, whether viral or non-viral, are focused on enhancing gene expression, cell-specificity, and carrying capacity.
Now, let’s examine the ongoing evolution of anti-VEGF treatments, a cornerstone of modern retinal care.
New Anti-VEGF drugs
The landscape of ophthalmology has undergone a dramatic transformation since the early 1970s when Judah Folkman first proposed the concept of tumor angiogenesis. His idea sparked research that ultimately led to the identification of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in 1989 and the development of anti-VEGF therapies, revolutionizing the treatment of neovascular eye diseases, dramatically improving outcomes for patients with wet AMD, diabetic retinopathy, and retinal vein occlusions.
Population-based studies have shown a substantial reduction (up to 47%) in blindness due to wet AMD since the introduction of anti-VEGF therapies. However, significant gaps remain despite this progress, especially regarding treatment durability. Anti-VEGF drugs require frequent intravitreal injections, which can be difficult for patients due to time commitments, financial costs, and potential discomfort. Although newer agents have extended treatment intervals, patient adherence and undertreatment challenges persist in real-world settings. Innovative approaches are being investigated to address these unmet needs to increase drug durability and reduce the treatment burden.
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors
One approach to increasing treatment durability is using tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs). TKIs are small-molecule drugs that act as pan-VEGF blockers by binding directly to VEGF receptor sites inside cells, offering a different action mechanism than traditional anti-VEGF drugs that target circulating VEGF proteins.
Currently, TKIs are being investigated as maintenance therapy, primarily in conjunction with sustained-release delivery systems. Two promising TKIs for retinal diseases are axitinib and vorolanib. In a bioresorbable hydrogel implant, Axitinib is being studied for neovascular AMD and diabetic retinopathy. Vorolanib, in a sustained-release delivery system, is also being investigated for neovascular AMD. These TKIs offer the potential for less frequent dosing, reducing the treatment burden for patients.
Port Delivery System
The Port Delivery System (PDS) is a surgically implanted, refillable device that provides continuous ranibizumab delivery for up to 6 months. While it’s FDA-approved for neovascular AMD, it’s also being investigated for other retinal diseases, such as diabetic macular edema and diabetic retinopathy.
Although the PDS faced a voluntary recall due to issues with septum dislodgment, it has returned to the market with modifications. The PDS offers the potential for significantly reduced treatment frequency for a subset of patients. However, challenges remain, including the need for meticulous surgical implantation and the risk of endophthalmitis.
Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology offers promising solutions to overcome limitations of current ocular drug delivery. The unique structure of the eye, with its various barriers, poses challenges for drug delivery. Topical administration often fails to achieve therapeutic concentrations, while frequent intravitreal injections carry risks. Nanotechnology can improve drug solubility, permeation, and bioavailability through nanoparticles, potentially extending drug residence time and reducing the need for frequent injections. Several nanoparticle systems, lipid and polymeric, are being studied for ocular drug delivery, offering hope for more effective and less invasive treatments.
Summing up
The advancements discussed in this article, encompassing AI, optogenetics, novel AMD/GA therapies, and refined anti-VEGF treatments, collectively signal a transformative era for ophthalmology. As highlighted by the survey results, AI probably encompasses most of the changes by redefining diagnostic and clinical workflows through its capacity for image analysis, biomarker identification, and personalized patient management.
Optogenetics offers a distinct pathway to vision restoration, bypassing limitations of traditional gene therapy. The progress in AMD/GA treatments, particularly gene editing and cell reprogramming, presents opportunities for targeted interventions. Finally, the evolution of anti-VEGF therapies, with innovations in drug delivery and sustained-release mechanisms, addresses persistent challenges in managing neovascular diseases.
These developments, driven by technological innovation and clinical research, promise to enhance patient outcomes and reshape the future of ophthalmic care.
Disclaimer: USA FDA 510(k) Class II; Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS); AI/ML models and components intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
-
ML Applied to 3D Optic Disc Analysis for Glaucoma Risk Assessment Across Different OCT Scan Protocols Without a Normative Database

 Angelina Hramatik
14.02.202520 min read
Angelina Hramatik
14.02.202520 min readMachine Learning Applied to 3D Optic Disc Analysis for Glaucoma Risk Assessment Across Different OCT Scan Protocols Without a Normative Database
1. Introduction
Glaucoma is one of the leading causes of irreversible blindness worldwide, affecting millions of people annually. The disease is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making timely diagnosis particularly challenging. Early detection of glaucomatous changes is crucial for preventing vision loss and improving long-term patient outcomes.
One well-established method for assessing glaucoma is the Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS), which evaluates structural changes in the optic nerve head (ONH) based on the extent of neuroretinal rim loss. This method categorizes glaucomatous damage severity by analyzing the relationship between the optic cup and neural rim, while also accounting for optic disc size without relying on a normative database. 1, 2, 3, 4.
While DDLS is recognized for its reliability and utility in clinical practice, it is not a standalone diagnostic tool. Rather, it is one of several methods used to identify signs of glaucoma, and its implementation is often limited to specific imaging modalities or scan protocols, such as 3D optic disc-only scans or fundus images.
In this article, we introduce an enhanced approach to DDLS analysis that overcomes these limitations. We want to present a solution, which is capable of performing DDLS analysis on any OCT scan protocol that captures the optic nerve, including 3D optic disc scans (which provide the most detailed view of the nerve), as well as OCT horizontal and vertical 3D wide scans. By leveraging advanced machine learning models, we achieve unprecedented flexibility and accuracy, ensuring reliable analysis across different scanning protocols and OCT systems.
Unlike traditional systems restricted to specific devices or data formats, our solution processes scans from multiple OCT systems. Moreover, it excels in challenging scenarios, providing clinicians with a robust and versatile tool for analyzing potential signs of glaucoma.
A Brief Theoretical Overview
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans vary in the anatomical regions they capture. One specific type is the optic disc OCT scan (Figure 2), which provides high-resolution imaging of the optic disc and the surrounding optic nerve head (ONH) structures. This scan type is commonly used in glaucoma assessment, as it allows for the evaluation of the optic nerve’s structure, including the neuroretinal rim, optic cup, and surrounding peripapillary retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) — key areas affected in glaucomatous damage.

Figure 1. Photograph of the retina of the human eye, with overlay diagrams showing the positions and sizes of the macula, fovea, and optic disc (Reference).

Figure 2. 6 mm OCT b-scan of the optic nerve head (ONH) region.
In contrast, macular OCT scans (Figure 3) focus on the central retina, providing detailed visualization of structures such as the foveal center, retinal layers, and macular biomarkers (such as drusen, hypertransmission, fluids etc). Since the macula is anatomically distinct from the optic nerve head, standard macular scans do not capture the ONH comprehensively.

Figure 3. 6 mm OCT b-scan of the macular region, showing the foveal pit and retinal layers.
A more comprehensive scanning approach is 12 mm wide scan OCT (Figure 4), which captures both the macular region and optic nerve head in a single scan. This broader field of view allows for the simultaneous assessment of central retinal structures and optic nerve-related changes, making it valuable for detecting and monitoring conditions that affect both regions, such as glaucoma and other neurodegenerative or vascular retinal diseases.

Figure 4. 12 mm wide scan OCT b-scan, which captures both the macular region and part of the optic nerve head.
2. Results
2.1. Experiment Setup
Brief Method Overview
To evaluate the effectiveness of DDLS analysis in assessing glaucoma severity, we designed an experiment comparing results obtained from processing 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and 3D Wide scan OCT scans with the corresponding reports generated by the OCT system. Our method follows four key steps:
- Detecting optic nerve landmarks like Bruch’s Membrane Opening (BMO) points (Eye Keypoints Retrieval / OCT Keypoint Detector Model);
- Segmenting the inner limiting membrane (ILM) (Retina Layers Segmentation Model);
- Reconstructing the neuroretinal rim geometry;
- Applying the Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS) for classification.
The dataset below was used to validate the algorithm.
Dataset Used for Validating the Entire Algorithm
For validation, we compared our algorithm’s DDLS measurements with the DDLS values generated by the built-in algorithms of the Optopol REVO NX 130 OCT system. This provided a baseline for assessing accuracy and consistency.
To validate our approach, we conducted an experiment comparing DDLS metrics derived from:
- 3D Optic Disc OCT scans, which are traditionally used for DDLS analysis.
- 3D Wide scans, which capture both the macular and optic nerve regions, providing a more comprehensive dataset for analysis.
The dataset includes imaging data from 37 patients examined using the Optopol REVO NX 130 OCT system, with each patient undergoing the following protocols on the same day:
- 3D Optic Disc OCT (6mm zone): 168 scans
- 3D Wide scan (horizontal protocol, 12mm): 128 scans
A report was obtained from the 3D Optic Disc OCT scans, containing all parameters calculated by the device.
Since no manual annotations are available for these data, our comparison is conducted directly against the device-generated results.
The distribution of data was as follows:
- Glaucomatous Optic Disc: 21 cases;
- Normal Optic Disc: 16 cases.
2.2. Final Validation Results: DDLS Accuracy and Error Metrics
To evaluate the performance of our DDLS analysis method, we compared its results with the corresponding DDLS values generated by the OCT device’s built-in algorithms. The device reports serve as a reference point for all calculations, meaning the accuracy, MAE/STD values presented below indicate the level of agreement between our method and the device’s measurements.
The parameters compared below are the key indicators for glaucoma stage assessment.
- The rim-to-disc ratio (RDR) represents the thinnest neuroretinal rim width relative to the vertical optic disc diameter. A lower RDR indicates a more advanced stage of rim thinning, as glaucoma leads to progressive narrowing of the neuroretinal rim due to the loss of ganglion cells axons.
- The rim absence angle (RAA) quantifies the extent of neuroretinal rim loss in degrees. It defines the angle where the rim is completely absent, exposing the optic cup. A wider RAA suggests a more severe stage of glaucoma, as it indicates greater rim loss across the disc circumference.
Both RDR and RAA provide complementary perspectives on structural optic nerve damage:
- RDR measures the smallest remaining rim thickness in proportion to the disc.
- RAA evaluates how much of the disc circumference has lost its rim.
By considering both parameters together, a more comprehensive assessment of glaucoma severity can be achieved. Based on RDR and RAA, a DDLS stage is assigned, allowing for standardized classification of glaucoma progression.

Table 1. Validation Results of DDLS Analysis on 3D Optic Disc and 3D Wide Scan OCT Scans
The table presents validation results comparing 3D Optic Disc OCT scan and 3D Wide scan OCT in DDLS analysis, focusing on Mean Absolute Error (MAE) and Standard Deviation (STD) for key parameters, along with overall DDLS staging accuracy. These metrics are calculated for the rim-to-disc ratio and rim absence angle by comparing their respective values from 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and 3D Wide scans against those from the device reports, providing a precise assessment of deviations from the reference values.
Key Observations
1. Our Goal: Consistency with Device Reports, Not Outperformance
The experiment does not aim to surpass the device’s accuracy but rather to demonstrate that our method produces results in alignment with the device-generated DDLS reports.
The device report serves as a reference, helping to interpret the figures we present, but this does not mean the device’s output is always the absolute truth.
2. High DDLS Staging Accuracy for Both Scan Types
3D Optic Disc OCT scan: 97.3% accuracy in determining DDLS glaucoma stage.
3D Wide scan OCT: 94.59% accuracy, demonstrating strong reliability despite a broader scan area and fewer scans capturing the nerve, leading to less available information.
Conclusion:
- Both types of scans allow the production of clinically reliable DDLS results, but as expected, 3D optic disc scans provide slightly better accuracy due to their higher resolution of the optic nerve head (ONH).
- The small accuracy gap and close values for key parameters between the two suggests that 3D wide scan OCT can still be a viable option for glaucoma assessment, despite offering less detailed information about the optic nerve compared to optic disc scans.
3. RD Ratio and Rim Absence Angle: High Precision Within Clinical Margins
RD Ratio (rim-to-disc ratio):
- Step size between DDLS stages: 0.1.
- Mean Absolute Error (3D Optic Disc OCT scan): 0.008 (significantly smaller than step size).
- Mean Absolute Error (3D Wide scan OCT): 0.024 (still relatively small).
Conclusion:
- Both 3D Optic Disc OCT scan and 3D Wide scan analysis provide high precision in RD ratio calculations.
- The small error ensures that stage classification remains reliable, especially in optic disc scans.
Rim Absence Angle:
- Step size between DDLS stages: Minimum 45°.
- Mean Absolute Error (3D Optic Disc OCT scan): 2.2° (very small compared to step size). Mean Absolute Error (3D Wide scan OCT): 4.2° (still well below stage transition threshold).
Conclusion:
- The method’s margin of error is far smaller than the clinical threshold for stage differentiation, confirming high accuracy in rim loss assessment.
- 3D Optic Disc scans again show better precision, reinforcing that they remain the preferred scan type for DDLS.
4. Our Advantage: Ability to Perform DDLS on Both Scan Types
- Unlike traditional DDLS implementations, which work only with 3D Optic Disc scans, our method can perform DDLS analysis on both 3D Wide scan and 3D Optic Disc OCTs.
- However, 3D Optic Disc OCT remains the preferred method for maximum precision, as it provides a higher-resolution view of the optic nerve.
Key Conclusions
- Our method is unique in its ability to process multiple scan types, while still maintaining high accuracy in both cases.
- On 3D Optic Disc scans, we achieve maximum precision, while on 3D Wide scans, we still maintain clinically reliable accuracy.
- Consistency: Across all glaucoma stages, our method produced stable results that closely matched ground truths provided by medical experts.
- Universal Compatibility: The algorithm performed equally well with scans from other manufacturers, demonstrating its versatility and robustness.
2.3. Patient Case Studies: DDLS Analysis in Real-World Scenarios
Accurate assessment of glaucoma severity relies on precise measurements of optic nerve parameters, such as disc area, rim-to-disc ratio, and rim absence angle. In the following examples, we analyzed four patient cases, including both normal optic discs and glaucomatous eyes, using 3D Optic Disc OCT scan, 3D Wide scan OCT, and device-generated reports as a reference standard.
By consolidating individual patient cases into a single comparative table, we can examine the consistency of DDLS analysis across different scan types and highlight key variations that may arise due to differences in scan coverage, segmentation accuracy, and anatomical structure. The following table summarizes the key optic nerve parameters measured for each patient and scan type.

Table 2. Comparative DDLS Evaluation Across Multiple Patient Cases
Key Findings & Interpretation
1. High Consistency Between Our Method and Device Reports
- Across all cases, the DDLS stage remains identical (4 for normal eyes, 7 or 8 for glaucomatous cases) regardless of whether the input scan was 3D Optic Disc OCT or wide scan, and this result corresponds to the device-generated report.
- Key optic nerve parameters such as disc area, cup area, and rim area closely align with the device reference, demonstrating strong algorithm performance.
2. Minor Variations in Cup and Rim Measurements
- Cup and rim area values show slight deviations between 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and 3D Wide scan scans, which is expected due to differences in scan coverage and segmentation sensitivity.
- For example, in Patient 3 (Glaucoma, Stage 8):
- Cup area was 1.86 mm² (3D Optic Disc OCT scan), 1.88 mm² (3D Wide scan), and 1.81 mm² (Device Report).
- Rim area was 0.55 mm² (3D Optic Disc OCT scan), 0.53 mm² (3D Wide scan), and 0.58 mm² (Device Report).
- These small variations do not affect final DDLS staging but highlight how scan type can introduce subtle segmentation differences.
3. Rim Absence Angle Varies Slightly but Remains Within Expected Tolerances
- The rim absence angle shows minor fluctuations across scan types, especially in glaucomatous cases.
- Example: In Patient 3 (Stage 8 Glaucoma), the device reported a rim absence angle of 162°, while our algorithm calculated 155° (3D Optic Disc OCT scan) and 151° (3D Wide scan).
- Since DDLS categories for severe glaucoma are defined in large increments (e.g., 45°+ thresholds), these small differences do not impact staging accuracy.
4. 3D Wide scan OCT Provides Comparable Results to 3D Optic Disc OCT scan
- Despite covering a larger field of view, wide scans produced DDLS staging results consistent with 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and device reports.
- In patients with coexisting macular pathologies, 3D Wide scan OCT may provide additional clinical insights while still maintaining high reliability for glaucoma staging.
Conclusion: Reliable DDLS Analysis Across Different Scan Types
This unified case study analysis confirms that our DDLS analysis algorithm produces highly consistent results across different scan protocols and patient conditions.
- DDLS stage assignment is identical to device reports across all scan types, ensuring high agreement with clinically validated reference values.
- Key optic nerve measurements (disc area, cup area, rim area) are closely aligned across 3D Optic Disc OCT scan, 3D Wide scan, and device reports, reinforcing algorithm accuracy.
- Minor variations in rim absence angle and segmentation metrics do not affect final glaucoma staging, highlighting the algorithm’s robustness.
- 3D Wide scan OCT offers a viable alternative for 3D Optic Disc OCT scans, particularly in cases where both macular and optic nerve regions need simultaneous evaluation.
5. Visual Comparison Shows Strong Similarity to Device Reports
- The disk and cup boundaries detected by our algorithm closely match those in the device-generated reports, maintaining consistent shapes and anatomical alignment across both 3D Optic Disc and 3D Wide scan OCT scans.
- However, wide scan-based segmentations tend to be slightly rougher, as less structural information is available compared to dedicated optic disc scans. This trade-off is expected due to the broader field of view in wide scans.
These findings validate our algorithm’s flexibility, adaptability, and clinical reliability, demonstrating its potential for seamless integration into real-world ophthalmic workflows.
2.4. Why Our Approach Stands Out: Key Advantages Over Traditional DDLS Systems
While the previous patient case studies demonstrated the accuracy and consistency of our DDLS analysis across different optic disc conditions, another critical advantage of our method is its ability to work seamlessly across various scanning protocols. Unlike traditional device-restricted solutions, our approach supports DDLS assessment on both standard 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and 3D Wide scans with different orientations.
The following table illustrates the same patient’s optic nerve head analyzed using three different scanning protocols: 3D Optic Disc OCT scan, 3D Wide scan Horizontal, and 3D Wide scan Vertical. This comparison highlights the method’s adaptability to different scan formats, ensuring reliable DDLS analysis regardless of the scanning protocol used. This example is taken from a Topcon Maestro 2 OCT system, providing an additional reference for processing across different OCT systems.

Table 3. Comparative DDLS Analysis Across Different Scanning Protocols: 3D Optic Disc OCT, 3D Wide scan Horizontal, and 3D Wide scan Vertical.
This capability significantly enhances clinical applicability, allowing our algorithm to process data from various scanning protocols and devices while maintaining high accuracy. The ability to analyze both 3D Optic Disc and 3D Wide scan OCT scans — across different orientations and machine types — ensures comprehensive glaucoma assessment even in cases where scan availability or quality may vary.
Key advantages over traditional DDLS analysis methods
1. Device Independence
- While most existing solutions are restricted to proprietary OCT data formats, our algorithm processes scans from any OCT system, ensuring broad compatibility across devices.
2. Consistent Accuracy Across Different Scan Types
- Our algorithm closely matches device-generated DDLS reports, achieving 97.3% accuracy for 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and 94.59% for 3D Wide scan OCTs.
- Patient cases confirm this consistency, with both normal and glaucomatous eyes correctly classified, even when analyzed with different scan types.
3. Robust Performance in Edge Cases
- Unlike traditional device-based DDLS assessments, which may struggle with low-quality images or atypical anatomical features, our approach maintains high accuracy in challenging clinical scenarios.
- Patient examples with small optic discs and advanced-stage glaucoma demonstrated that our algorithm successfully identified key DDLS indicators even when scan quality or nerve structure was less distinct.
4. Expanded Assessment Through 3D Wide scan OCT
- The ability to perform DDLS analysis on Horizontal and Vertical 3D Wide scans allows for a more comprehensive evaluation by incorporating both macular and optic nerve data.
- In patients with coexisting macular pathologies, wide scans enabled earlier detection of glaucomatous changes that would have been missed if only optic disc scans were used.
3. Detailed Approach Description
To assess glaucoma stage on OCT scans using DDLS analysis, the following steps should be performed:
- Optic Nerve Landmarks Detection – Localization of the optic nerve in the b-scan view of each scan by identifying key anatomical landmarks.
- ILM Detection – Segmentation of the inner limiting membrane (ILM) in the b-scan view of each scan to establish a reference for neuroretinal rim measurement.
- Neuroretinal Rim Reconstruction – Construction of the neuroretinal rim geometry based on detected nerve landmarks and ILM segmentation.
- DDLS Analysis – Application of the Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS) to assess glaucoma severity based on neuroretinal rim measurements. This includes assigning a DDLS stage according to rim width and optic disc size, with a focus on detecting localized thinning and asymmetry.
3.1. Keypoint Annotation Process / Nerve Detection
The foundation of our approach lies in a high-quality, annotated dataset meticulously labeled by a team of four expert ophthalmologists. The annotation process focused on identifying key anatomical landmarks in both the macular region and the optic disc nerve zones, both of which are critical for detecting glaucomatous changes and performing Disc Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS) analysis.
These keypoints serve as essential data for evaluating disease progression and training machine learning models. The dataset was carefully selected based on key clinical features, such as the presence or absence of nerve fibers, foveal pits, and other pathological markers, ensuring a comprehensive representation of various conditions and scan types.
The annotated dataset consists of approximately 370 unique OCT examinations with more than 56,000 b-scans, covering a range of physical scanning areas, pathology types, and optic nerve conditions to enhance the model’s robustness. The scans are categorized as follows:
- Optic Disc with no excavation: ~15 examinations;
- Glaucomatous Optic Disc: ~105 examinations;
- Normal Optic Disc: ~105 examinations;
- Wide scans (covering both the macular and optic nerve regions): ~60 examinations;
- Normal Retina Scans: ~40 examinations;
- Pathological Retina Scans: ~45 examinations.
This detailed annotation process ensures high precision and reliability, enabling the algorithm to generalize across diverse cases while maintaining clinical accuracy in real-world scenarios.
3.2. Eye Keypoints Retrieval / OCT Keypoint Detector
Our keypoint detection model represents a logical evolution of the model for exam center detection, designed to efficiently and accurately identify key anatomical landmarks in OCT scans. The architecture integrates elements from UNet 5 and CenterNet 6, incorporating YOLO-inspired 7 techniques for keypoint prediction. Additionally, the backbone has been adapted to a transformer-based model 8, enhancing feature extraction capabilities.
Training Process
The training process follows a multi-stage approach, ensuring robustness, accuracy, and efficiency:
- Stage 1: Detects general keypoints, establishing a foundation for precise landmark localization.
- Stage 2: Groups and refines the identification of specific keypoints, progressively improving the model’s understanding of anatomical structures.
This structured approach enhances the model’s reliability across different scan types while maintaining computational efficiency.
Key Features
Data Preprocessing
- The data is augmented using unsupervised techniques, leveraging libraries such as Albumentations 9 to introduce variations such as rotations, scaling, and noise addition.
- This ensures the model encounters a wider variety of real-world scenarios during training, improving its generalization capability.
Training Process
- The model is trained using supervised learning techniques, optimizing a loss function through backpropagation and gradient descent.
- This approach allows for continuous refinement and adaptation to complex variations in OCT scans.
Parameterization & Tuning
- The model includes millions of adjustable parameters (weights), which are fine-tuned to increase accuracy.
- Key hyperparameters such as learning rate, batch size, and network depth are carefully selected to maximize performance.
- Advanced optimization techniques, including grid search, random search, and Bayesian optimization, are used to find the best hyperparameter configuration.
3.3. Retina Layers Segmentation Model
The Retina Layers Segmentation Model is our production-stage model, actively used within the Altris AI platform. It was incorporated into this experiment without modifications, ensuring that the results reflect real-world performance as seen in our deployed system.
Our Retina Layers Segmentation Model enables precise segmentation of key retinal layers in OCT scans, crucial for detecting structural changes linked to glaucoma and other retinal diseases. The model identifies:
- ILM, RNFL, GCL, IPL, INL, OPL, ONL, ELM, MZ, EZ, OS, RPE, BM
The training dataset consists of 5,000 expert-annotated OCT b-scans, covering a diverse range of patient demographics, including different ages and ethnic backgrounds. The segmentation model is designed to detect and delineate key retinal layers with high accuracy.
Training & Architecture
The model is based on U-Net with a ResNet backbone, optimized for OCT images. Training includes:
- Expert Annotation: Medical specialists labeled layers for ground truth.
- Augmentation: Albumentations-based transformations enhance robustness.
- Supervised Learning: Predicts segmentation masks using backpropagation.
- Hyperparameter Optimization: Grid search, random search, and Bayesian tuning maximize performance.
Model Validation & Performance
- The model was validated using a holdout validation approach, with separate validation and test sets that were not exposed during training.
- Real-world testing was conducted using scans from various clinical settings to ensure robustness.
- Performance was evaluated using the Mean Dice Coefficient across all layers, achieving a score of 0.80, with layer-specific scores ranging from 0.63 to 0.92, confirming high segmentation accuracy.
- Cross-domain testing demonstrated consistent performance across different OCT systems, and stability was confirmed over scans collected across different time periods.
This efficient, accurate, and generalizable model strengthens DDLS analysis and enhances AI-driven retinal diagnostics.
3.4. DDLS Algorithm
The DDLS algorithm evaluates glaucomatous changes by analyzing the geometric relationship between the neural rim and optic cup in the optic nerve head. Key steps include:
- Localization: Identifying boundaries of the optic cup and neuroretinal rim by reconstructing geometry on a b-scan view using disc landmarks and an inner limiting membrane.

Figure 5. B-scan Geometry Visualization.
- Measurement: Calculating the DDLS stage based on the ratio between the rim and disc boundaries.
- Cross-Scan Application: Adapting the analysis for 3D Wide scans (both Horizontal and Vertical protocols) as well as 3D Optic Disc-specific scans.
Our implementation enhances this traditional method by leveraging wide scans, enabling a more comprehensive assessment of glaucomatous changes.
3.5. Evaluation
To ensure the reliability and effectiveness of our DDLS algorithm, we conducted a rigorous evaluation process, adhering to best practices in data usage, ethics, and performance validation.
Data Integrity
- Measures were implemented to prevent data leakage, ensuring that scans from the same patient did not appear in both training and testing sets.
Ethical Considerations
- The analysis strictly relies on OCT-related data (e.g., scan zone size, laterality, pixel spacing) without incorporating any personal patient information.
Performance Metrics
- Keypoint detection accuracy was evaluated using Mean Squared Error (MSE), comparing model-predicted keypoints with expert annotations.
- Additional metrics included correctness of scan center-related landmarks and accuracy in the optic nerve region, ensuring precision in clinical applications.
The evaluation results confirmed the algorithm’s robustness, demonstrating significant performance gains, particularly in edge cases, where traditional methods often struggle.
Discussion
Our DDLS analysis method represents a significant advancement in glaucoma detection. Key benefits include:
- Universal Compatibility: The ability to process data from various devices ensures broad applicability.
- Enhanced Accuracy: By incorporating data from both macular and optic nerve regions, our approach captures more subtle glaucomatous changes.
- Edge Case Performance: Advanced machine learning techniques enable accurate analysis even in challenging scenarios.
Compared to traditional methods, our system provides a more flexible, reliable, and comprehensive solution for early glaucoma detection.
Disclaimer: USA FDA 510(k) Class II; Altris Image Management System (Altris IMS); AI/ML models and components intended to use for research purposes only, not for clinical diagnosis purposes.
Conclusion
By integrating 3D Wide scans and state-of-the-art machine learning models, we have enhanced DDLS analysis for glaucoma detection, ensuring high accuracy, broad compatibility, and robustness across diverse clinical scenarios.
Unlike traditional solutions, our algorithm:
- Works across multiple OCT devices, eliminating the constraints of proprietary data formats.
- It closely matches device-generated DDLS reports, achieving 97.3% accuracy for 3D Optic Disc OCT scans and 94.59% for 3D Wide scans.
- Performs reliably in edge cases, such as small optic discs and advanced-stage glaucoma, where traditional methods may struggle.
- Supports both Horizontal and Vertical 3D Wide scans, enabling more comprehensive assessments that incorporate both macular and optic nerve data.
- Enhances early glaucoma detection, particularly in patients with coexisting macular pathologies, where wide scans provide additional clinical insights.
By delivering consistently accurate DDLS staging, regardless of scan type or manufacturer, our system establishes a new benchmark for universal glaucoma assessment. This technology has the potential to significantly improve early detection and management, ultimately preserving vision and enhancing patient outcomes.
References
- Spaeth, G. L. (2005). The Disc Damage Likelihood Scale. Glaucoma Today. https://glaucomatoday.com/articles/2005-jan-feb/0105_18.html
- Cheng, K. K. W., & Tatham, A. J. (2021). Spotlight on the Disc-Damage Likelihood Scale (DDLS). Clinical Ophthalmology, 15, 4059–4071. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8504474/
- Zangalli, C., Gupta, S. R., & Spaeth, G. L. (2011). The disc as the basis of treatment for glaucoma. Saudi Journal of Ophthalmology, 25(4), 381-387. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1319453411000993
- Review of Optometry Staff. (2023, January 23). Optic disc staging systems effective in grading advanced glaucoma. Review of Optometry. https://www.reviewofoptometry.com/article/optic-disc-staging-systems-effective-in-grading-advanced-glaucoma
- Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. [Preprint]. Posted May 18, 2015. https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597
- Duan K, Bai S, Xie L, et al. CenterNet: Keypoint Triplets for Object Detection. [Preprint]. Posted April 17, 2019. https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.08189
- Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You Only Look Once: Unified, Real-Time Object Detection. [Preprint]. Posted June 8, 2015. https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02640
- Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, et al. An Image is Worth 16×16 Words: Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale. [Preprint]. Posted October 22, 2020. https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.11929
- Buslaev A, Iglovikov V, Khvedchenya E, et al. Albumentations: Fast and Flexible Image Augmentations. [Preprint]. Posted September 18, 2018. https://arxiv.org/abs/1809.06839
Recently Posted
-

Optometry Practice Management Software: Top 8 Applications
 Mark Braddon
13.02.20239 min read
Mark Braddon
13.02.20239 min readOptometry practice management software is designed for eye care specialists to manage their practices more efficiently and effectively. The software can automate a wide range of administrative tasks, making it easier for practitioners to focus on patient care.
Unlike other medical practices, optometry involves the management of a much larger number of optical instruments, processes and aids. Therefore, software for optometrists is more complex and multifunctional. It usually includes features such as appointment scheduling, patient registration, billing and insurance claims processing, patient data management, and secure messaging and email communication. The software can also integrate with other technologies, such as electronic health records (EHRs), OCT image management systems and diagnostic equipment.
data, optometry practice management software can help eye care clinics improve their operations, increase efficiency, and provide better patient care. The software can be customized to fit the specific needs of individual practices and is often offered on a subscription basis, making it an affordable and accessible solution for eye care clinics of all sizes.
In this article, we will highlight the main benefits of practice management optometry soft, and provide you with a list of the Top 8 software to look at.
What are the benefits of practice management optometry software?
Optometry practice management software can help doctors in multiple ways besides increasing their revenue, efficiency, and productivity. Some of the key benefits of optometry practice management software include the following items.
- Improved patient management. The software can store and organize patient data, including medical history, examination results, fundus or OCT images, and treatment plans. This information can be easily accessed by practitioners and used to inform patient care.
- Efficient appointment scheduling. The software can automate appointment scheduling, which can help to reduce the risk of double-booking and minimize wait times for patients.
- Accurate billing and insurance claims. The software can help to ensure that billing and insurance claims are processed accurately and efficiently, reducing the risk of errors and delays.
- Increased revenue. By streamlining billing and insurance claims processes, optometry practice management software can help eye care clinics to reduce errors and increase revenue.
- Easy access to patient records. The software can store and organize patient records, including OCT images, making it easy for doctors to access the information they need to provide the best care possible.
- Improved patient communication. Some optometry practice management software includes features that allow for secure messaging and email communication between patients and practitioners, making it easier to communicate outside of office visits.
- Increased productivity. By automating repetitive tasks, such as appointment scheduling and billing, optometry practice management software can free up time for eye care practitioners to focus on providing an individual approach to each patient.
- Better patient outcomes. With access to patient data and treatment history, eye care practitioners can provide more informed and effective care. This can lead to better patient outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
Overall, optometry practice management software can help eye care clinics to provide better patient care, increase efficiency and productivity, and improve their bottom line. Now let’s take a look at the best optometry software.
Altris IMS – for Smarter OCT Management
The majority of optometry centers offer OCT diagnostics today, and if your center is not an exception, then you will benefit from Altris Image Management System for OCT Analysis. Altris IMS system is created to organize OCT data securely and efficiently. With our system optometrists receive the chace to:
- Work with OCT scans from 9 Major OCT Manufacturers
- Enable historical data analysis
- Quantify and analyze 40+ retinal biomarkers relevant to reserach of 30+ retinal conditions. For Research Use Only.Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
- Fuel your Research with 40+ retinal biomarkers relevant to reserach of 30+ retinal conditions. For Research Use Only.Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
- Study progression patterns of 40+ retinal biomarkers relevant to reserach of 30+ retinal conditions. For Research Use Only.Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
If OCT is sill puzzling and complex method for the store, it’s worth seeing how Altris IMS can bring clinical and commercial benefits.

It is important to mention that the patient’s diagnosis is always on the eye care practitioner’s side. Altris AI is a tool that provides assistance in support in decision-making and allows its users to see a broader perspective of a patient’s eye health.
Acuitas activEHR 2.0
In case you are working at or owning a midsize or large optometry practice, this hybrid electronic health record solution will be quite useful. Acuitas activEHR 2.0 can be hosted in the cloud as well as deployed on-premise, depending on your preferences. This software offers its users a wide range of tools, including electronic medical records, billing software, scheduling, PACs, accounting software and billing services.
What is more, Acuitas activEHR 2.0 can provide optometry clinics with various marketing and upselling features, and you can also customize BI reporting and track benefits. Healthcare providers can reach out to patients via either SMS or email, which makes it much easier to schedule an appointment.
In addition, the optometry practice management software supports such features as IDA (Immediate Data Access), which allows practitioners to automatically update the frames. Acuitas activEHR 2.0 also offers a variety of application integrations.

MedFlow EMR
Next on our list — Medflow EMR software, which was designed to serve as either a standalone EMR (electronic medical record) or as a combination of EMR + practice management (PM) system. Like other optometry practice management software from our list, Medflow EMR was created specifically for eye care, but it can be used by eye care specialists providing both ophthalmology and optometry.
Medflow has a bunch of features, but the main one is the software has built-in templates designed for comfortable and time-saving work, including retina scans and surgery, cataracts, glaucoma, digital drawings, eye measurements, LASIK procedures, and more. In addition, it also has a base package, where ASC and optical modules are included.
Overall, this practice management software will suit a clinic of any size, be it solo practice or a large hospital. The Medflow interface can be easily integrated with other practice management systems or image interpretation applications. Also, the software can be used as a hosted solution or installed on-premise.

Liquid EHR
Liquid EHR software will be a perfect solution rather for small and midsize optometry practices than large hospitals. The broad range of its features includes medical records management, medical billing, scheduling and a lot more. The optometry practice management software provides eye care specialists with the ability to generate a mailing list, track systems workflow, manage documents, do compliance checks, integrate e-prescribing, and configurable exam records.
What is more, Liquid EHR has a number of specific optometry tools, such as historical IOP charts, drawing tools, built-in eye charts, frames data integration and image management. Optometrists can incorporate lab test results, view clinical summaries and send patient reminders.
In addition, the software also allows practitioners to have instant access to electronic insurance filing tools, patient recalls, drug interactions and allergy interaction checks, problem lists, active medication lists, medication recommendations, educational resources, smoking status, vital signs and more.

EyePegasusEHR
The EyePegasus optometry practice management software offers a solid number of tools and features for optometry practices. You can schedule appointments online, turn on the automatic appointment reminders, work with a patient portal, scan documents, use an optical calculator and an iOS app with patient check-in features.
Using EyePegasus, eye care specialists can customize different tabs by choosing a proper layout, and create templates for treatment documentation. Moreover, optometrists are able to scan medical images and upload them directly into a patient’s chart. The is also a possibility to create referral letters using auto-populated EHR data. Other EyePegasus tools include building and dispensing optical orders and online appointment management.
In addition, the optometry practice management software allows managing inventory of different items, such as lenses. EyePegasus also can be integrated with a variety of applications.

Eye Cloud Pro
Another optometry practice management software created for optical professionals is Eye Cloud Pro. The list of its data managing tools is really impressive and includes e-prescribing, inventory management, integrated credit card processing, electronic claims submission, device integrations, two-way texting (SMS), and ECP Billing.
The system also provides improved patient communication via secure messaging and email services. Clinic managers can configure various appointment types and lets clients request bookings via mobile or desktop devices. The software can be customized mailing lists, referral reports, account information, and sales reports to help with business strategy.
In addition, one more benefit of Eye Cloud Pro software is that it has an integrated payment processing system with automated invoice and receipt generation. It will make a clinic’s data safe and retained.

OD Link
Taking about comprehensive optometry practice management software, OD Link is one of the most suitable variants for any clinic. It has both PM and EMR/EHR tools, helping to manage patient records, exams, appointments, inventory, billing/insurance information, and much more.
OD Link software allows optometry practitioners to communicate with patients via SMS or email, work with electronic insurance claim processing centers, and create automated patient entrance forms.
It also has a mobile app for iOS users, can accept data input from electronic optometry equipment, and can be integrated with different applications.

ManagementPlus
Last but not least, ManagementPlus practice management software for optometrists was designed as a fully-fledged and customizable solution with a bunch of functions. With the help of this soft, eye care specialists can work with EHR, PM, ASC forms and inventory. It is also quite helpful in managing revenue cycle services, practice building and reputation management, business analytics and capital funding.
What is more, ManagementPlus solutions allow optometrists and clinic managers to work in one platform, which makes communication clear and unified. Users can track workflows and handle all billing from eligibility to collections.
In addition, ManagementPlus has an in-built reporting tool, which allows specialists to report on most fields in the system, while the practice management system provides a choice of two scheduling modules. Users have the option of choosing either cloud-based or on-premise deployment.
Summing up
Optometry management software is a perfect choice for any medical practice, including solo practices, midsize clinics, and large hospitals. It is a perfect tool not only for managing patients, optical instruments and aids. The software is also helpful in improving operations, increasing efficiency and revenue and streamlining the working process. Such solutions keep all the data in one place, powering optometrists to document the patient history directly from diagnosis, and managers to avoid unnecessary paperwork.
-

Eye Hospital Management Software: Top 8 Solutions for your Clinic
 Maria Znamenska
04.01.202310 min read
Maria Znamenska
04.01.202310 min read -

The Application of Machine Learning in Ophthalmology: The View from the Tech Side
 Philip Marchenko
30.11.202215 min read
Philip Marchenko
30.11.202215 min read -

-

Will Artificial Intelligence Replace Ophthalmologists & Optometrists?
 Maria Znamenska
17.11.20228 min read
Maria Znamenska
17.11.20228 min read -