AI-powered OCT workflow with Altris AI


Maria Znamenska, Retina Expert, PhD Ophthalmology, Altris AI Medical Director
AI-Powered OCT Workflow: How does it work?
My name is Maria Znamenska. I am an ophthalmologist with a PhD in ophthalmology and the Medical Director of Altris AI. I have been practicing and teaching OCT for more than 16 years. I want to show you how artificial intelligence can be used for OCT analysis with real OCT scans of AMD (drusen), DR, and GA retina pathologies.
OCT is an indispensable tool for any modern ophthalmology specialist. AI-powered OCT workflow provides a second opinion on complex OCT scans, allows the detection of early or minor biomarkers and pathologies, and assists in tracking the progression of biomarkers quantitatively, making the work of ophthalmologists faster and more accurate.
Navigating dAMD (Drusen), dAMD (GA), DR
Altris AI AI for OCT Workflow for Ophthalmologists
AI-powered OCT Analysis is 1 click away
Free Trial
AI for OCT Workflow for ophthalmologists
-


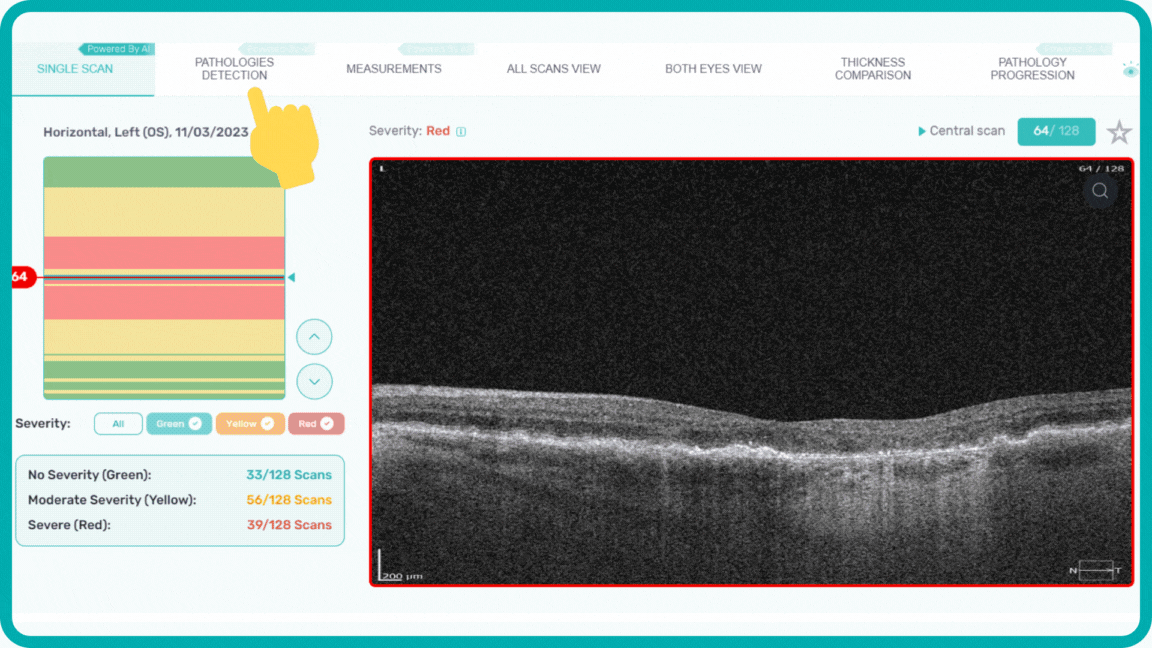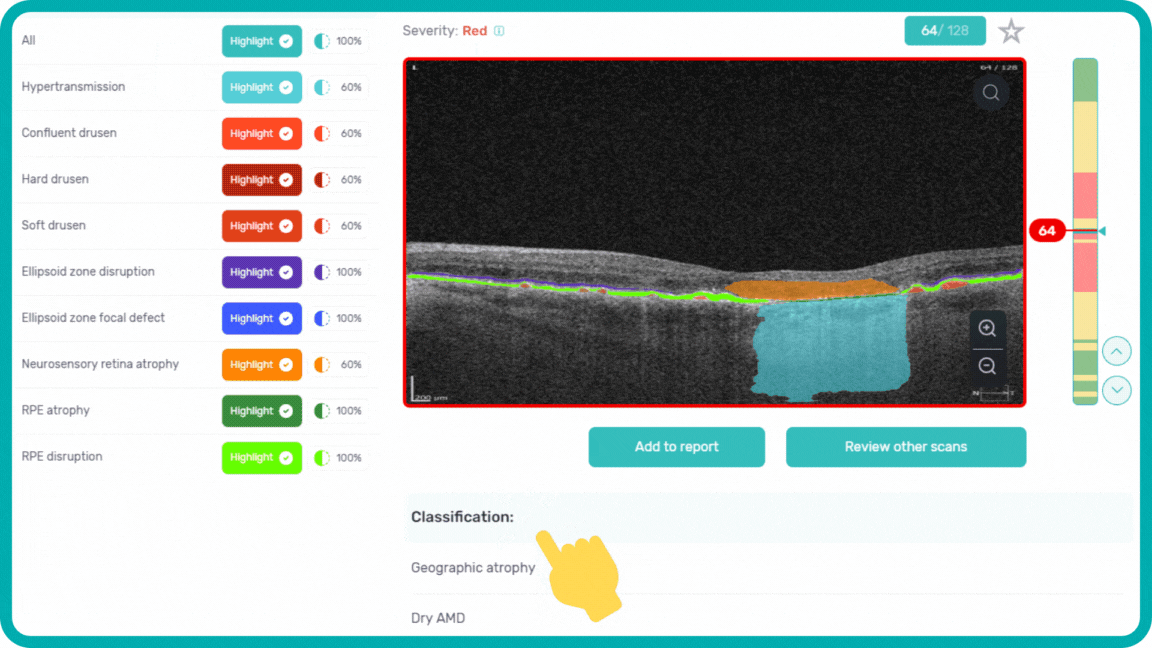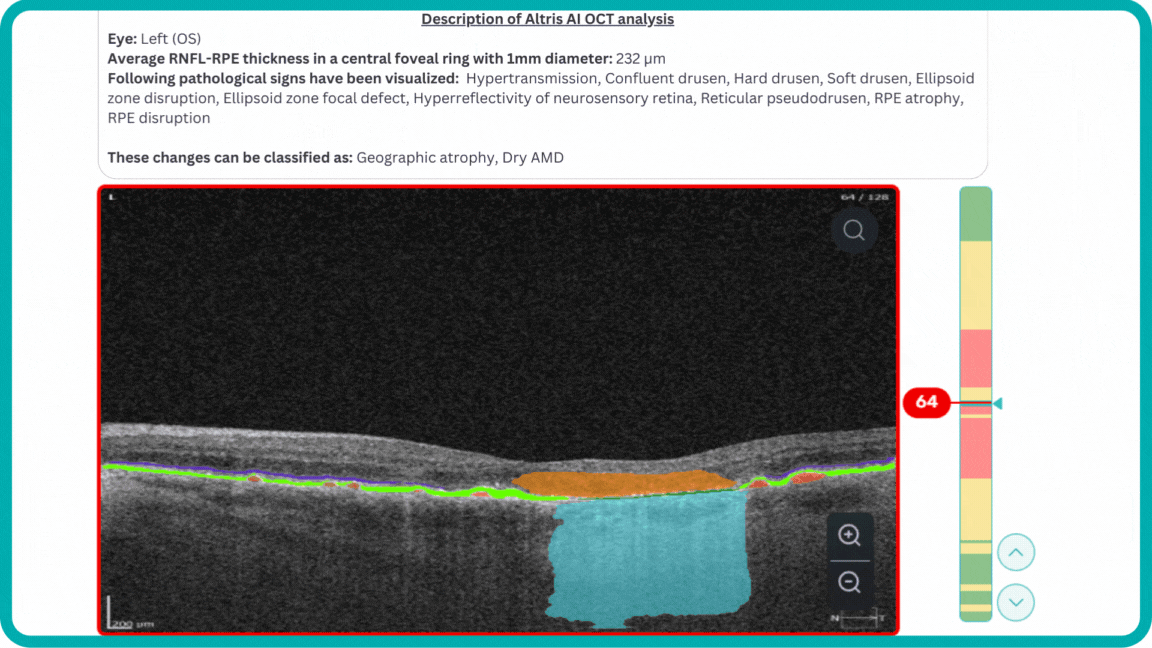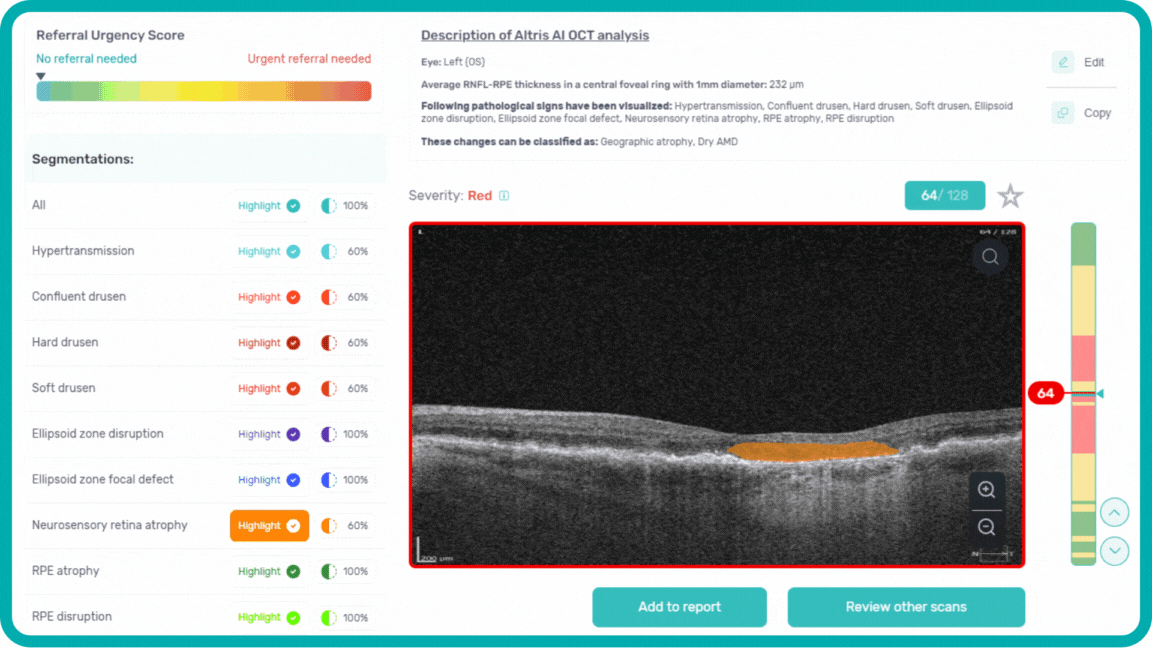
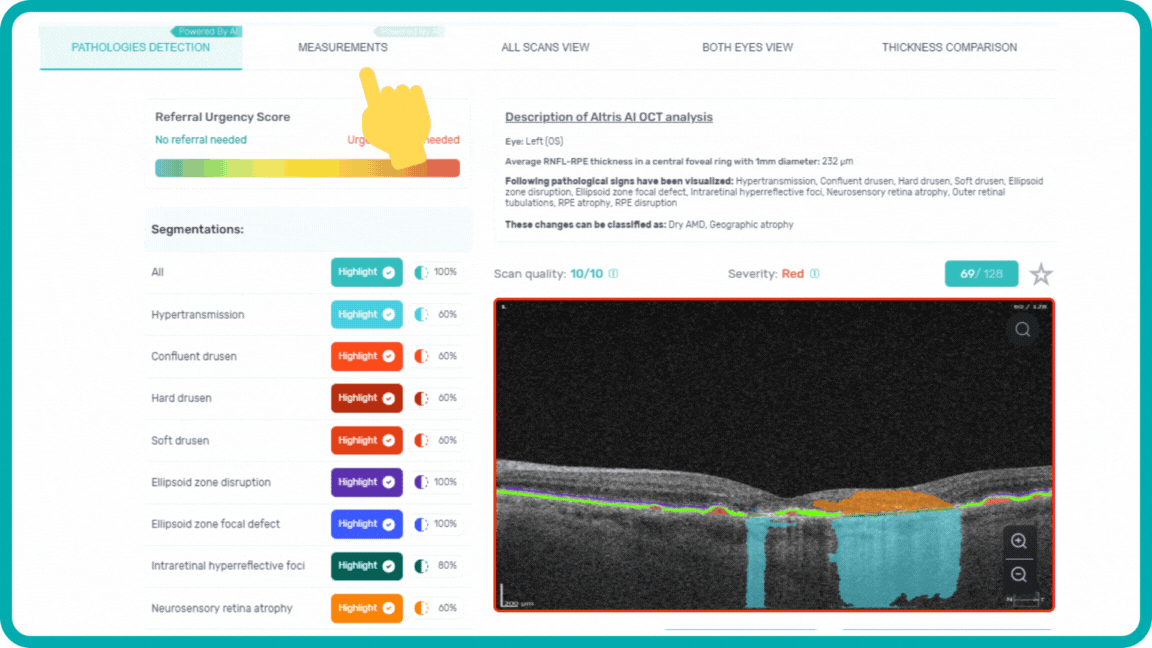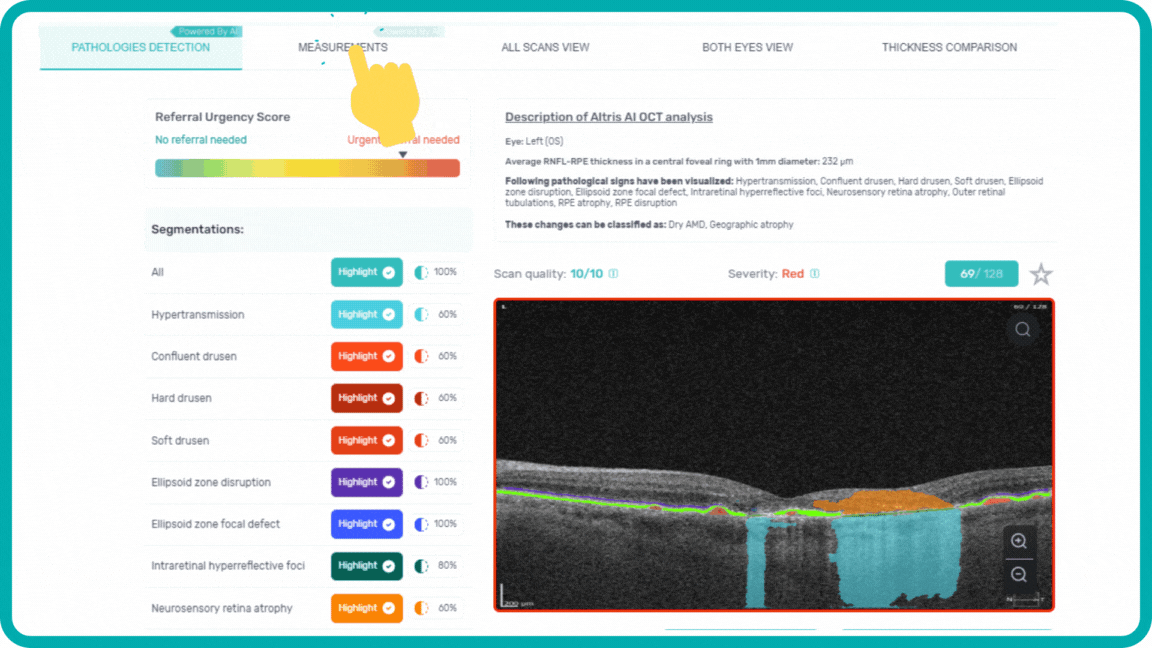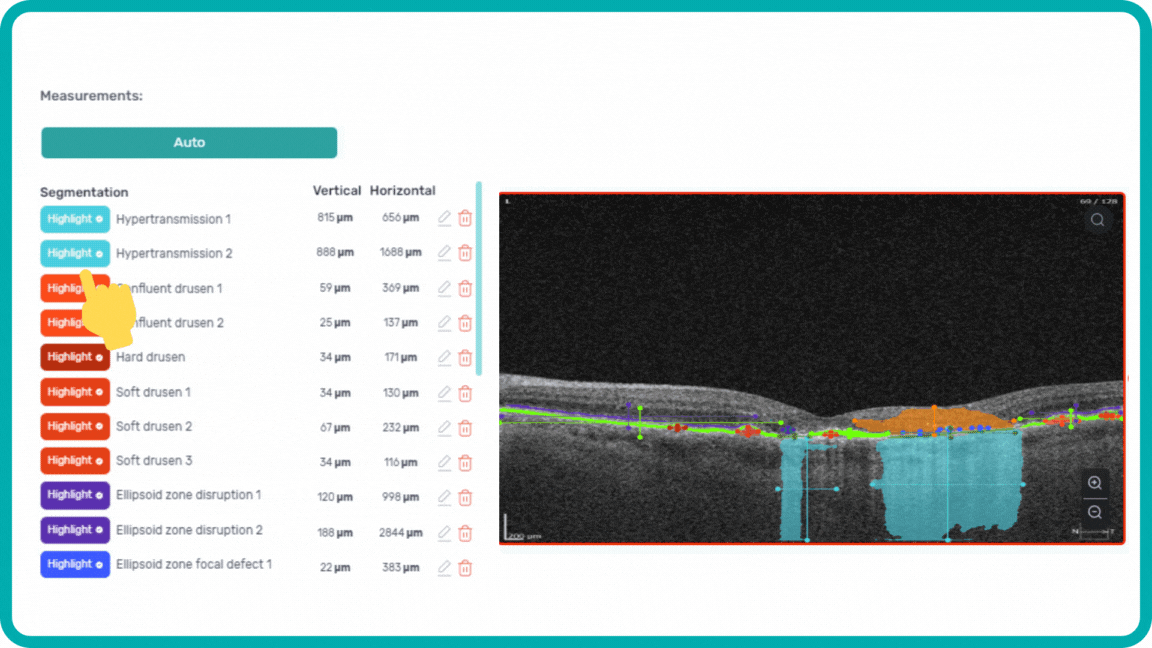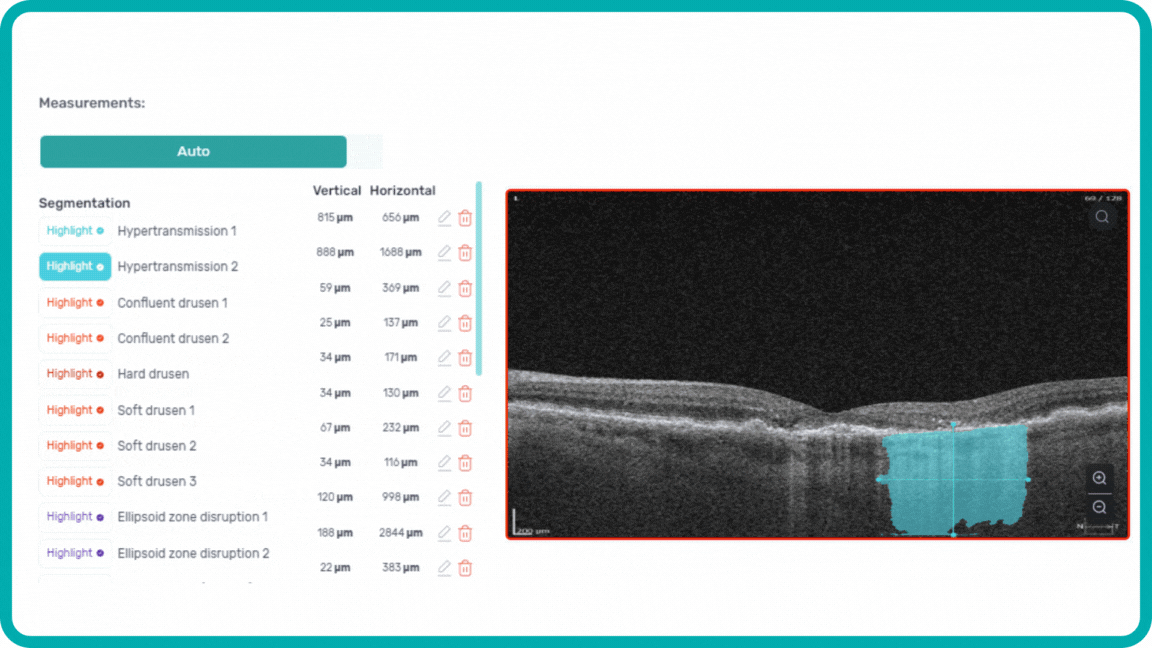
When you come across a pathological scan that you want to explore in detail, you go to the AI Pathologies Detection Module. Inside this module, AI analyzes the scan for the presence of 70+ biomarkers and retina pathologies.The system highlights each of them in color.
-


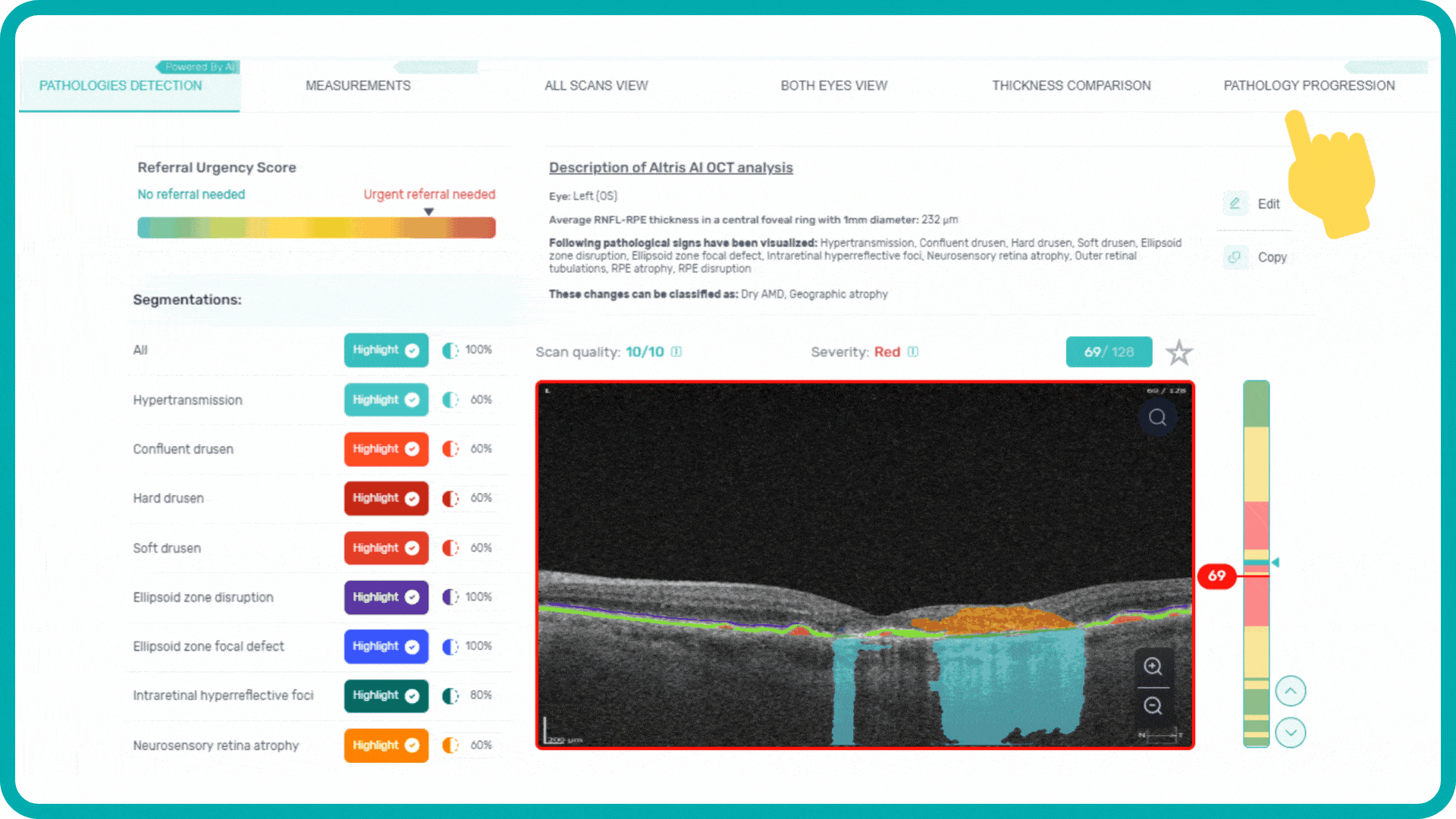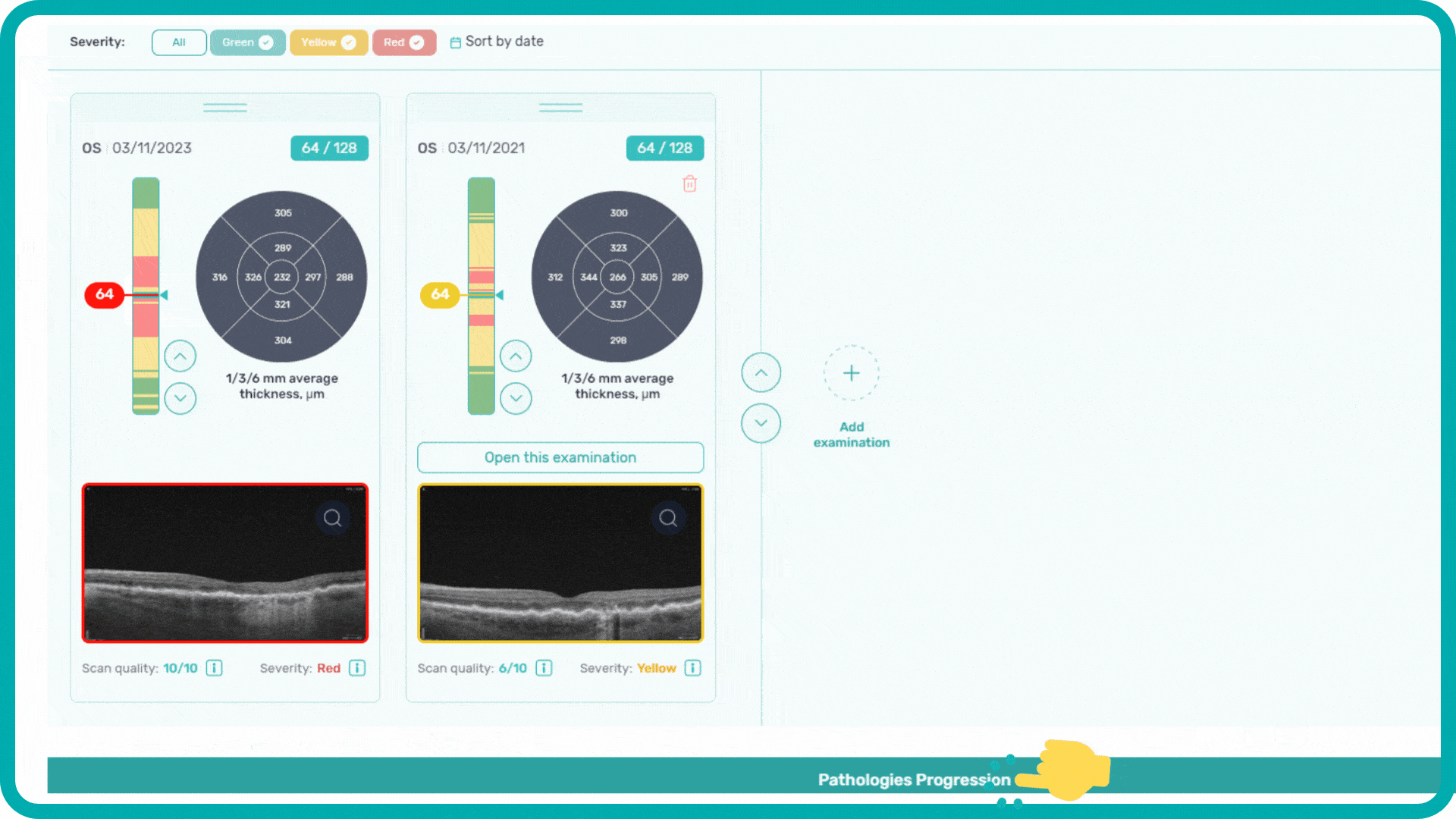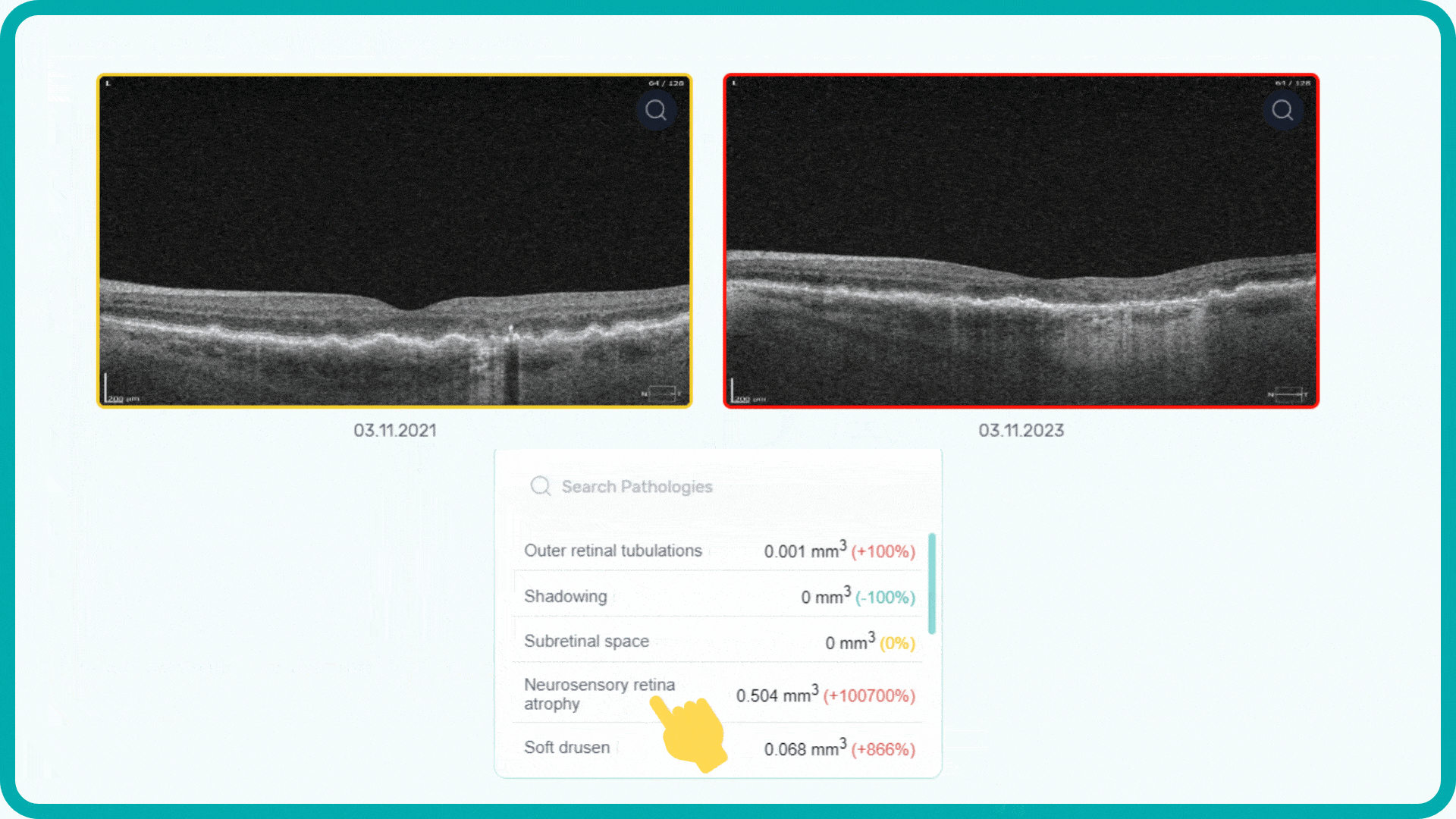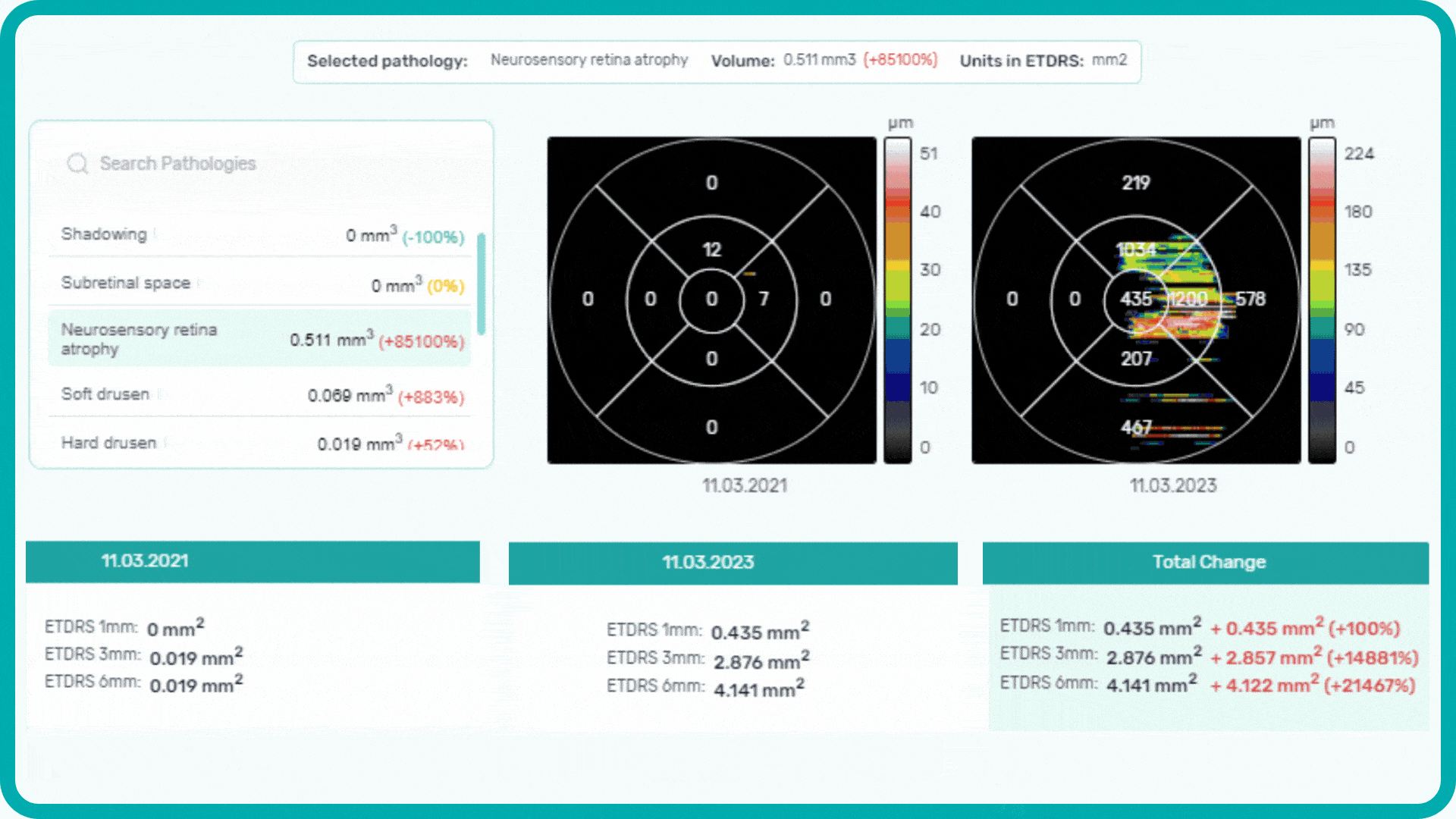
Each biomarker can be measured in terms of segmentation volume and area automatically with excellent precision.
-


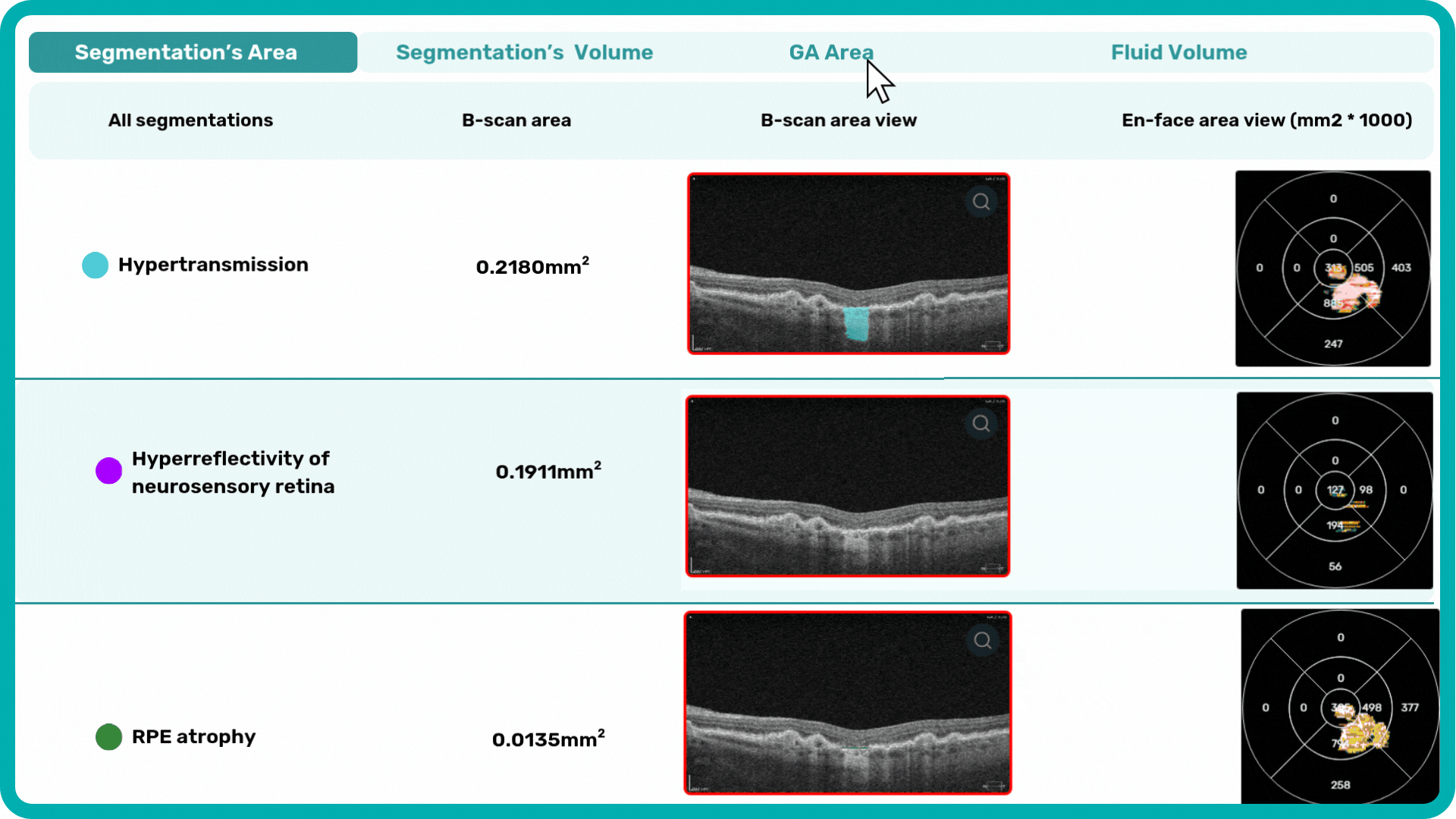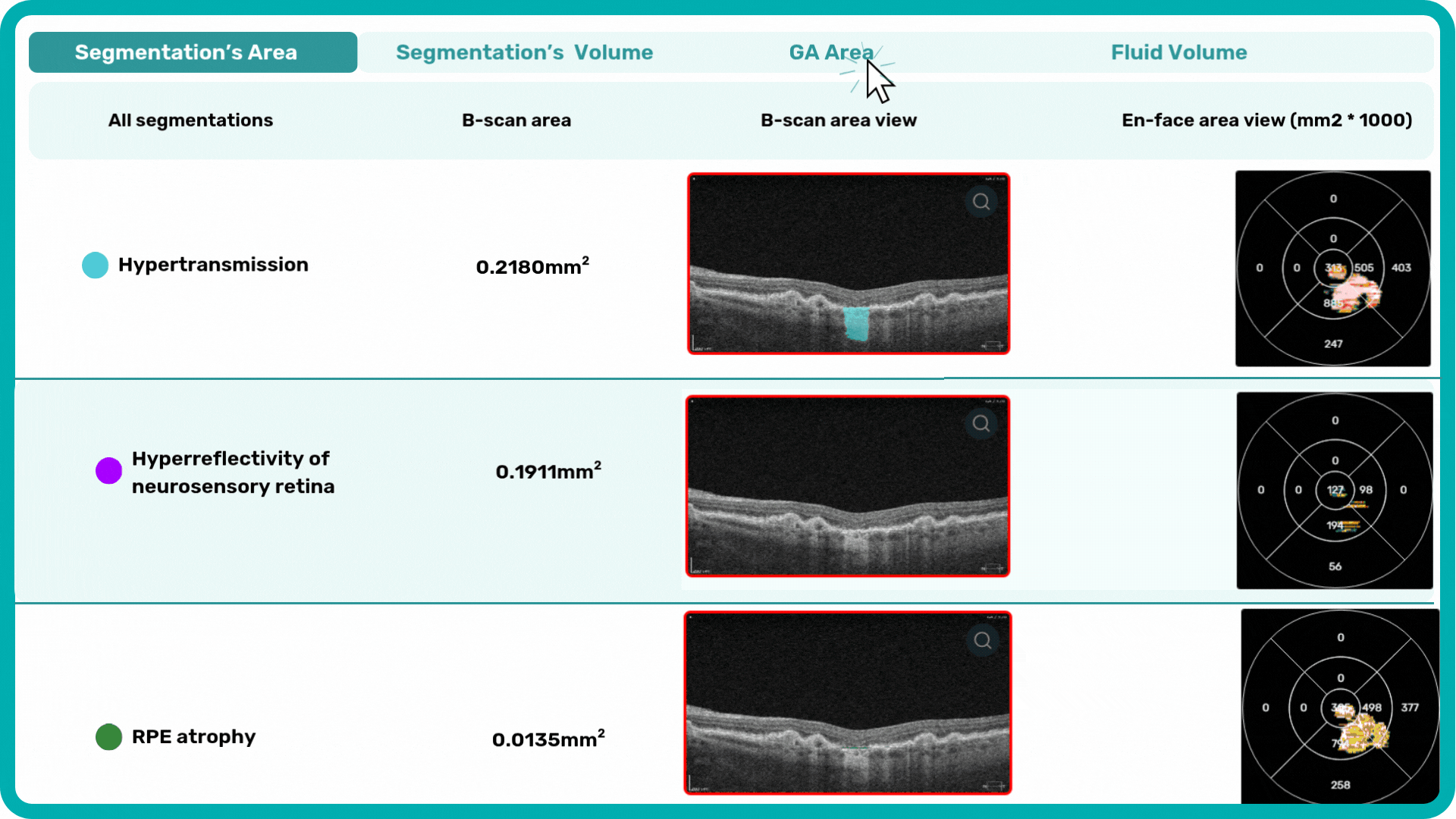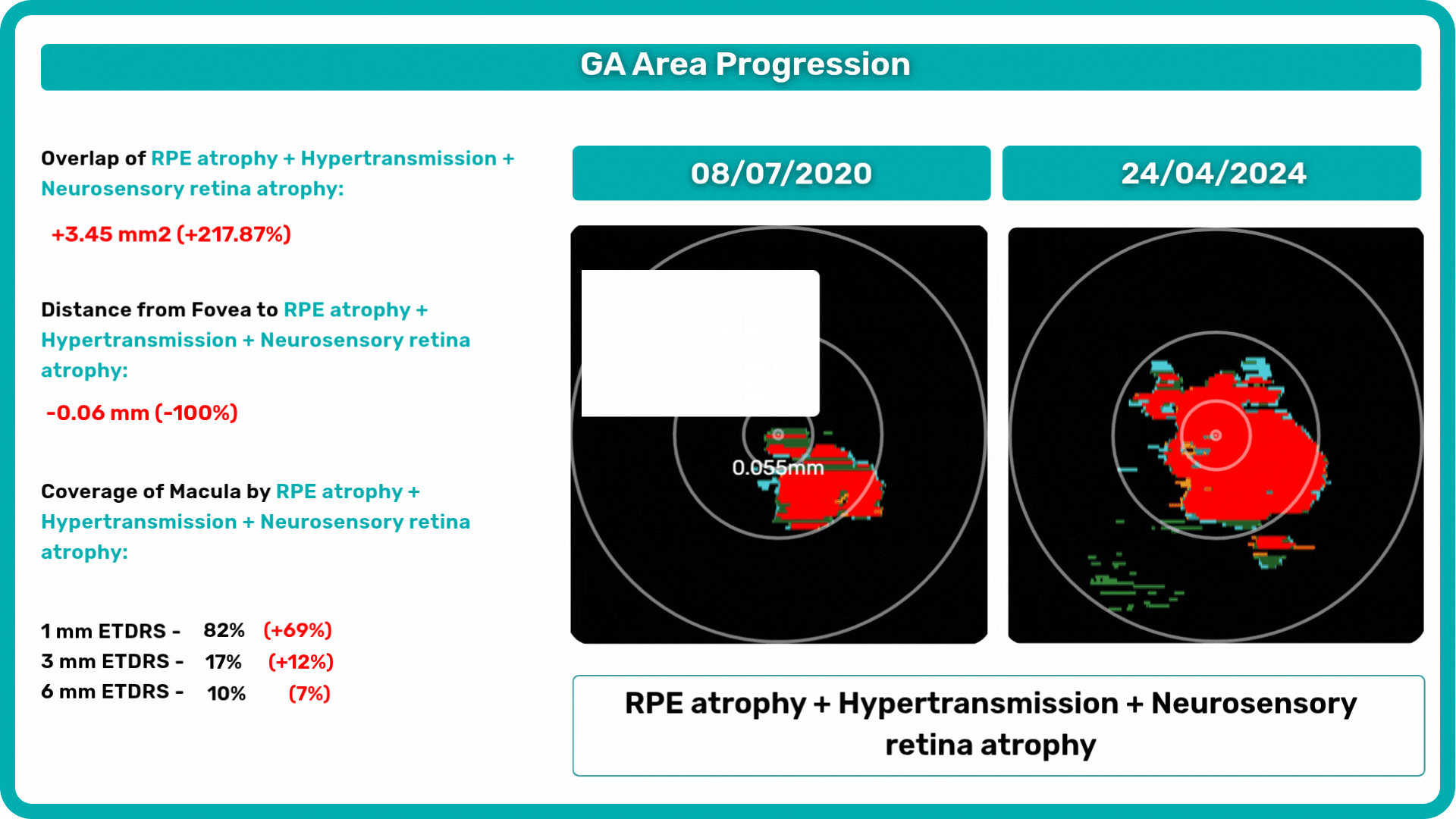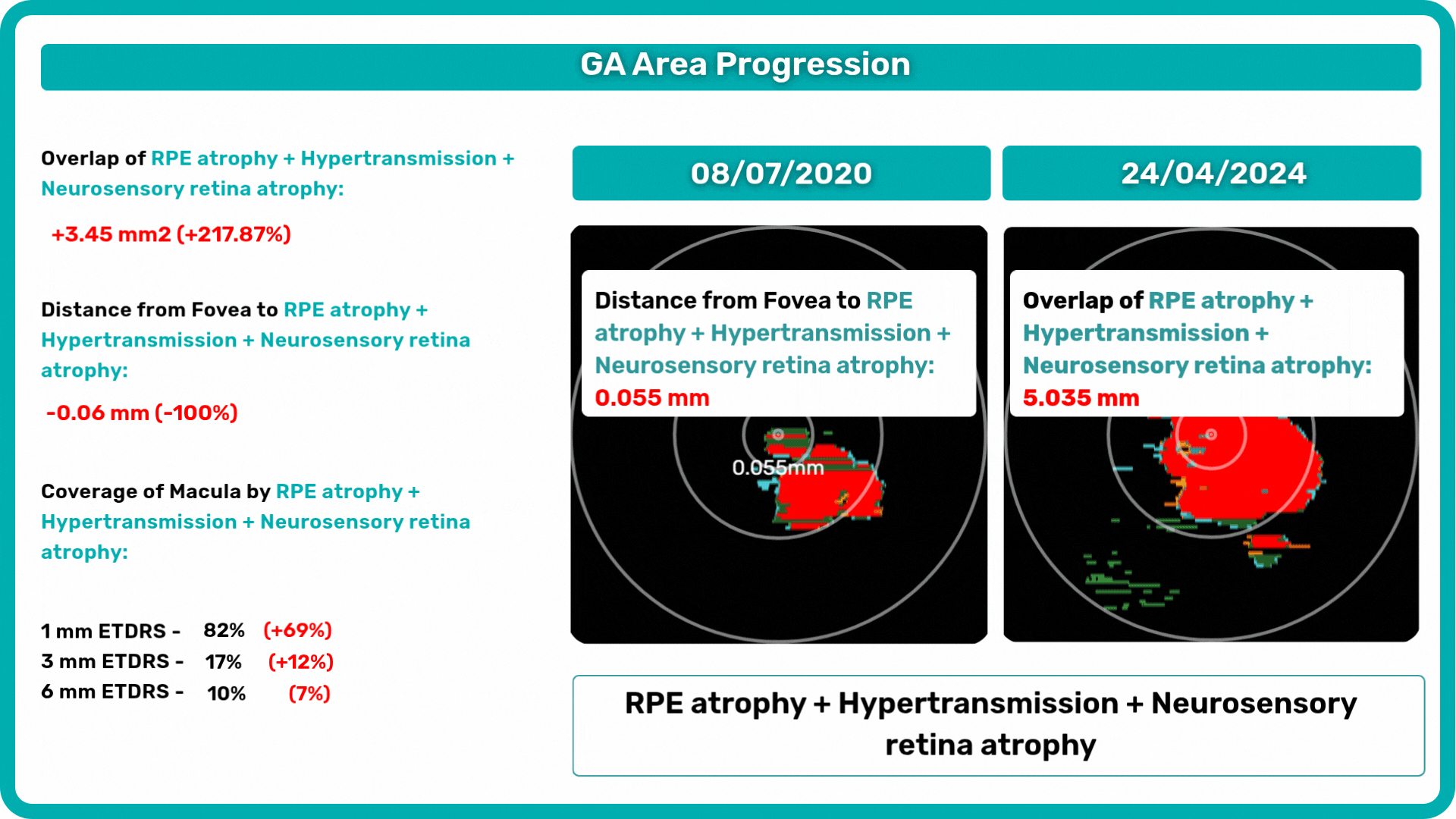
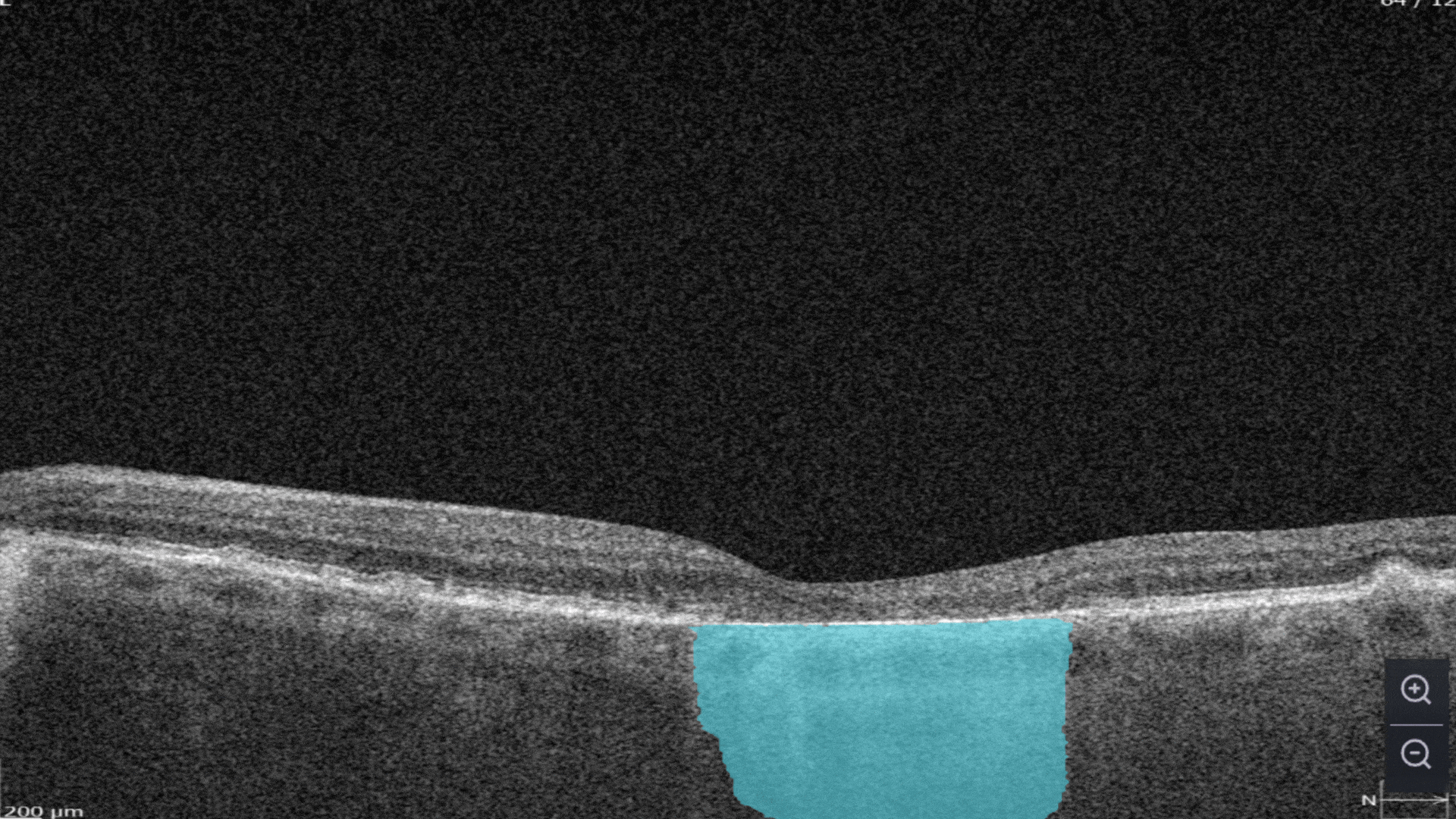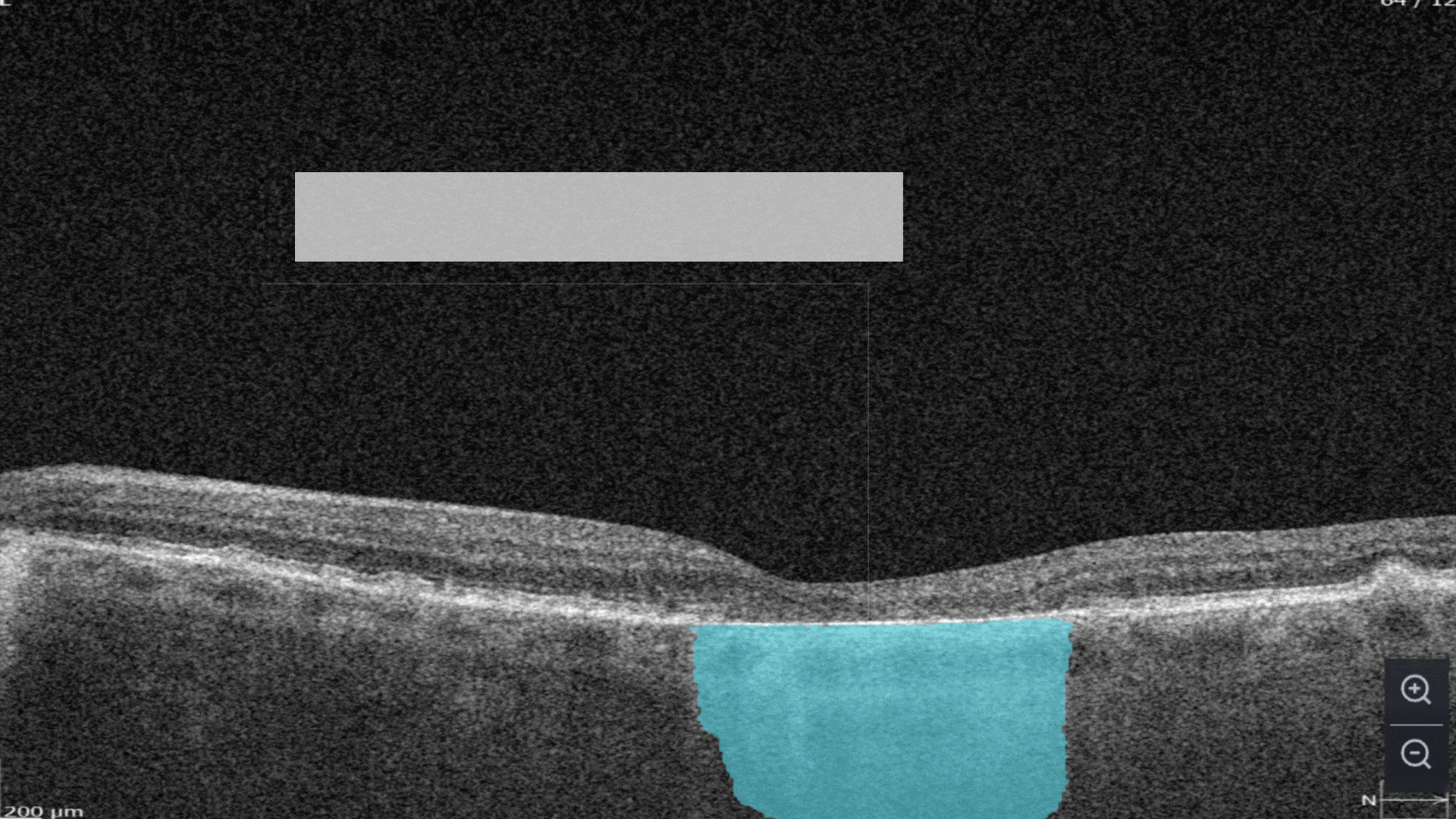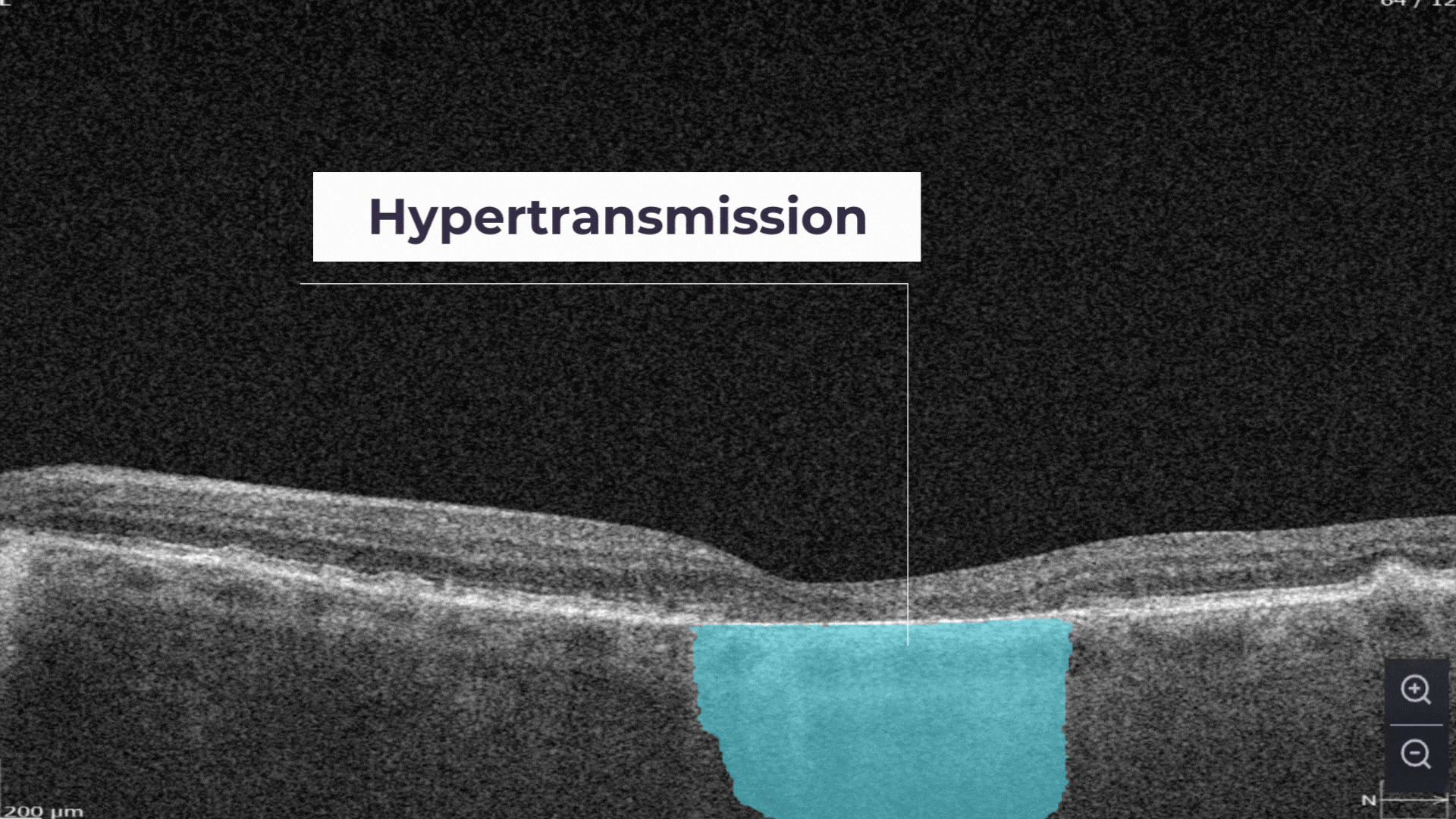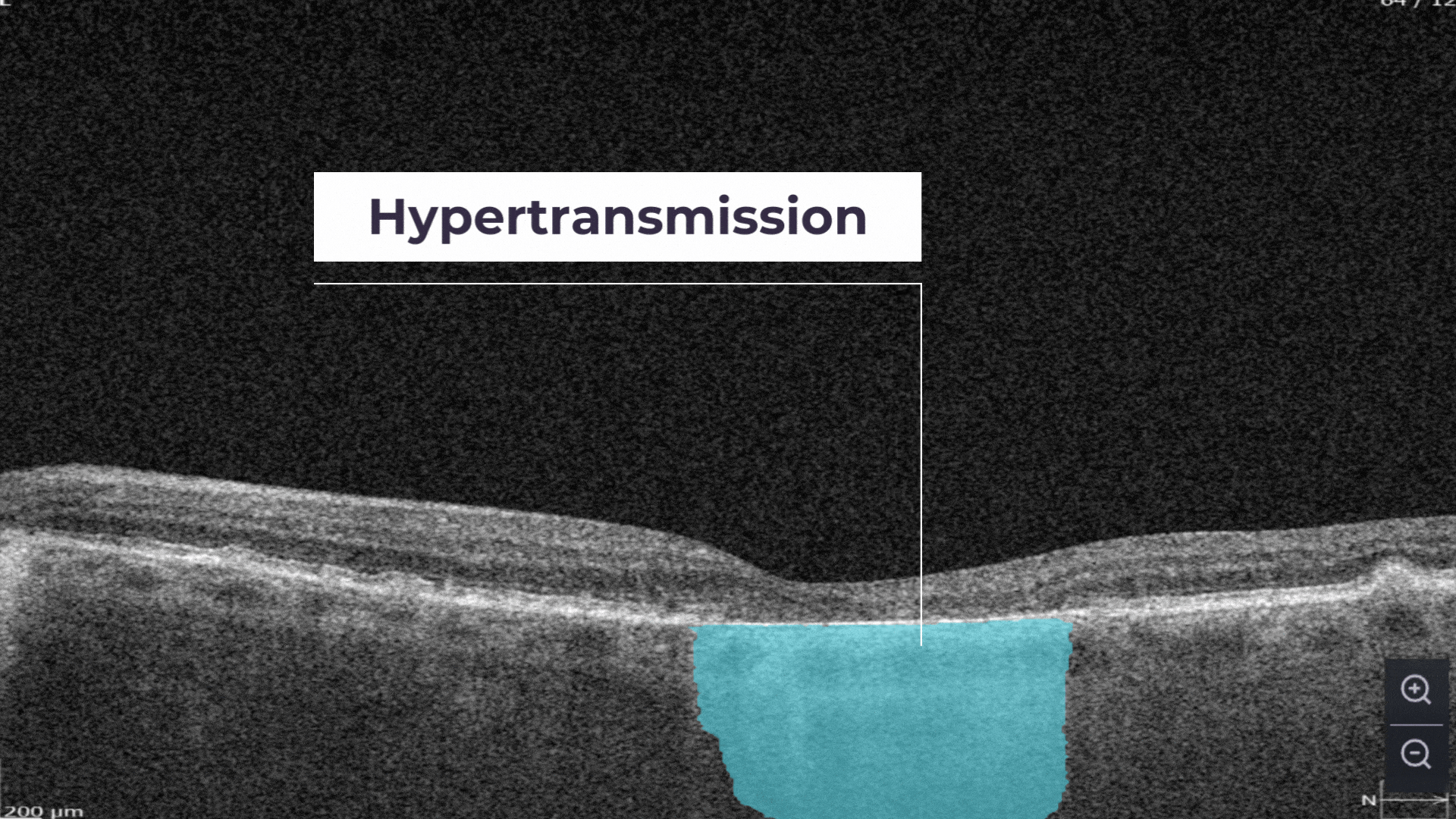
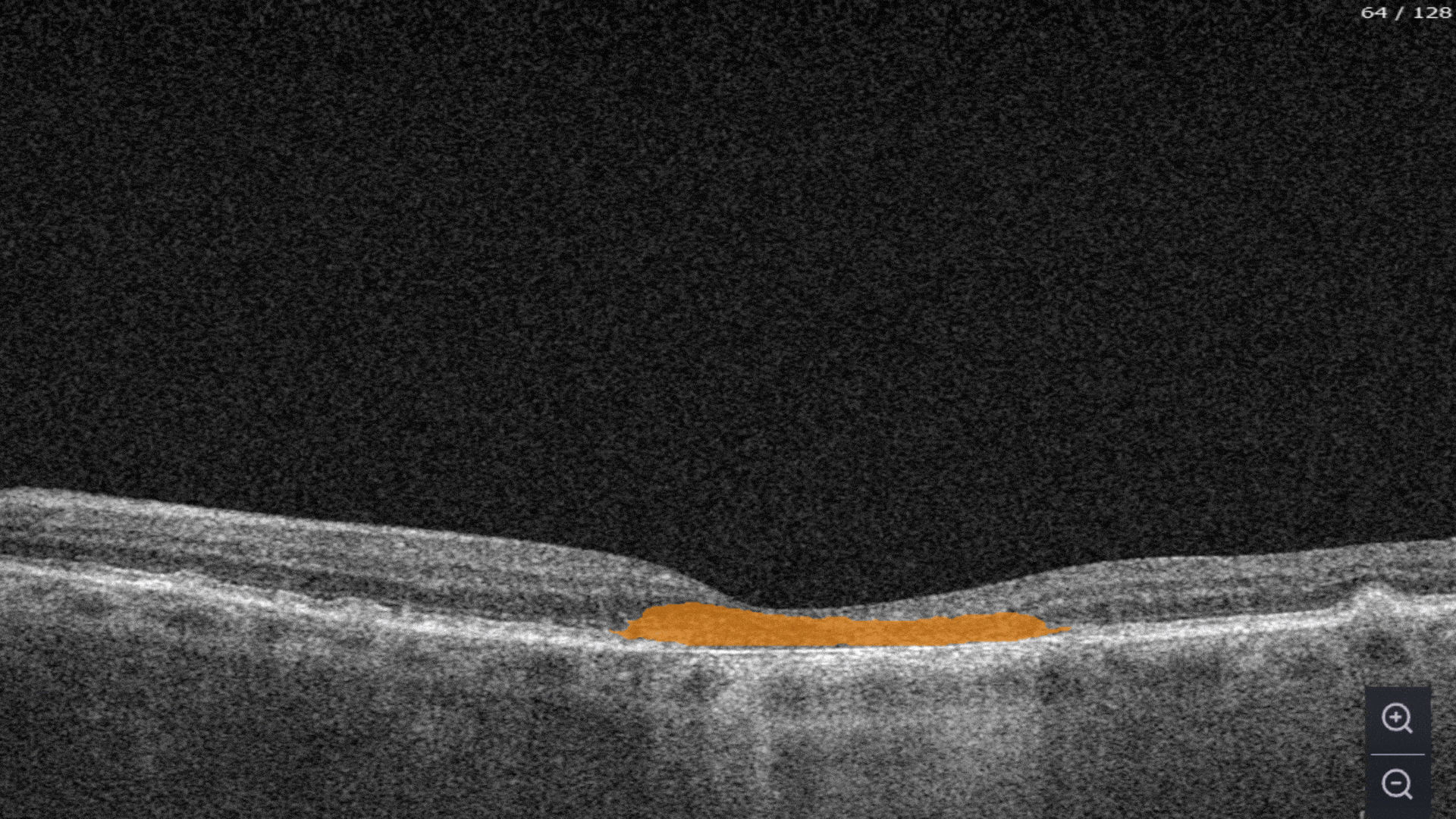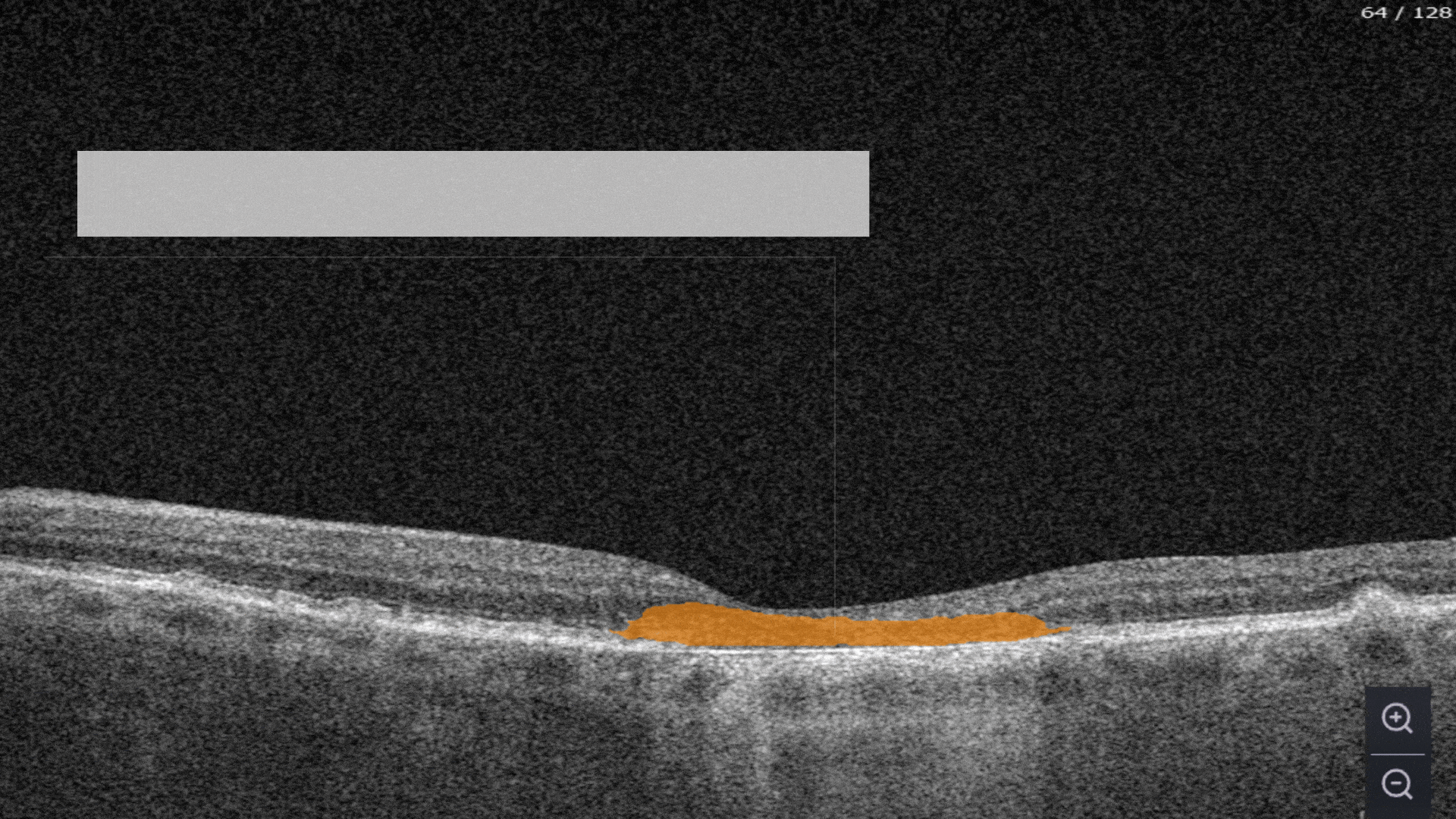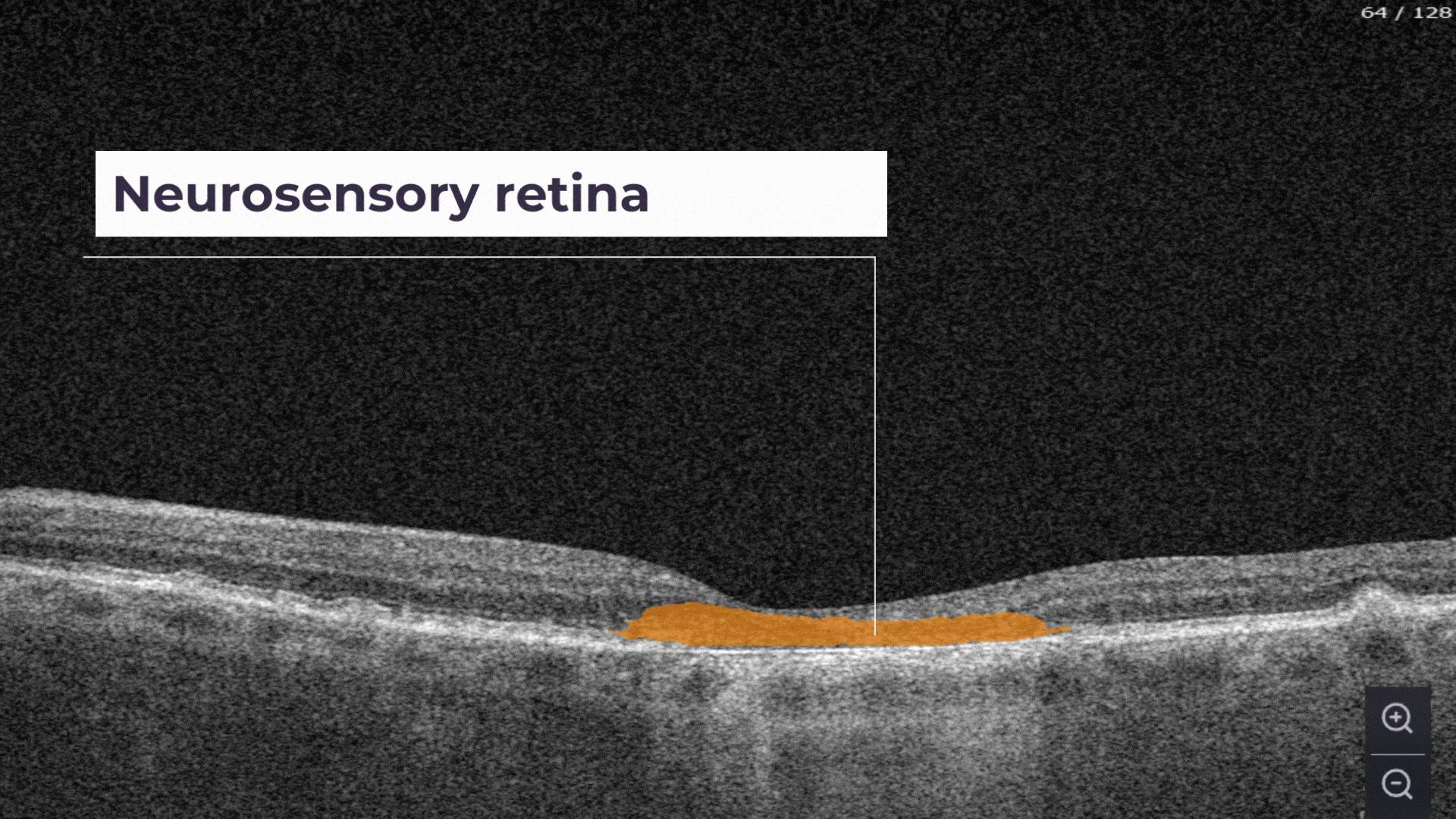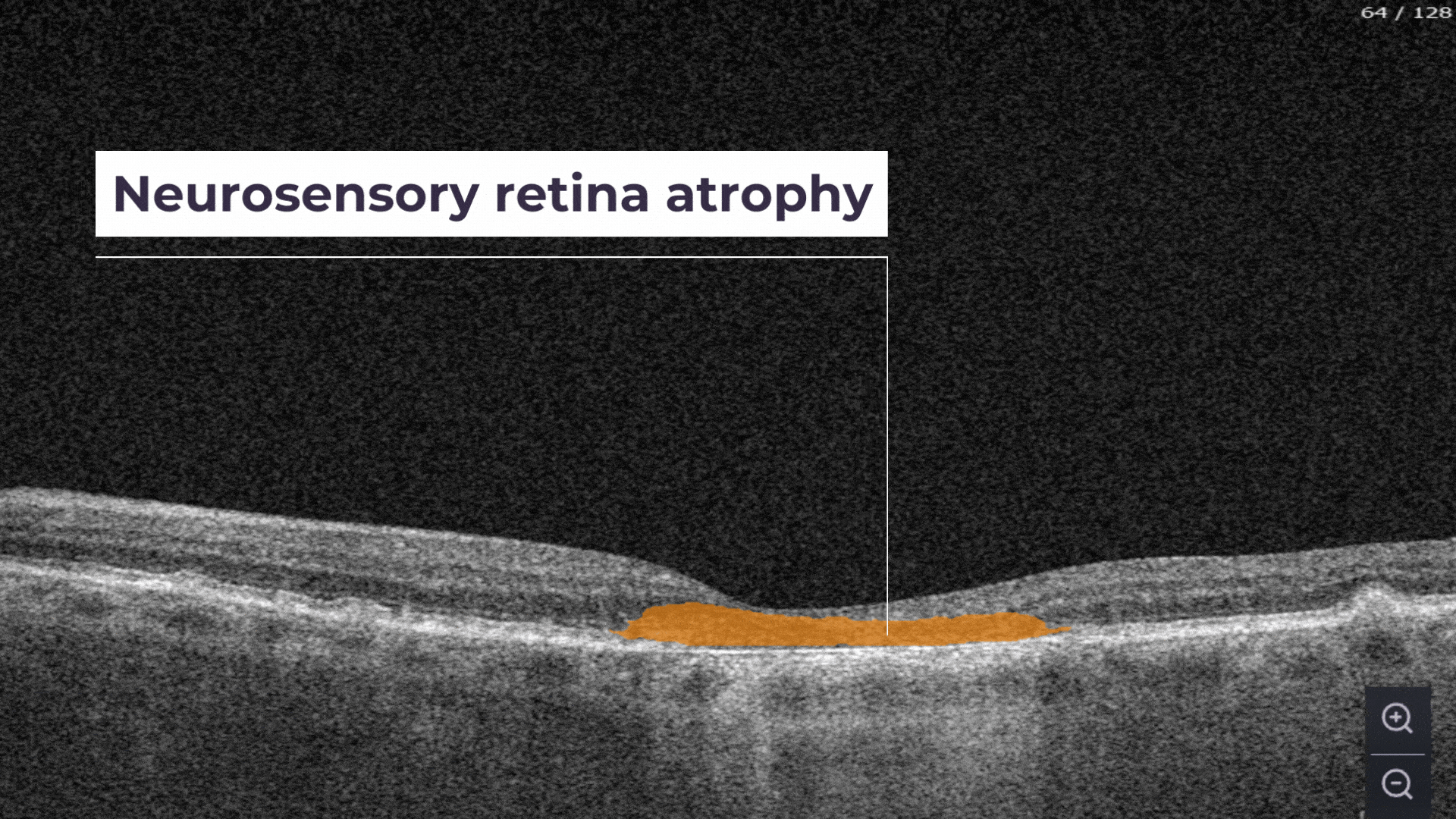
The Measurements module also includes a dedicated feature for calculating the GA area automatically by measuring the overlap between two (Hypertransmission and RPE Atrophy) or three biomarkers (adding Neurosensory Retina Atrophy).
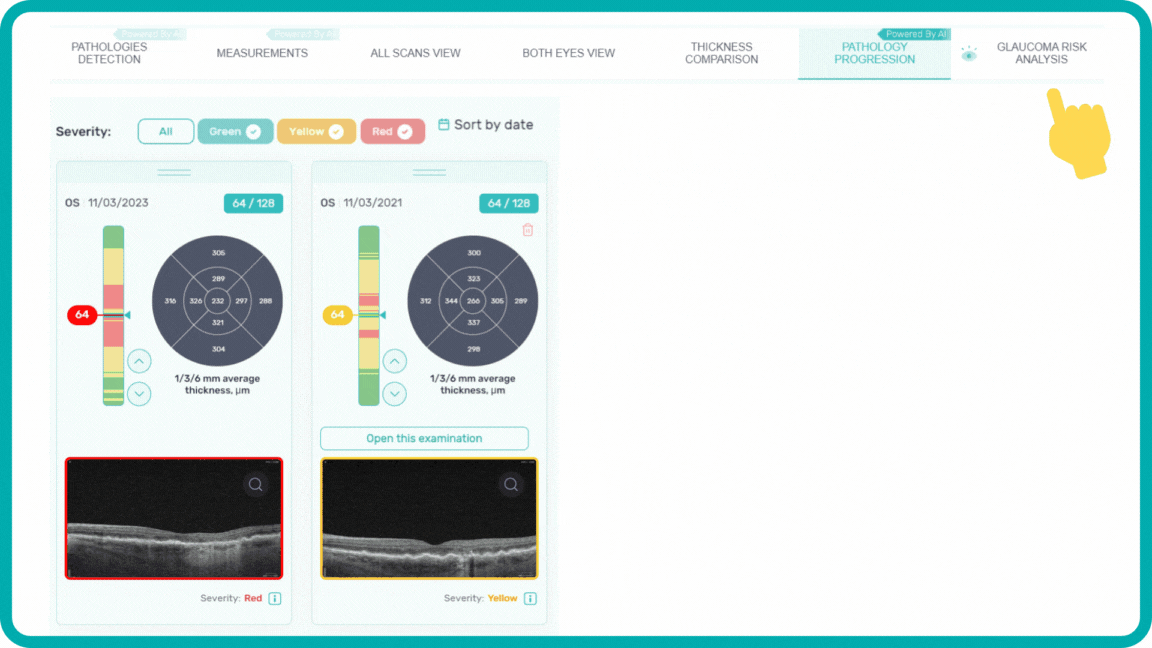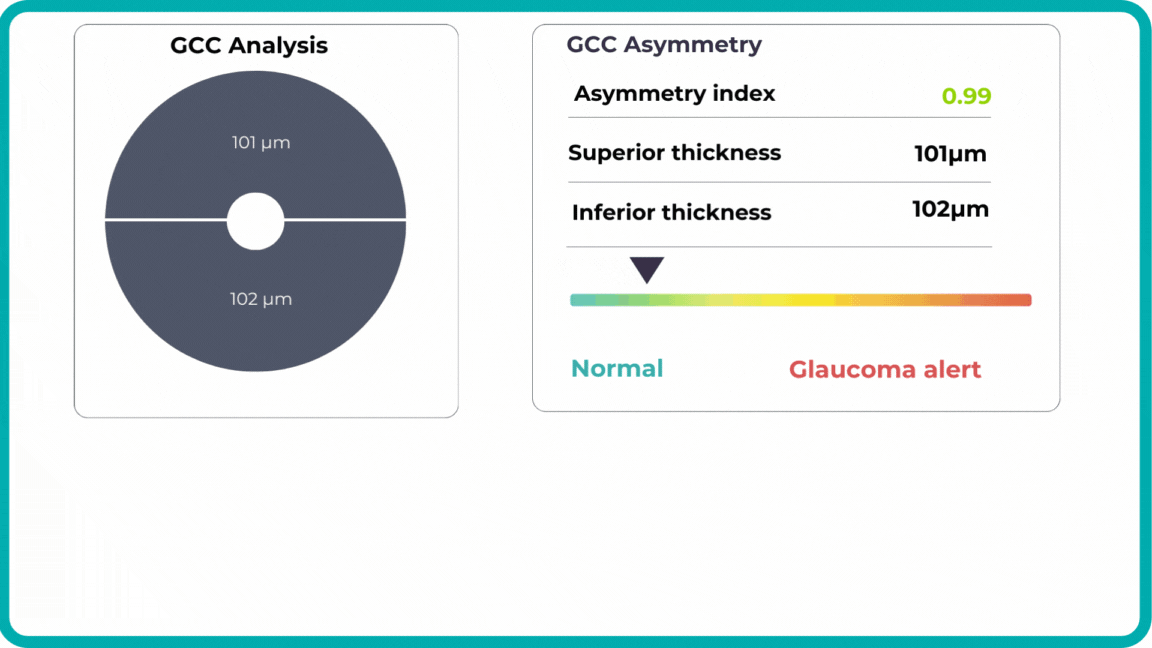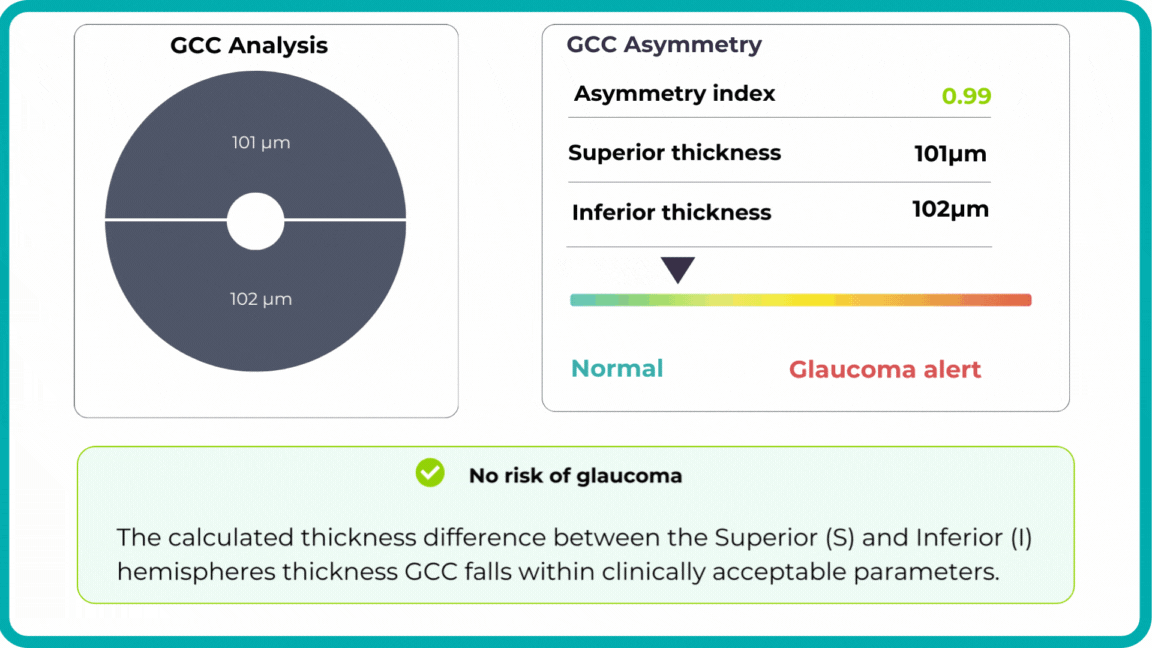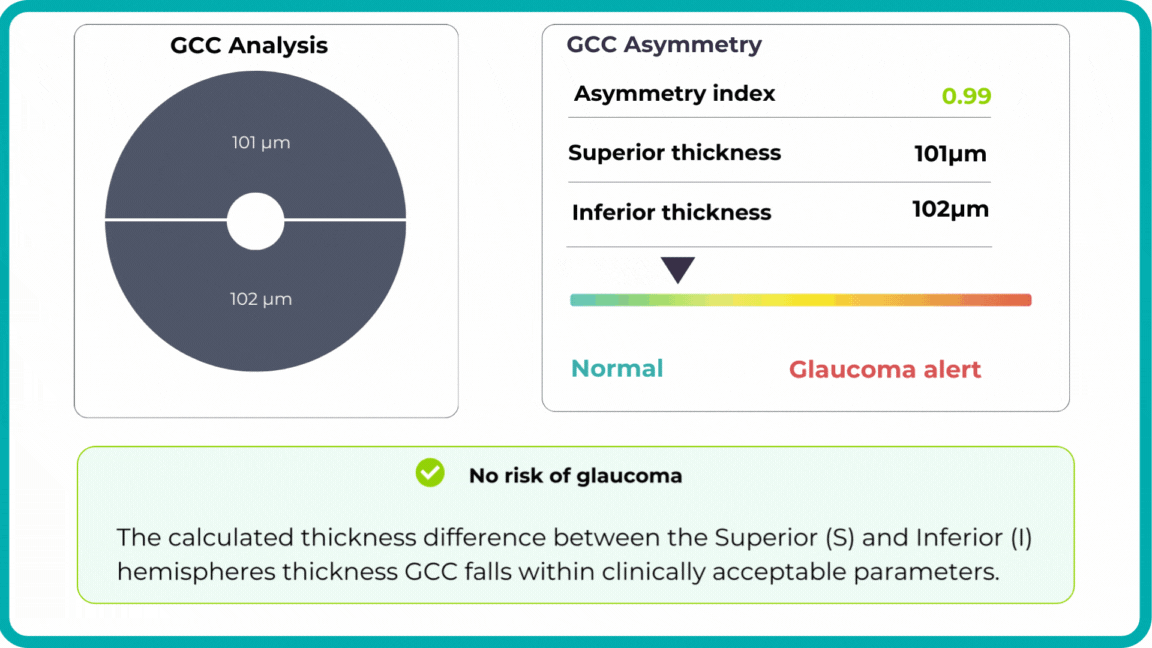
To track a patient’s condition over time across multiple OCT exams, use the GA Area Progression feature within our Pathology Progression module.
-


Progression analysis allows adding examinations from different visits in historical order and seeing the transformation of biomarkers and retina pathologies.
-


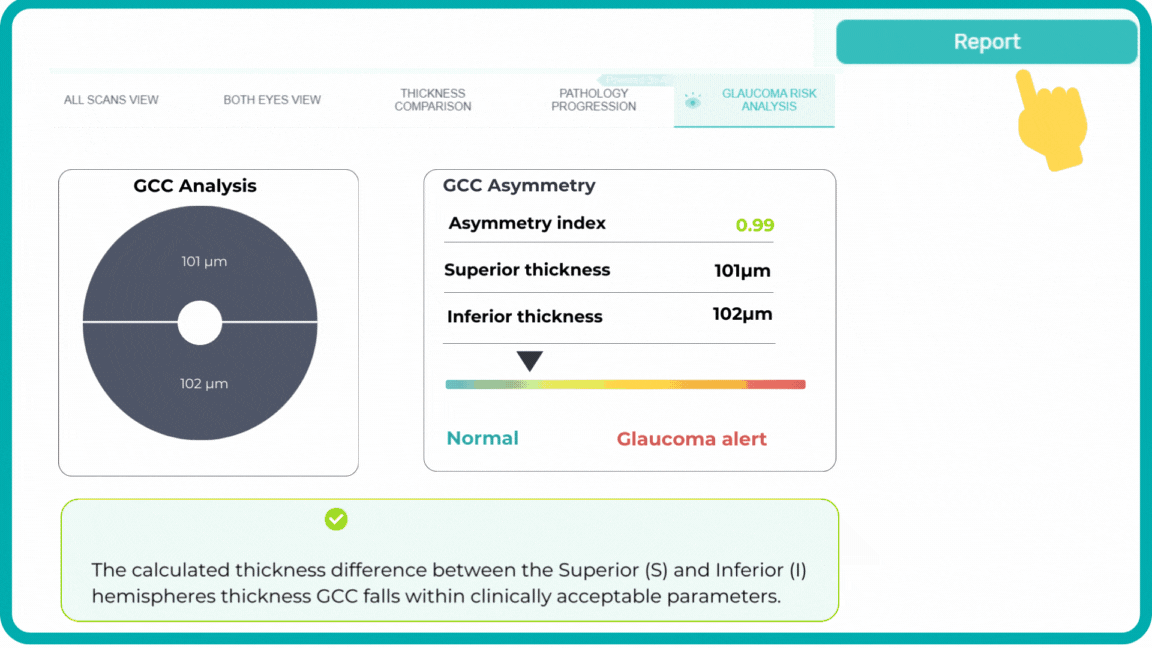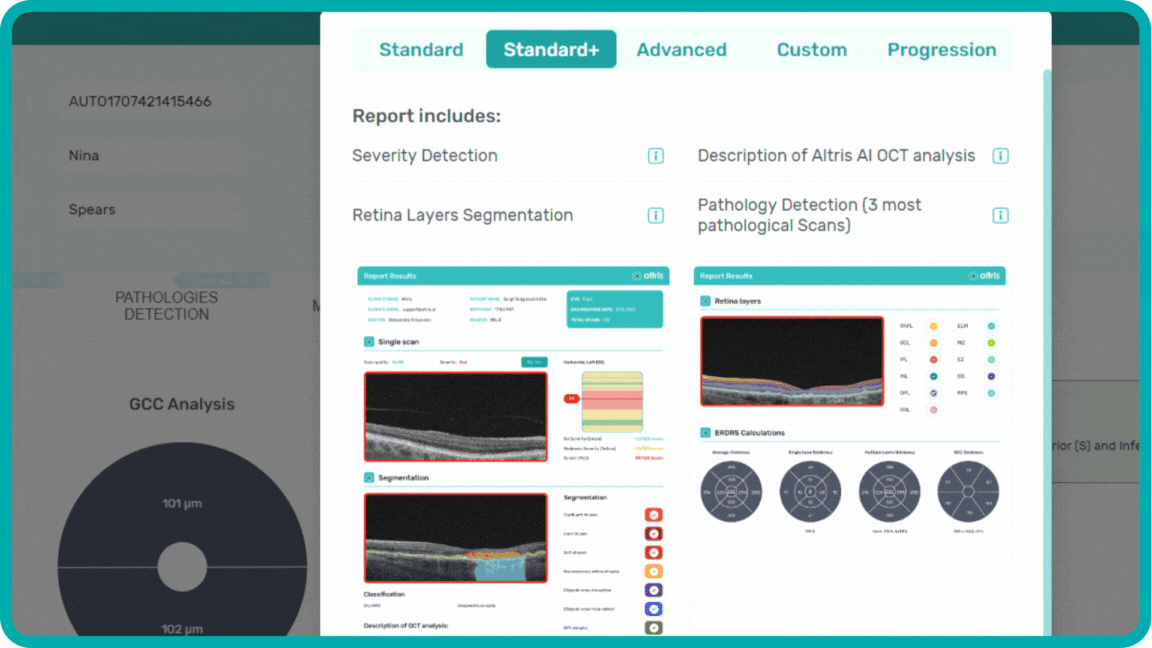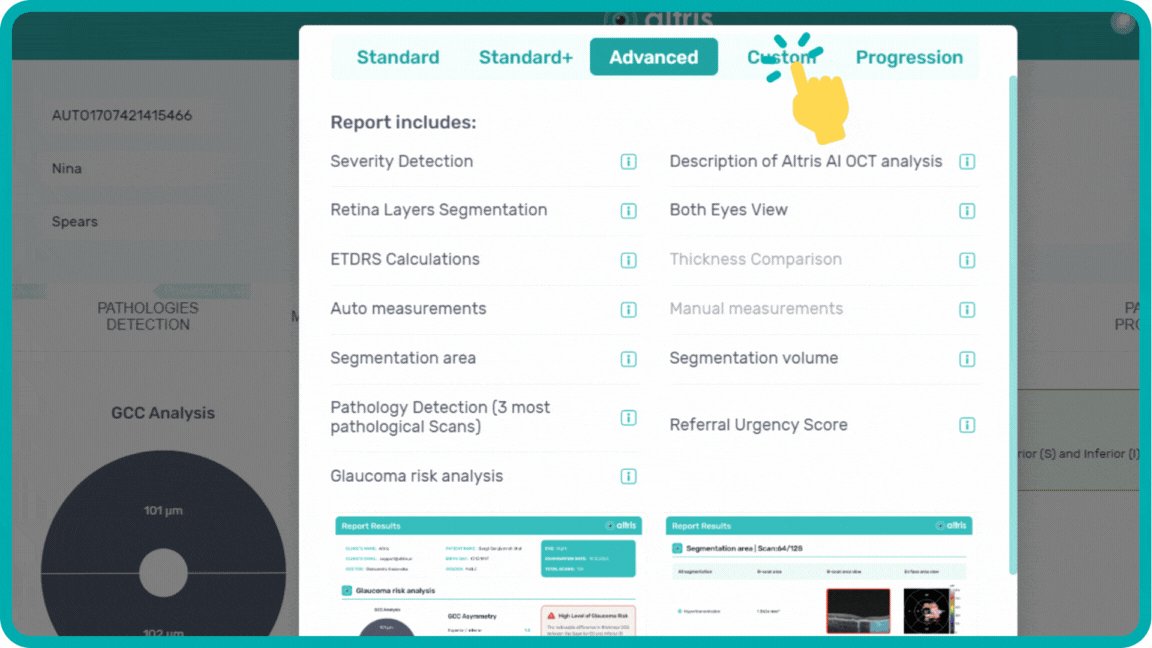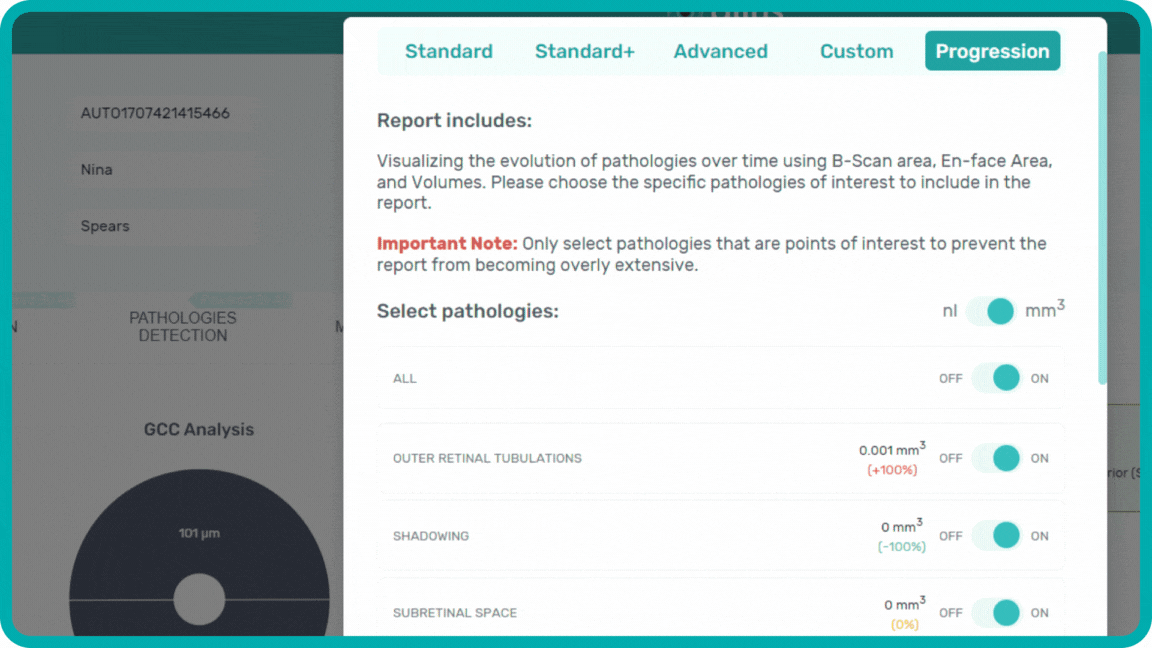
Early glaucoma risk assessment is based on the analysis of GCC asymmetry and informs about high risk of early glaucoma.
-


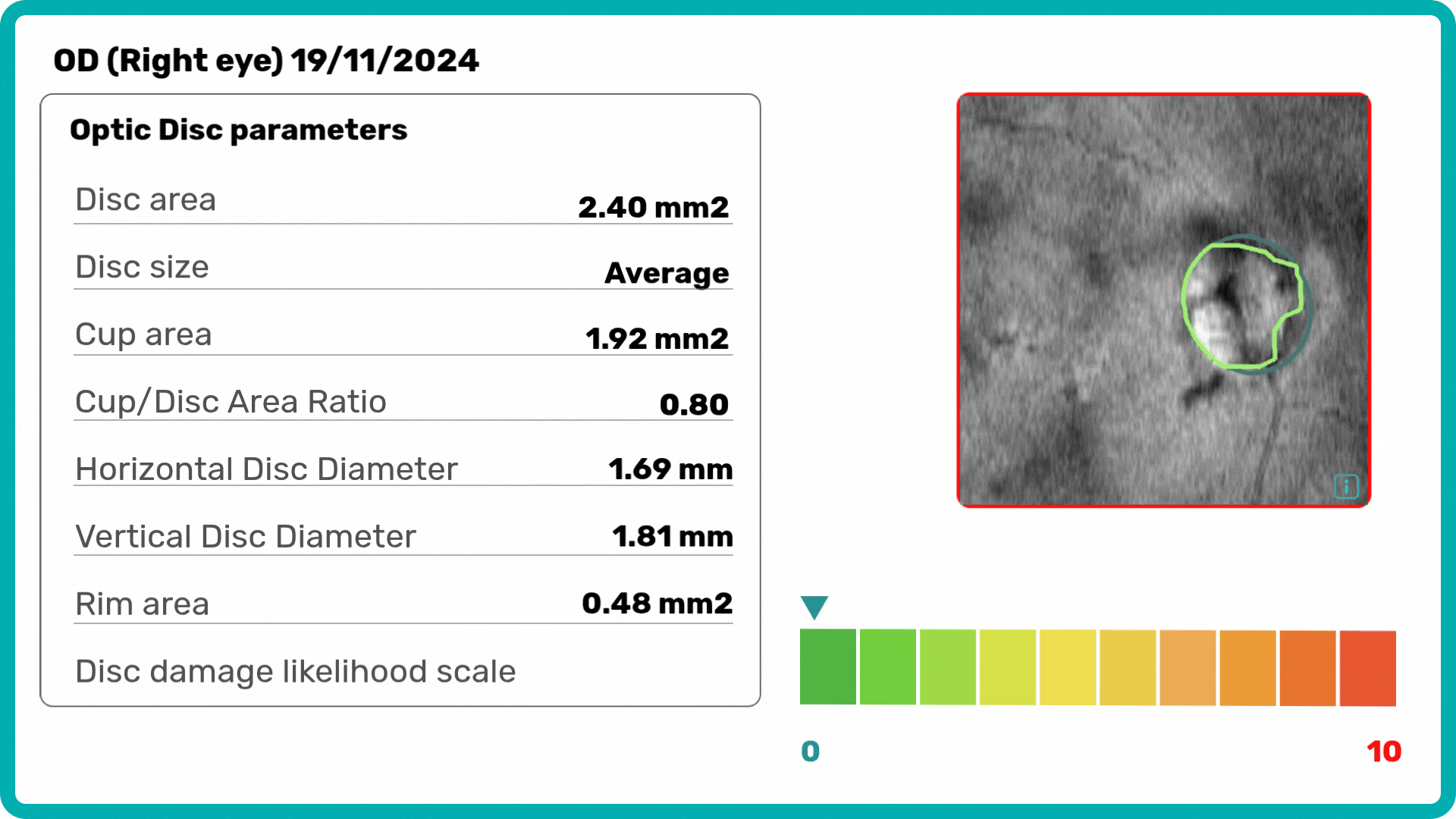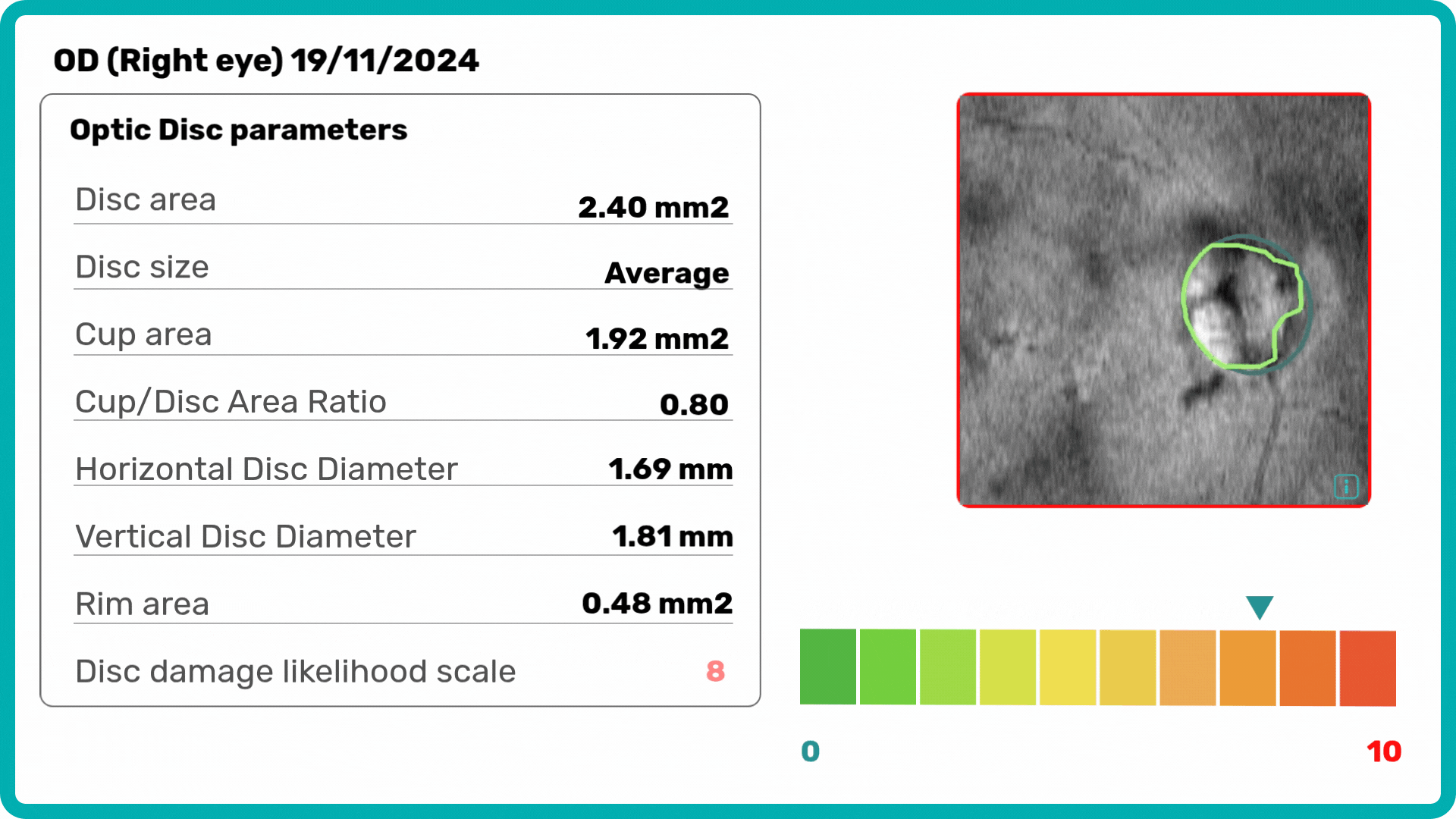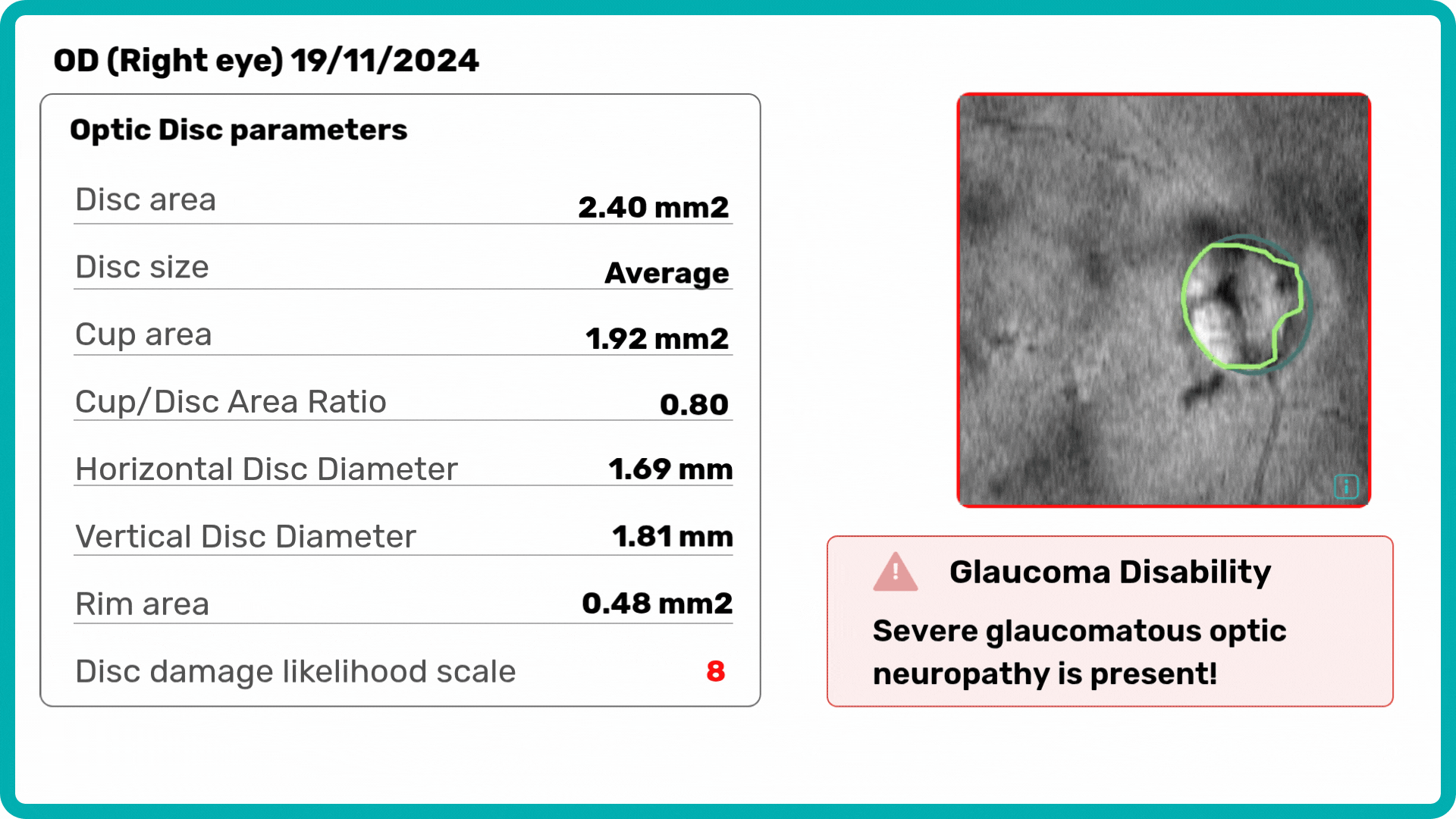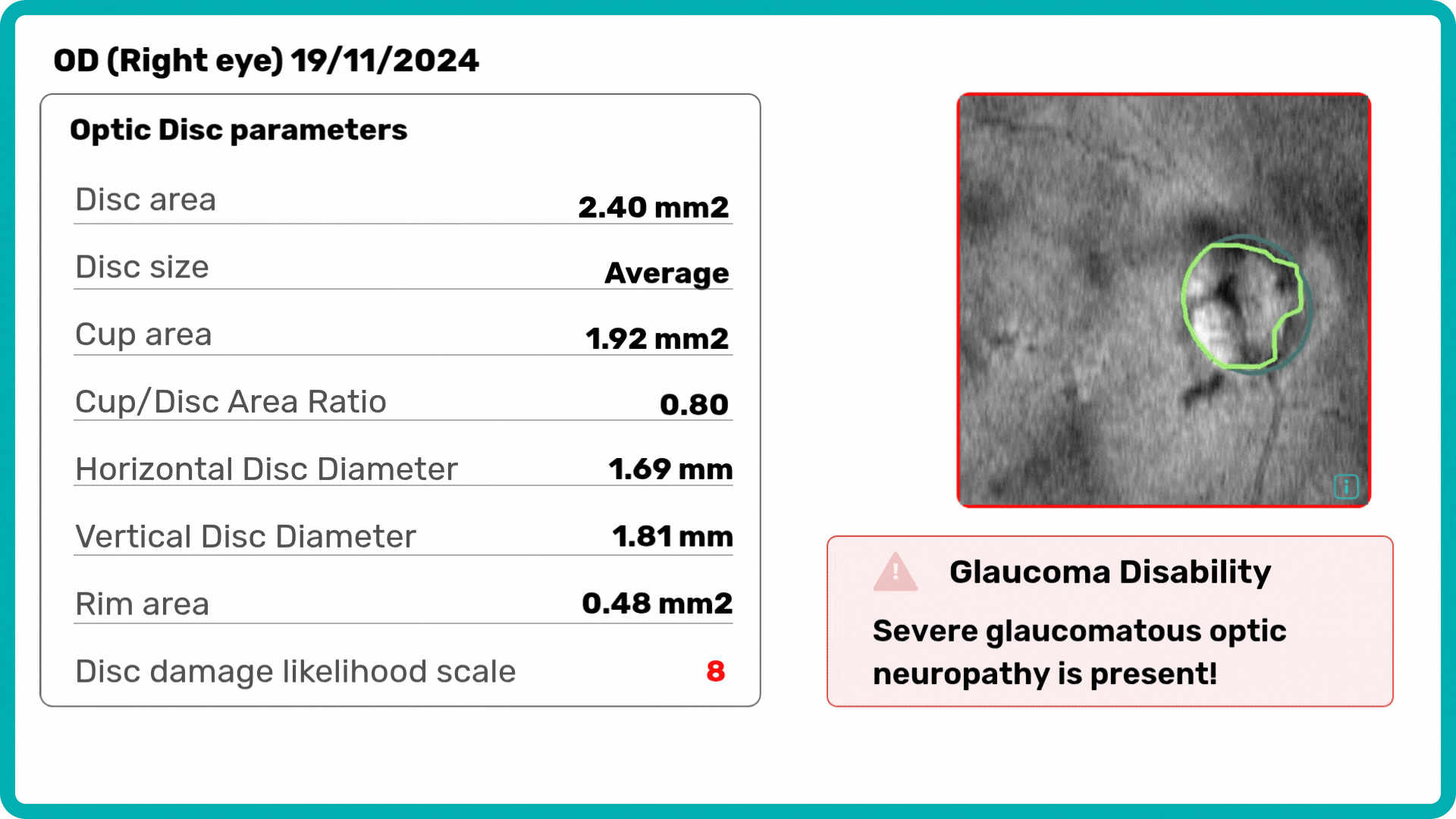
Building on our GCC Asymmetry Analysis, the Advanced Optic Disc Analysis measures key optic disc parameters, including Disc Area, Cup Area, Cup Volume, Cup Depth, Cup/Disc Area Ratio, and Rim Absence Angle. Using these personalized calculations, the AI assigns a severity score from 1 to 10 on the Disc-Damage Likelihood Scale.
-

 Examination results can be saved or printed as a customizable report, detailing basic information, severity detection, layer segmentation, specific pathologies, making OCT workflow effective.
Examination results can be saved or printed as a customizable report, detailing basic information, severity detection, layer segmentation, specific pathologies, making OCT workflow effective.
Choose a patient's journey
AI-powered OCT workflow for the patient with DR
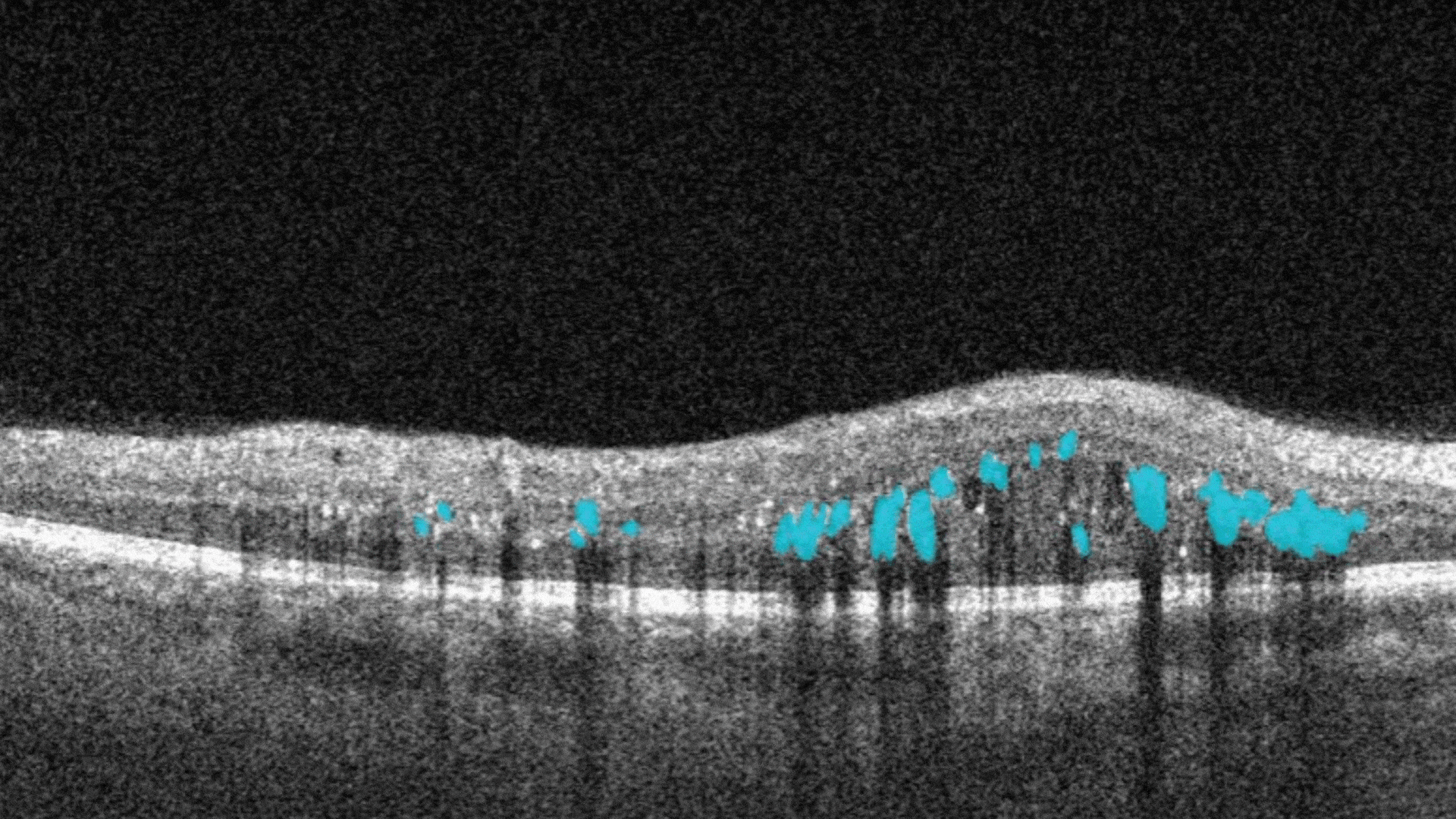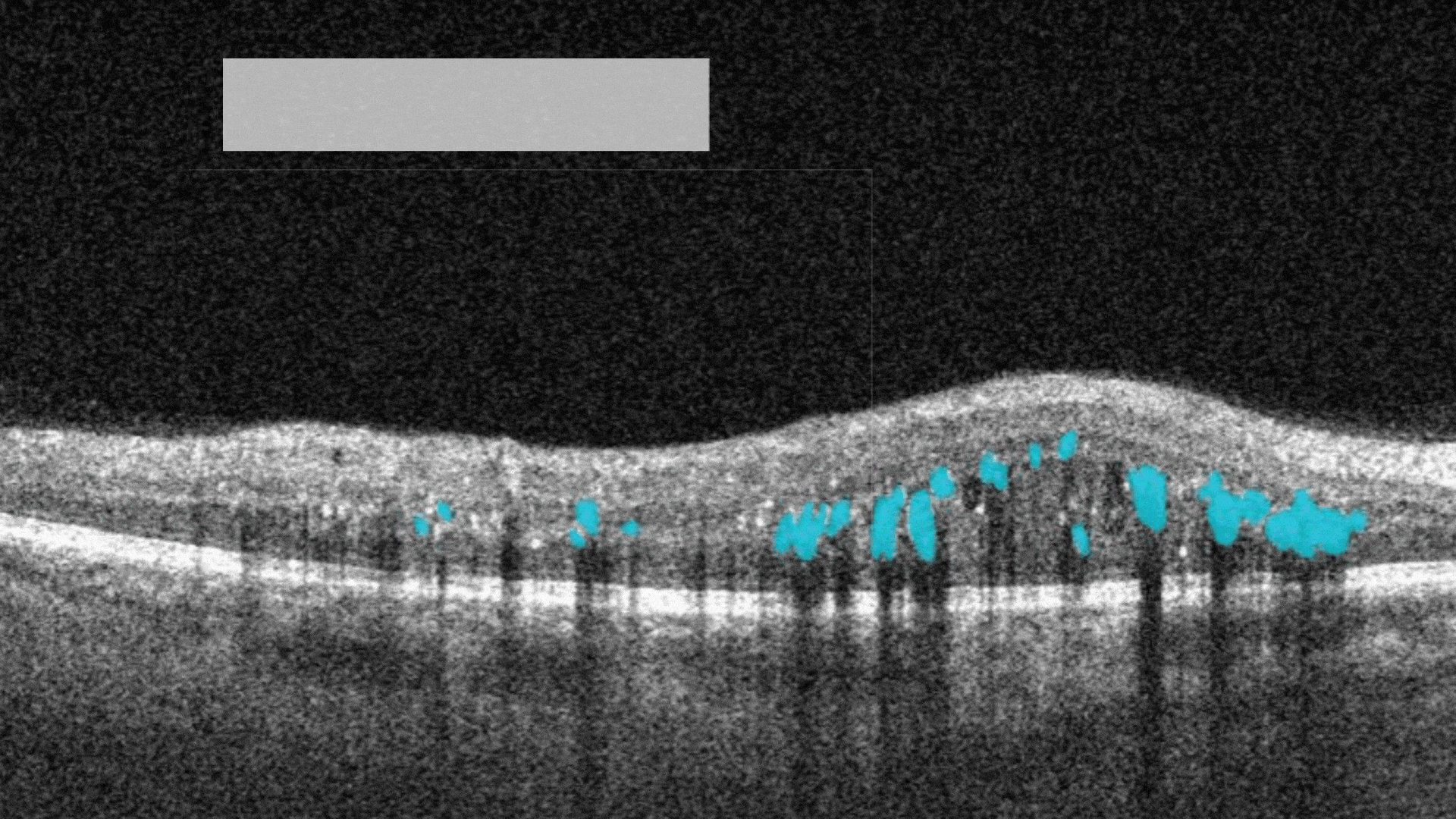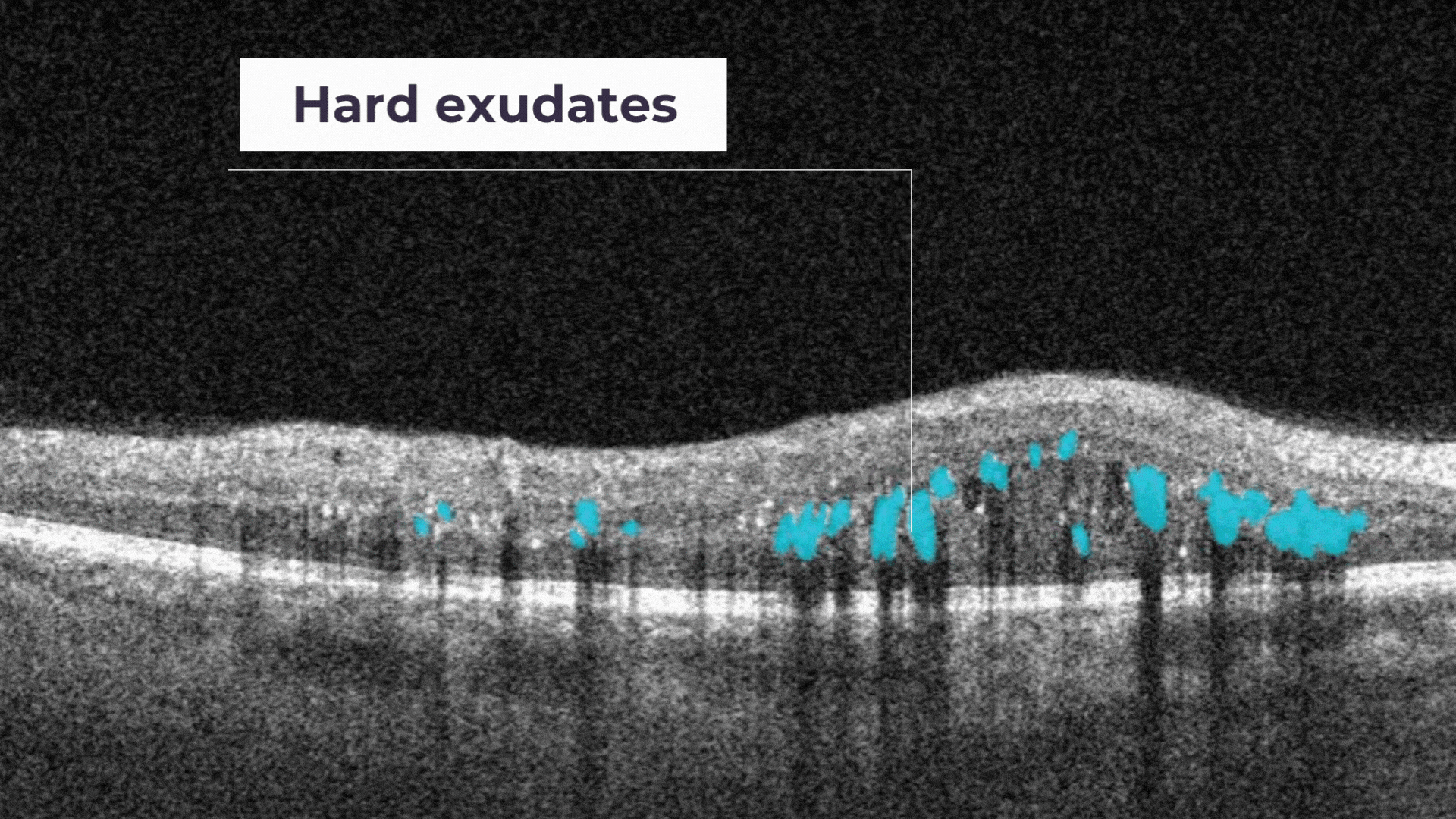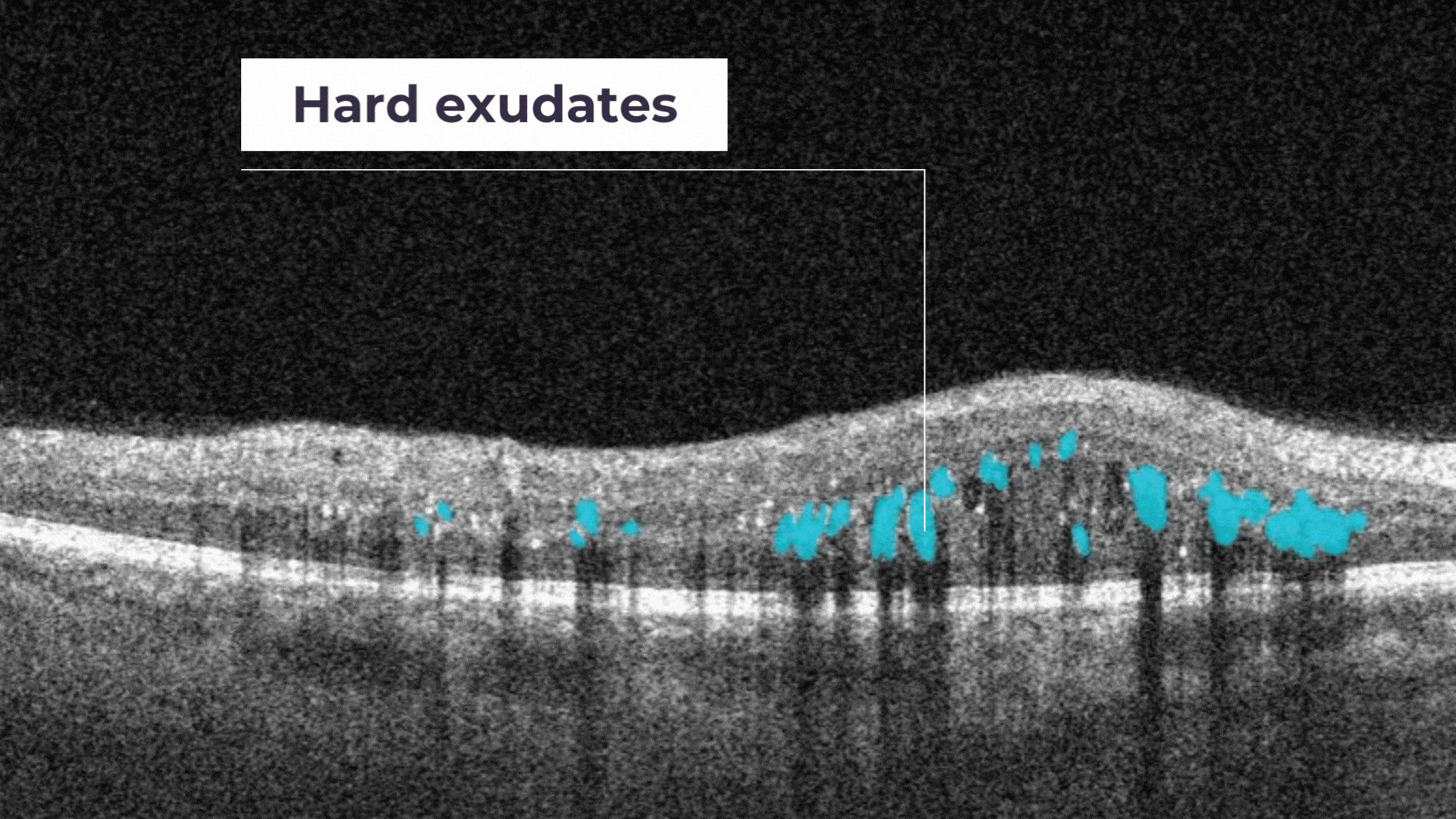
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is a microvascular disorder caused by vision-threatening damage to the retina, a long-term sequela of diabetes mellitus.
-


Hard exudates. They are composed of lipid and proteinaceous material, such as fibrinogen and albumin that leak from the impaired blood–retinal barrier.
-


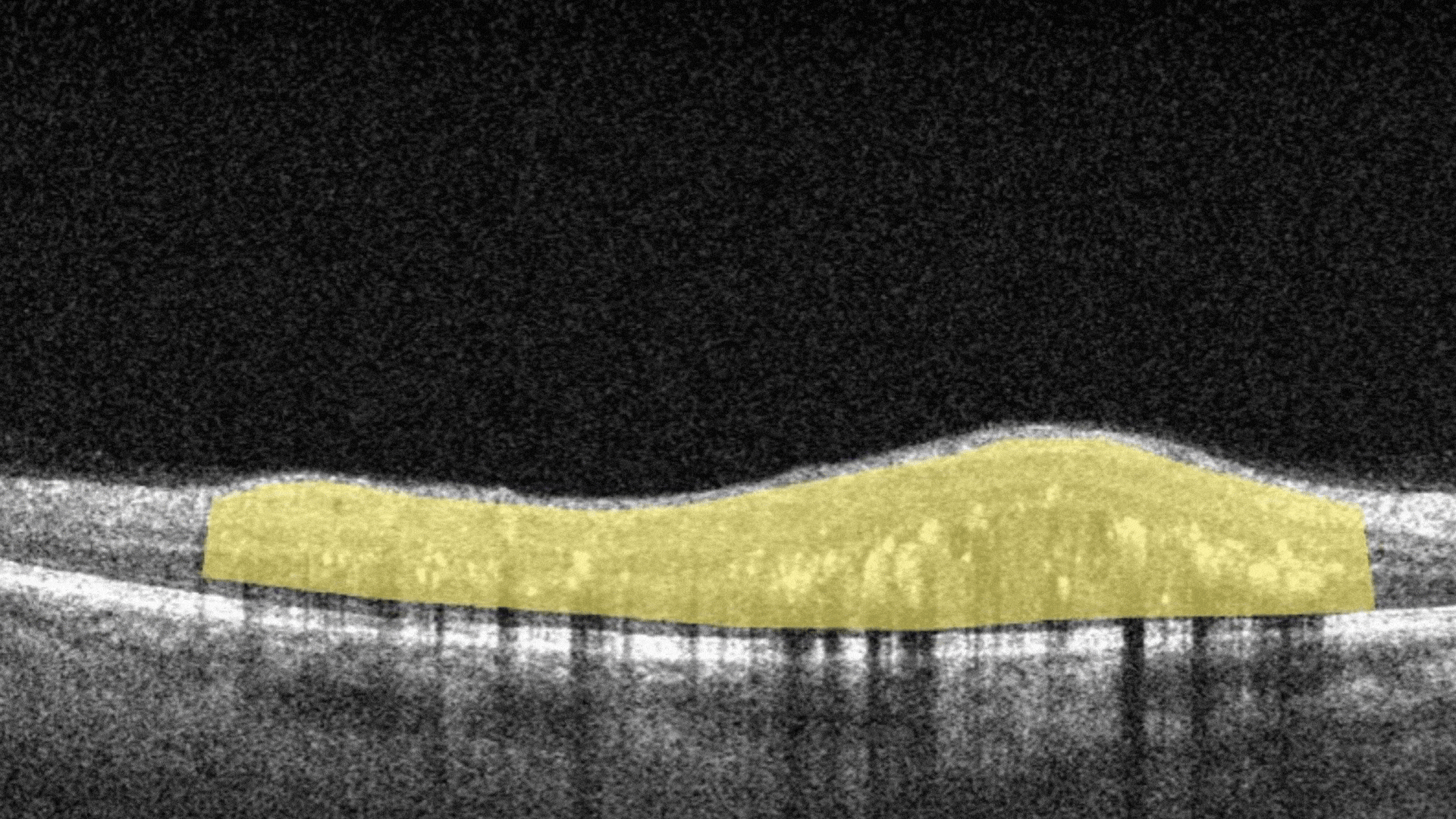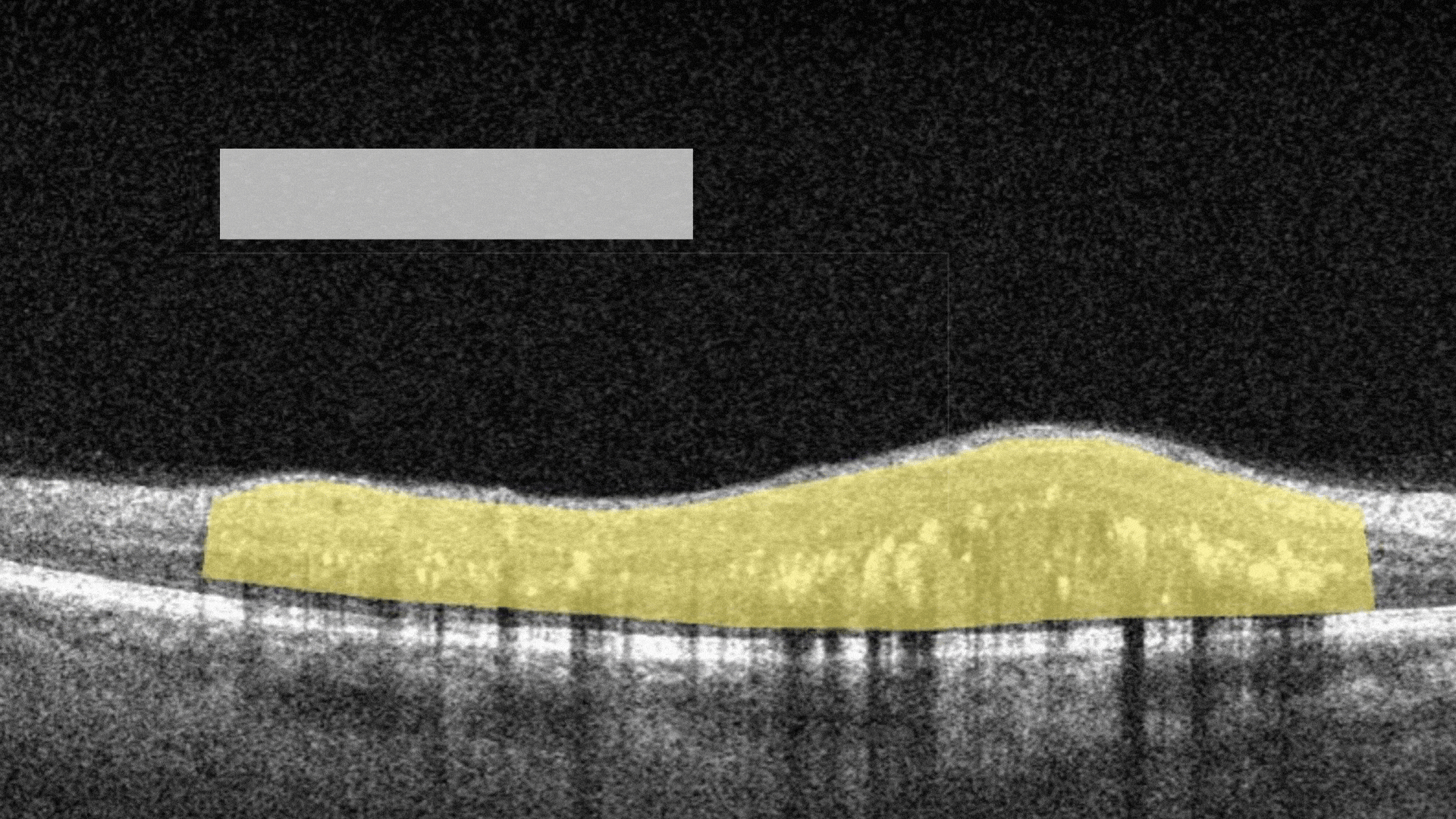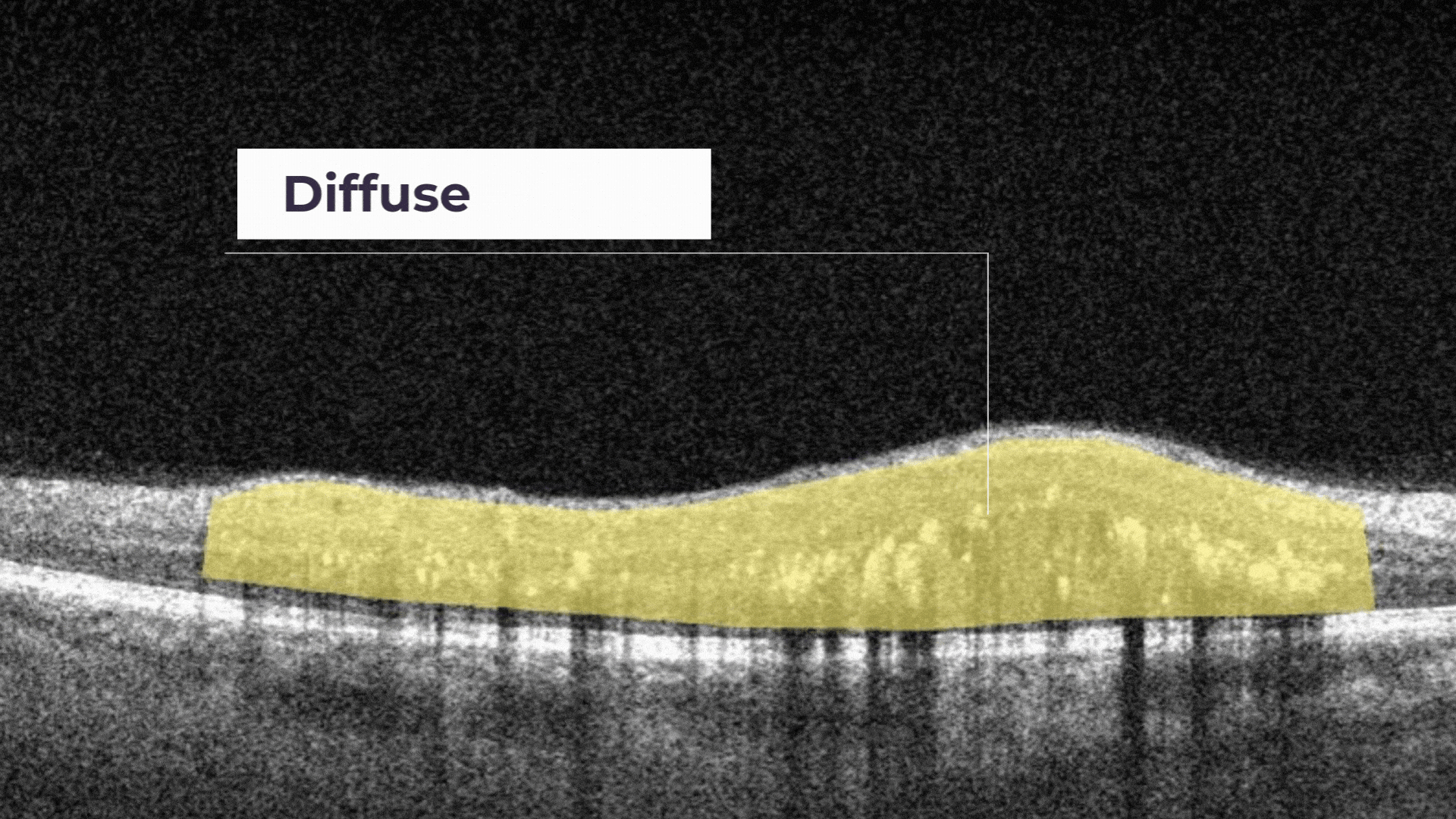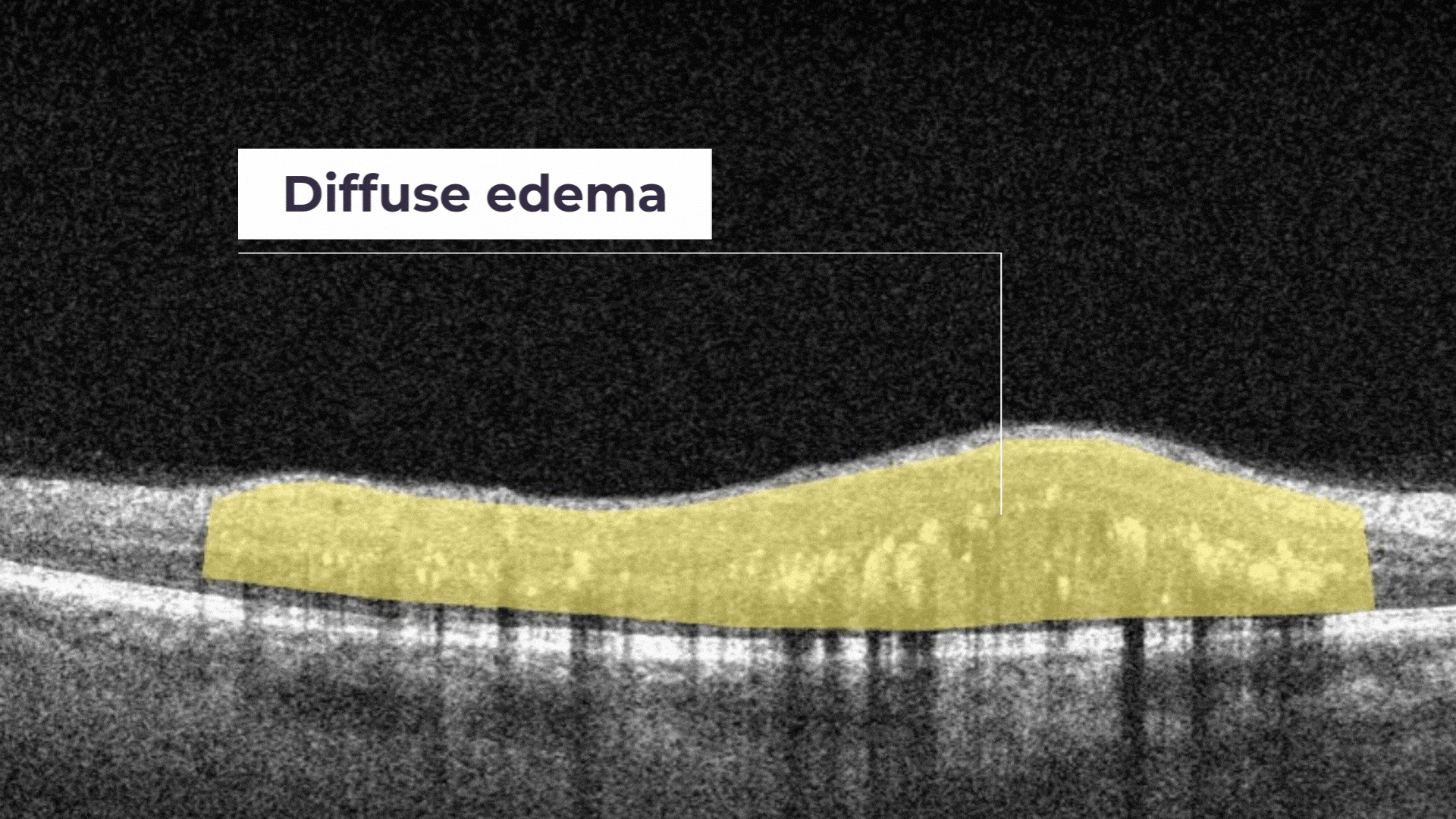
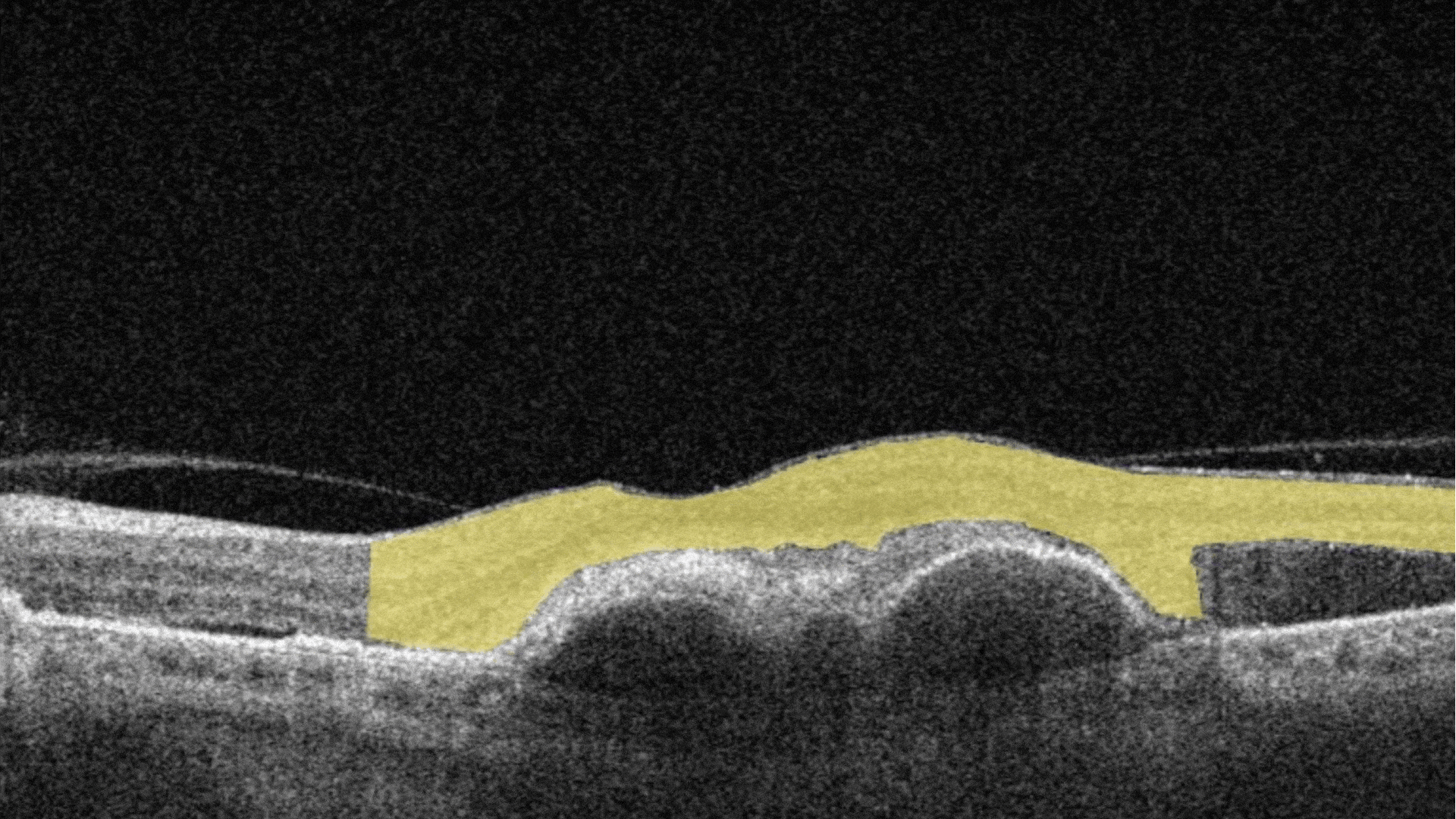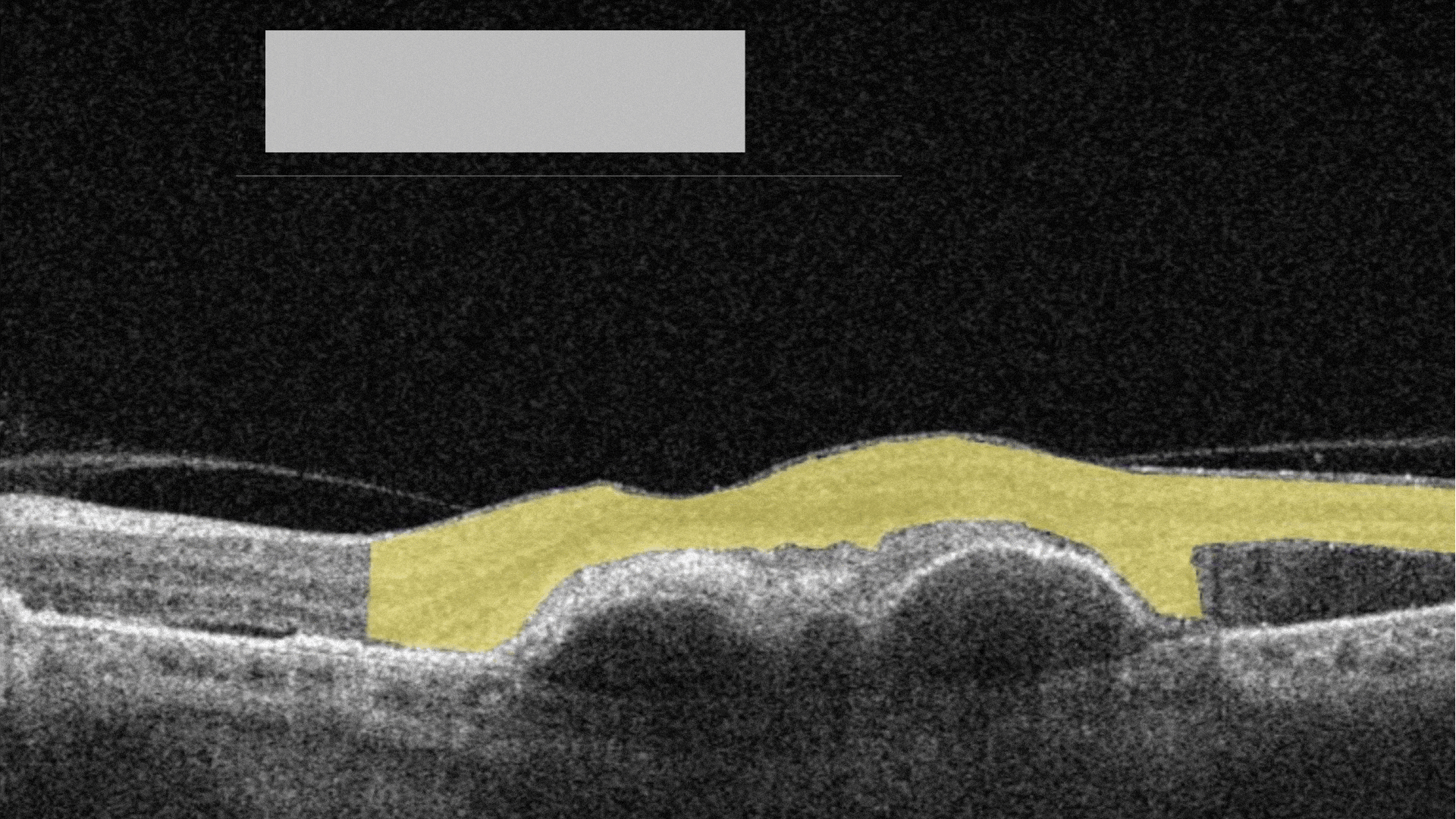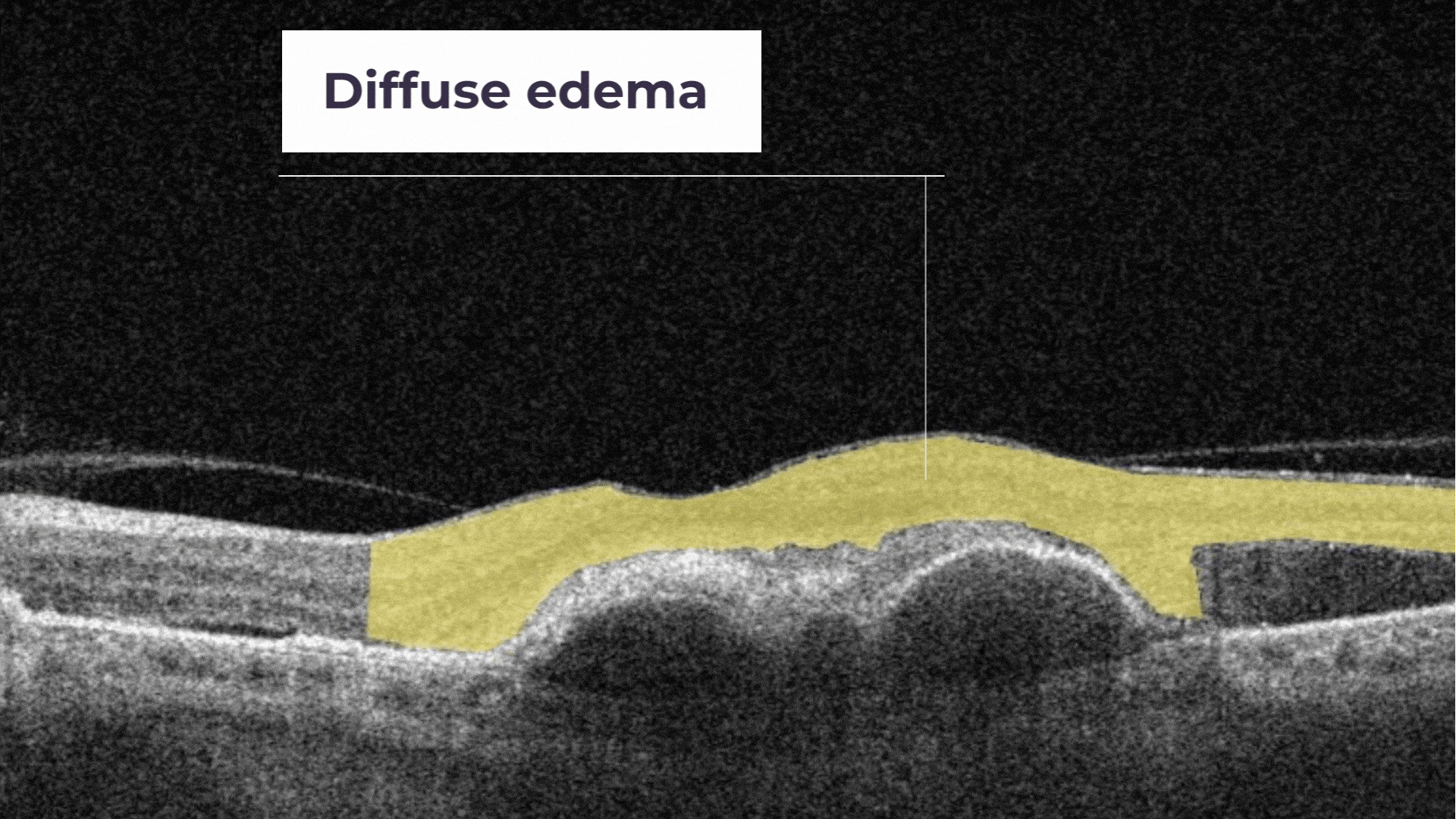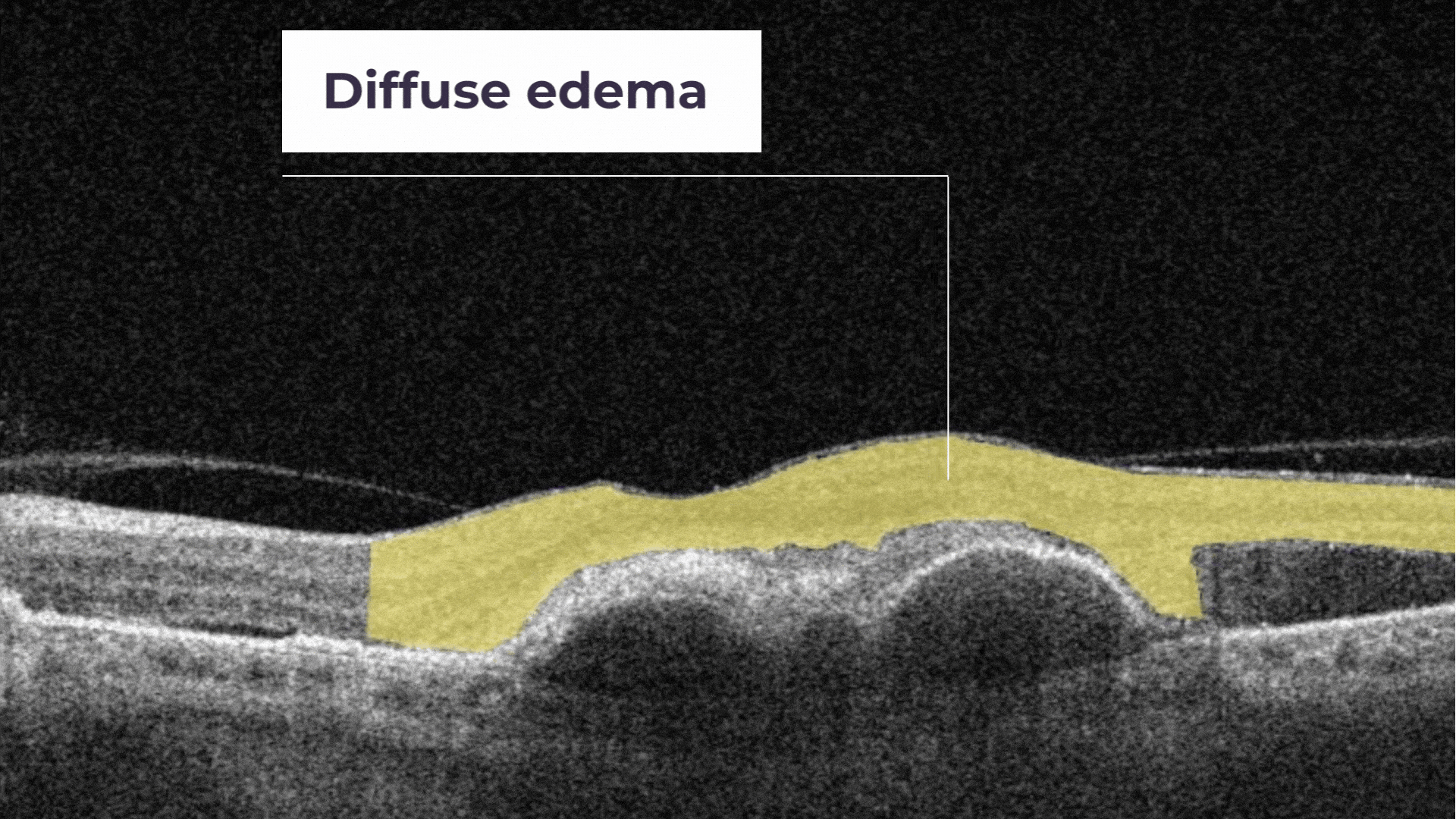
Diffuse Edema. It is a thickened area of lower reflectivity in the outer retina but specifically without cystoid spaces.
-


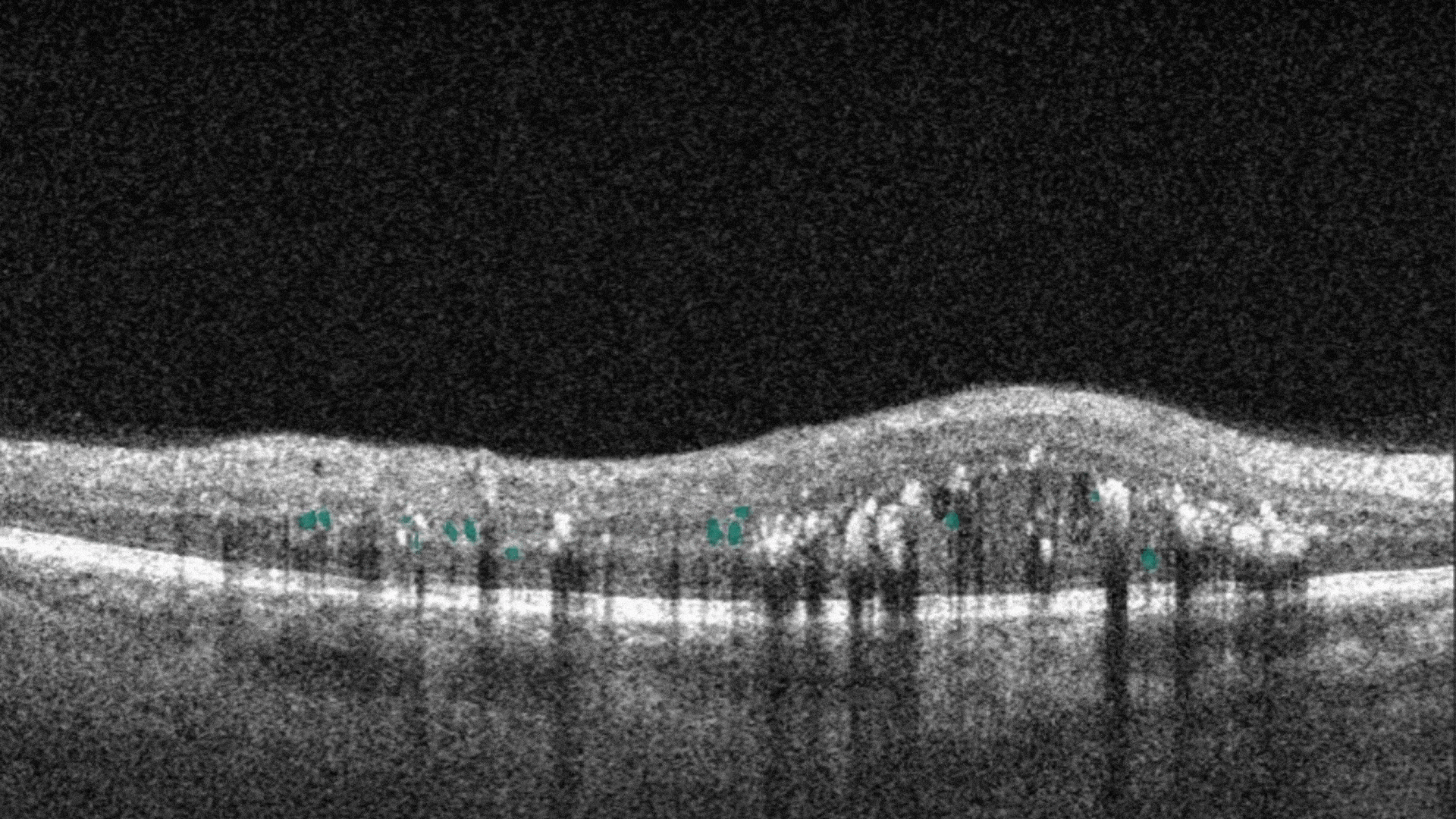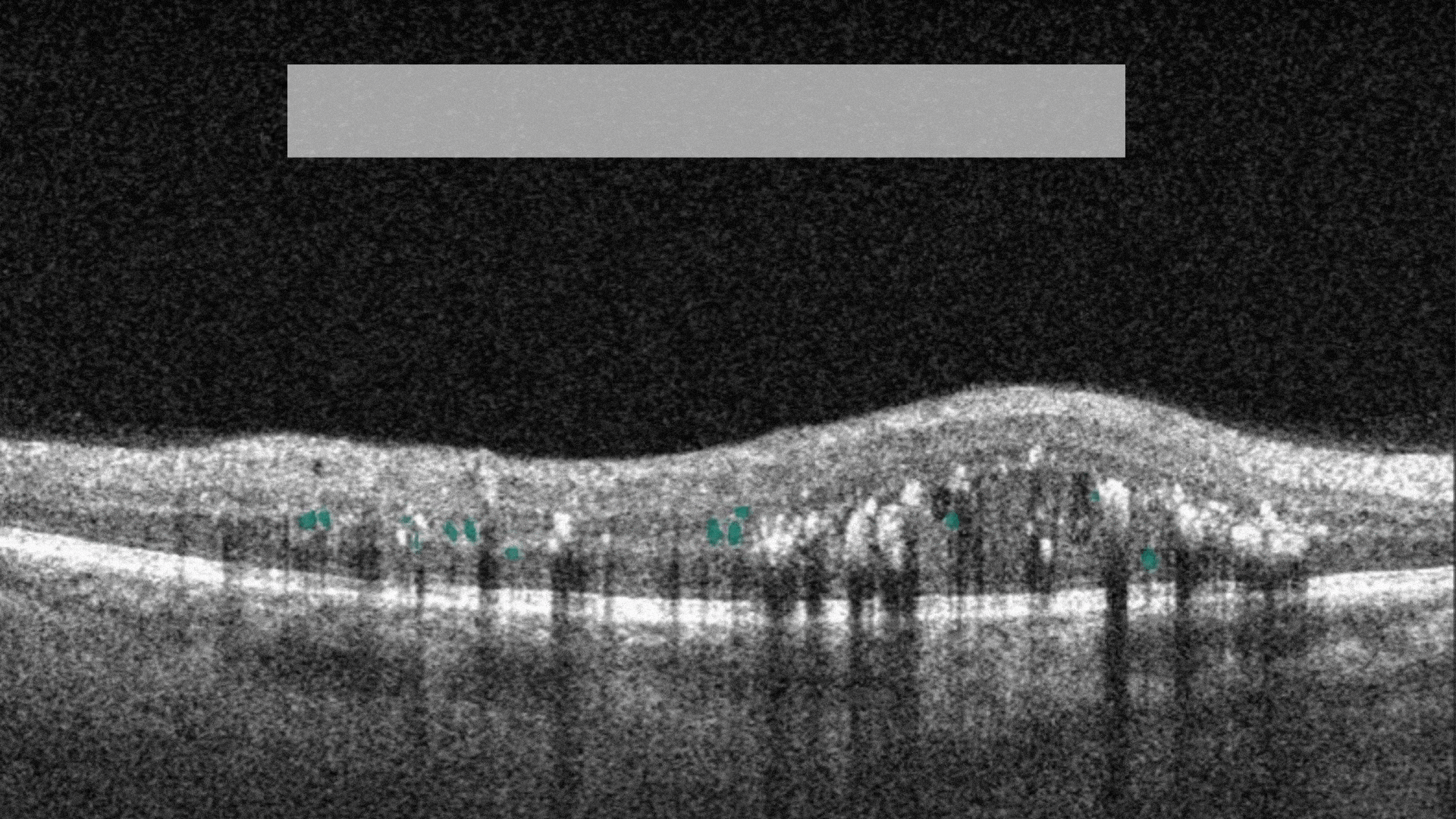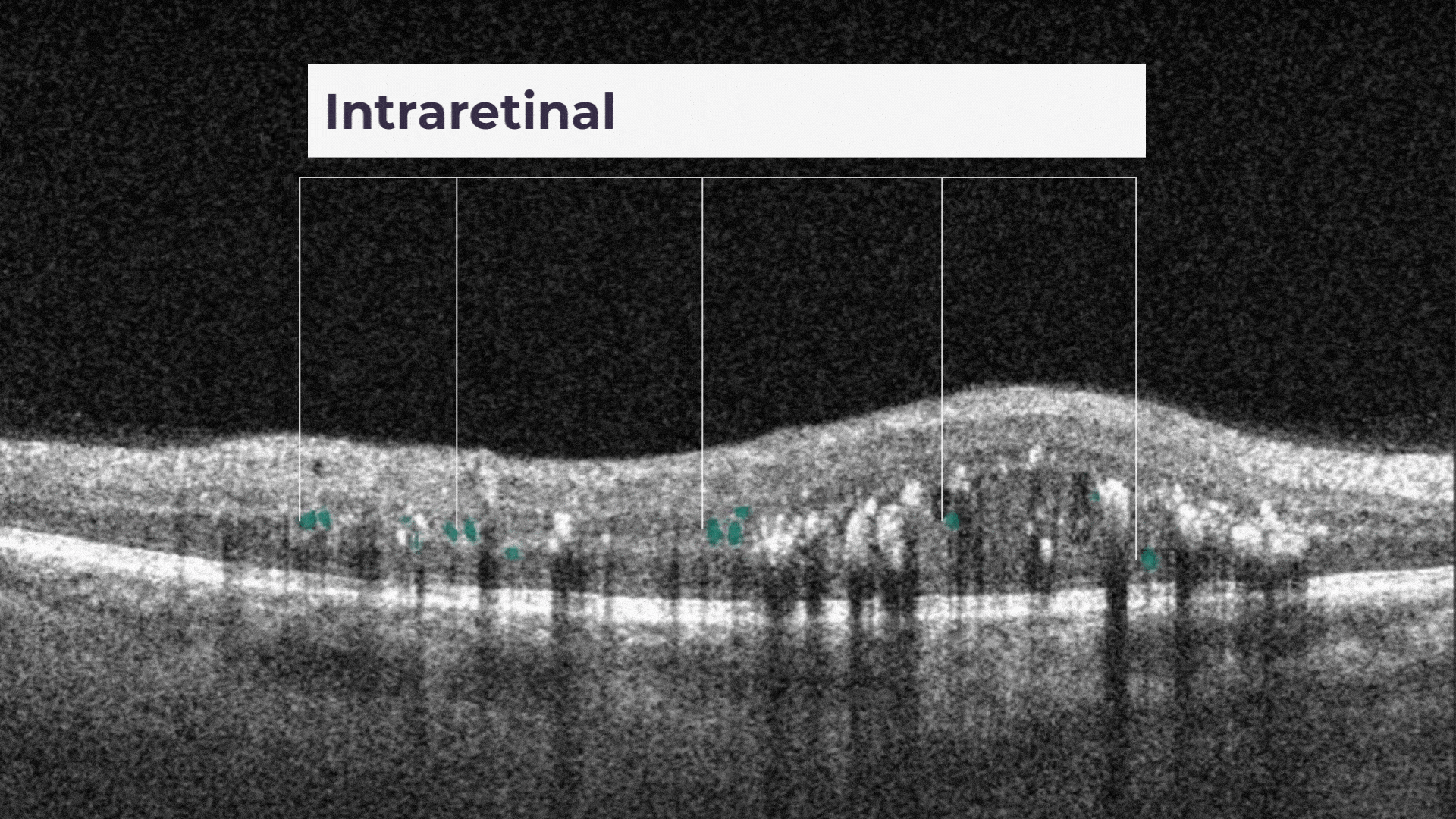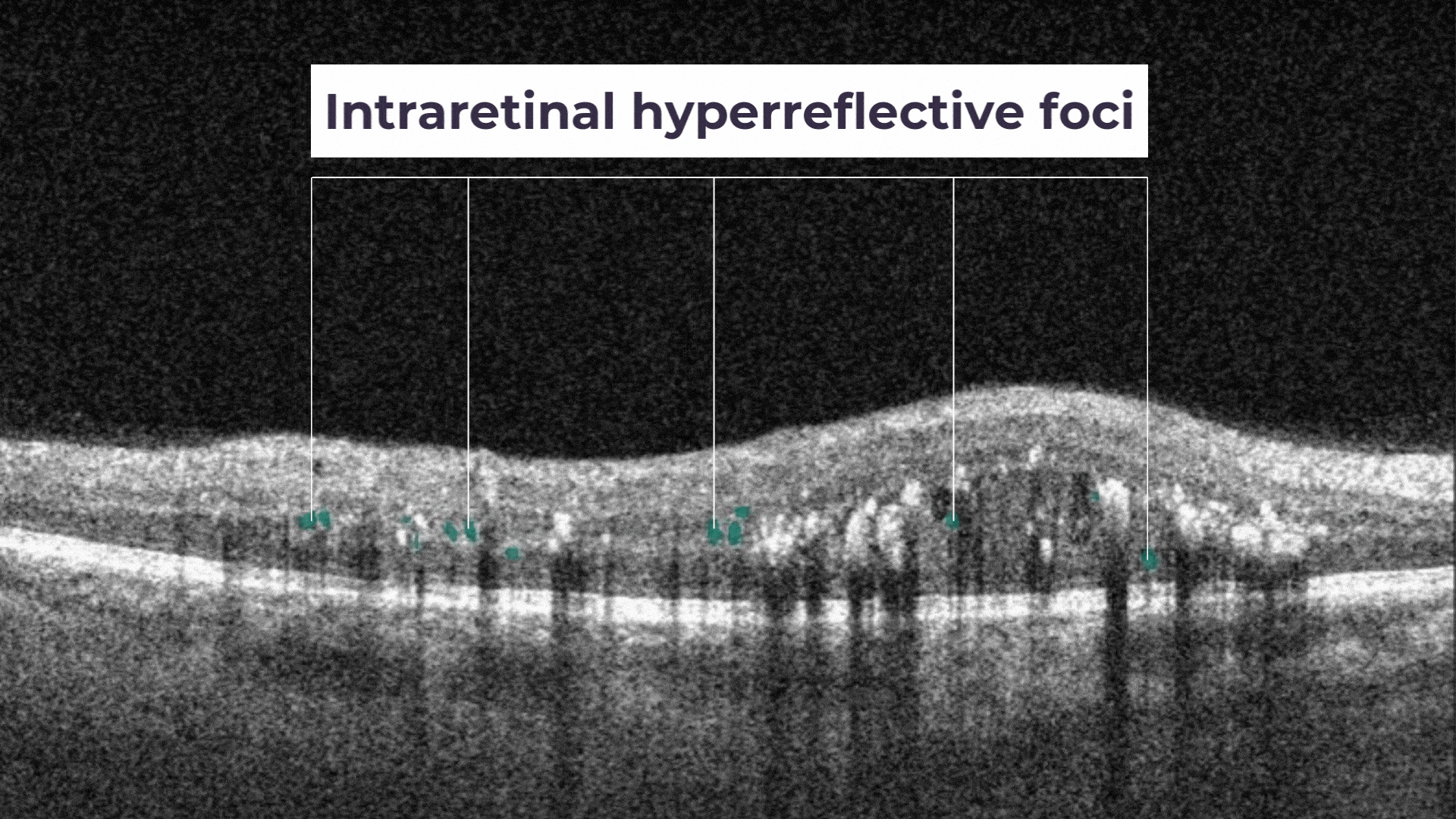
Intraretinal hyprereflective foci are typically dot-like or round, regular lesions seen in all the retinal layers and choroid.
-


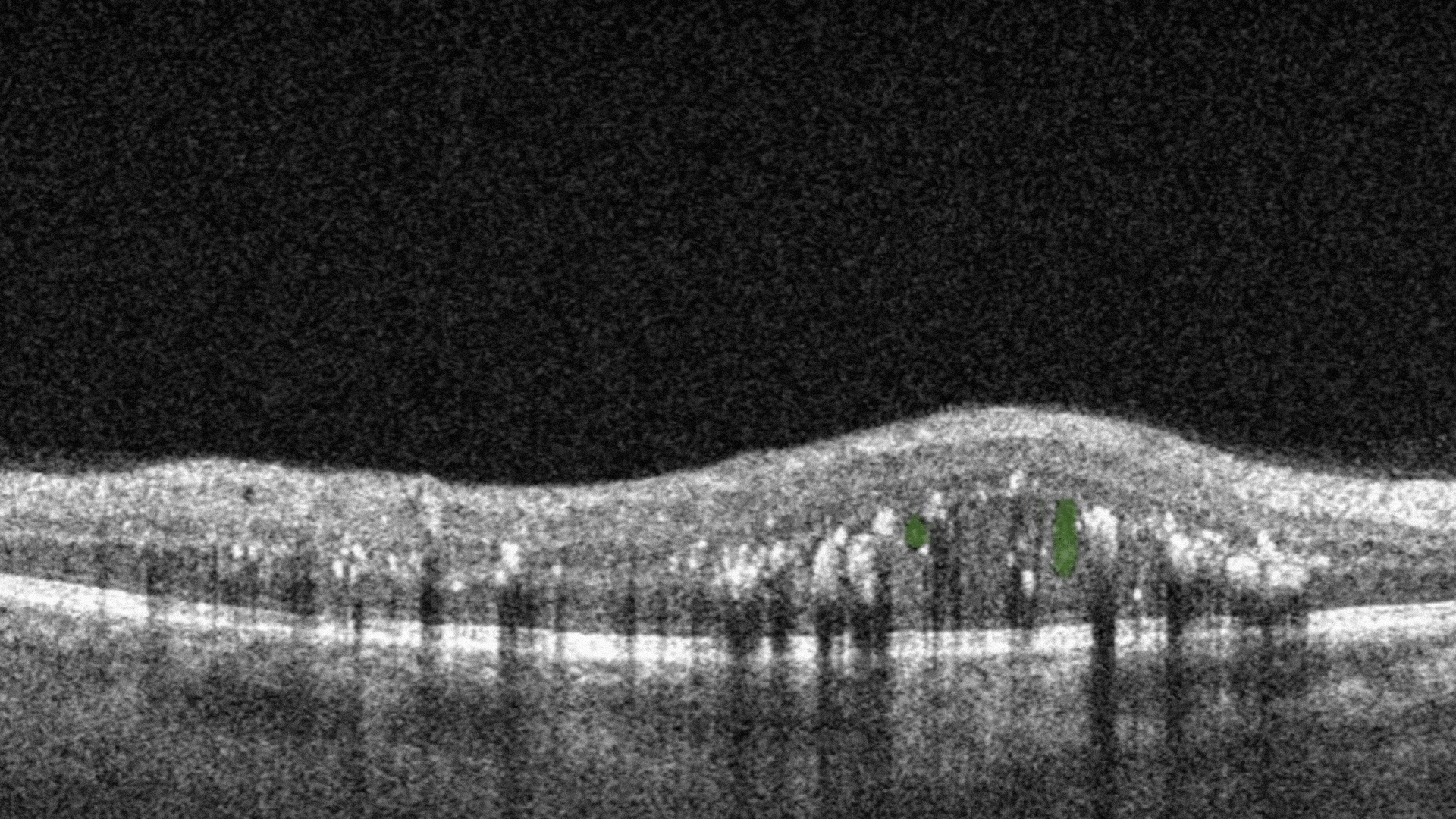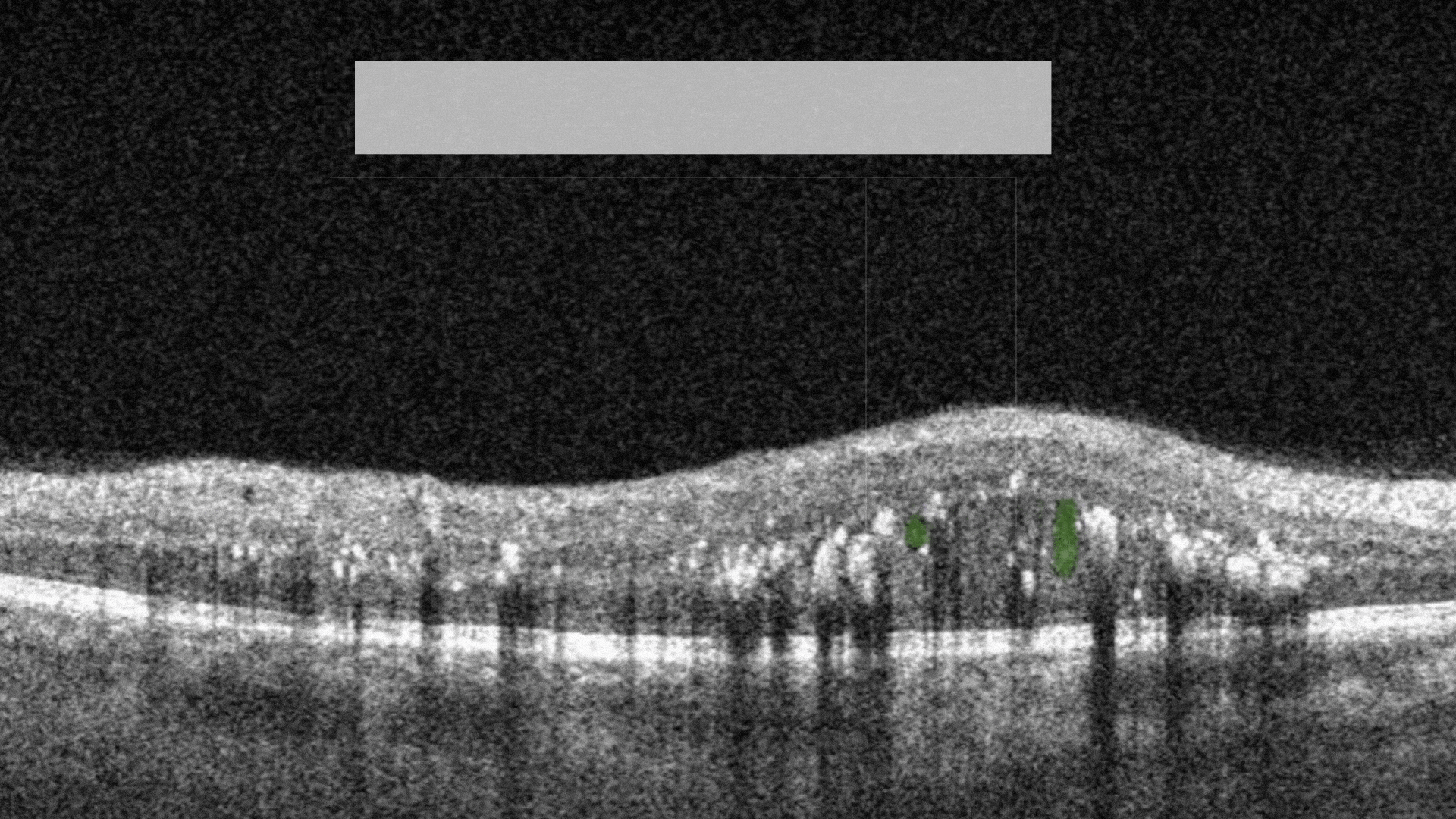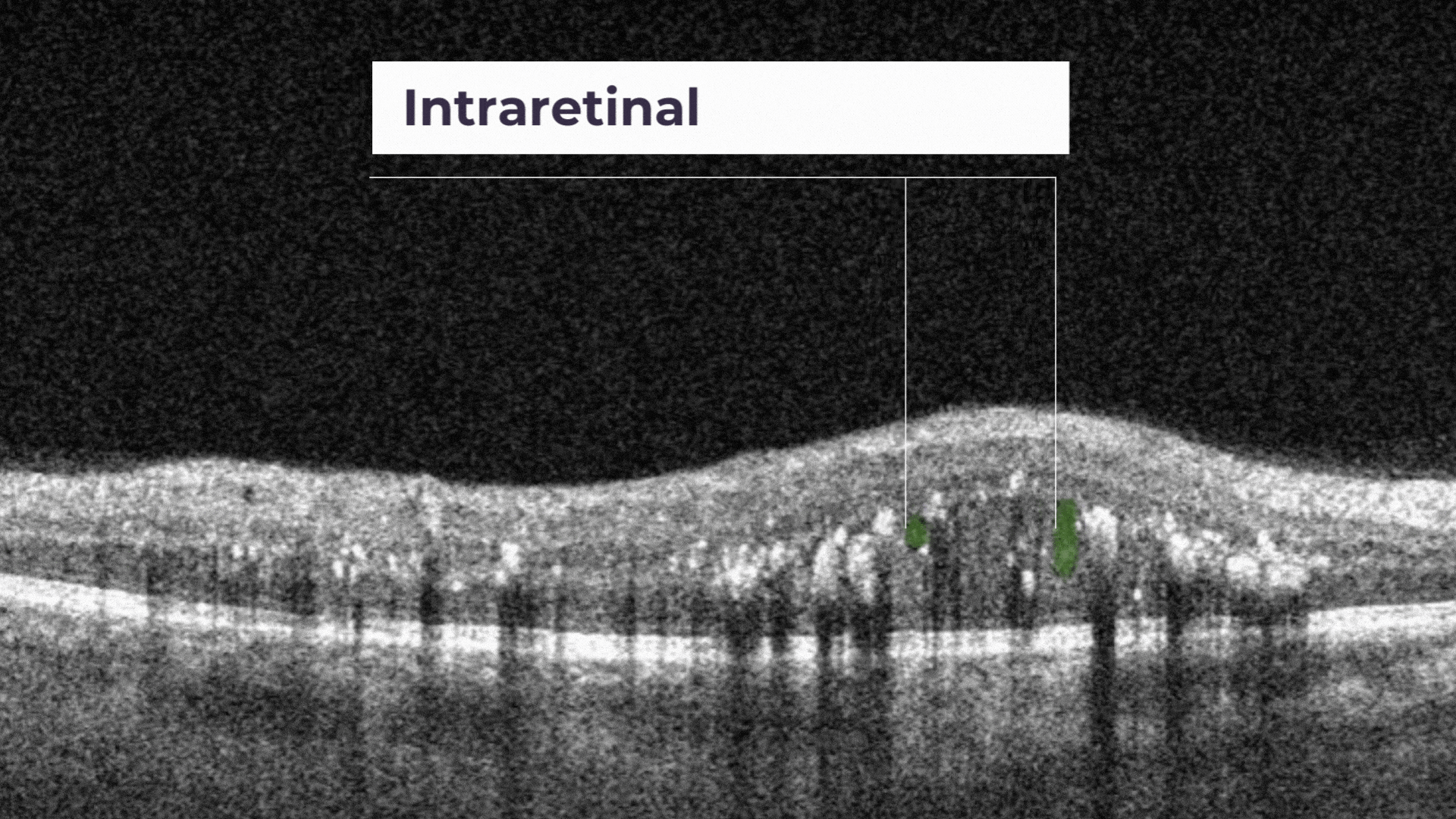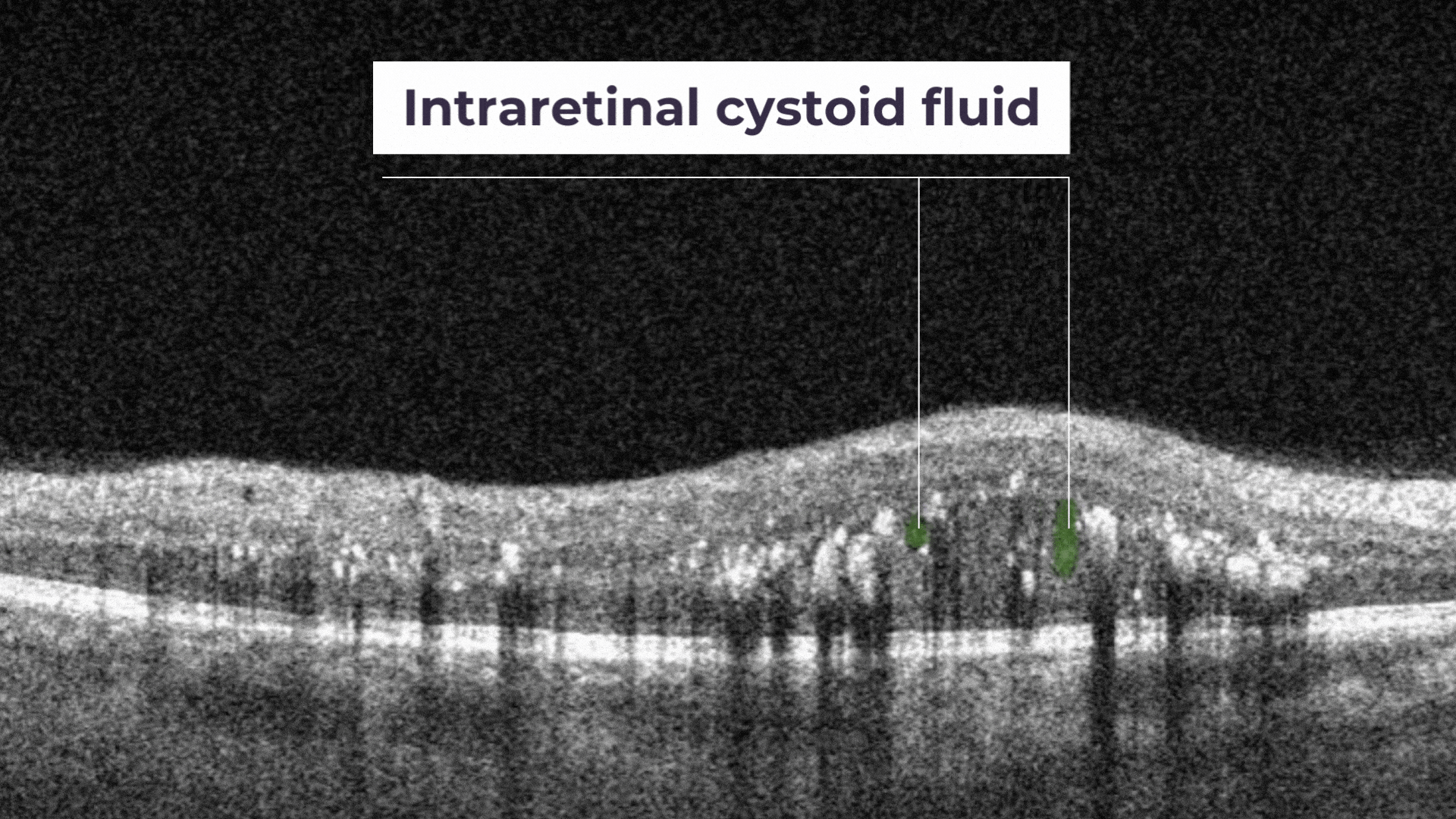
Intraretinal cystoid fluid. The fluid inside the retina which is accumulated as cystic cavities.
AI-powered OCT workflow for the patient with dAMD (Drusen)
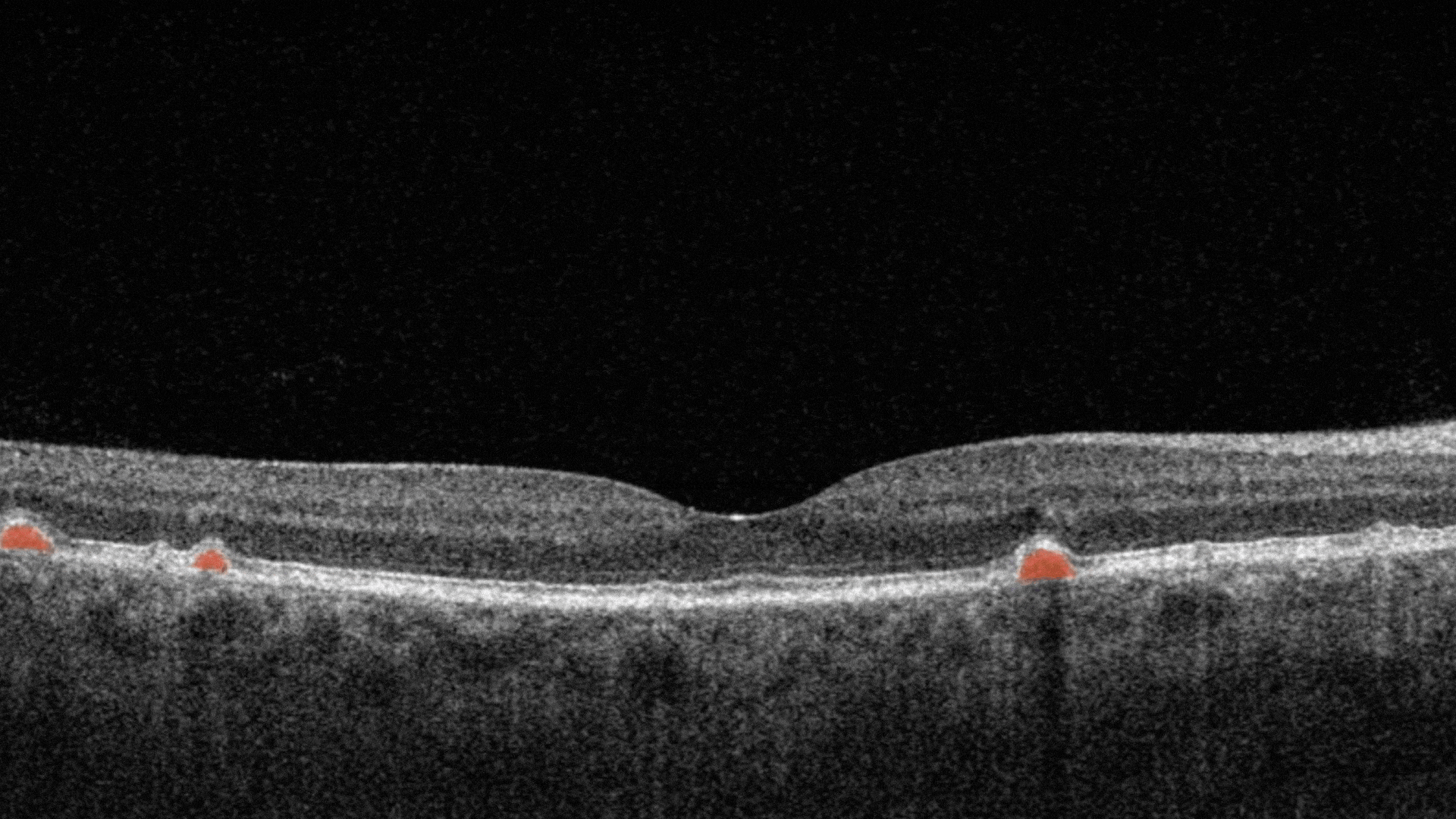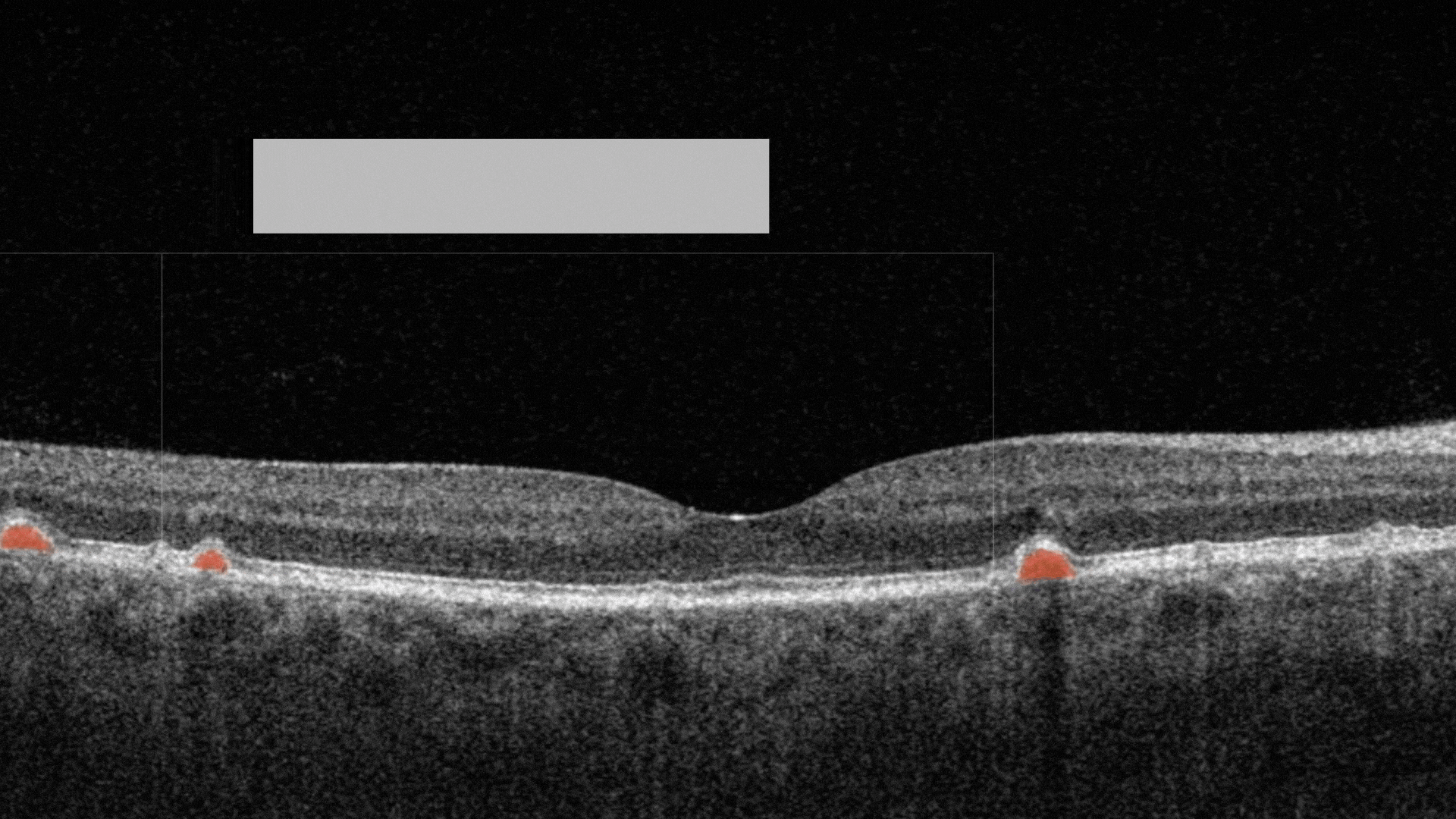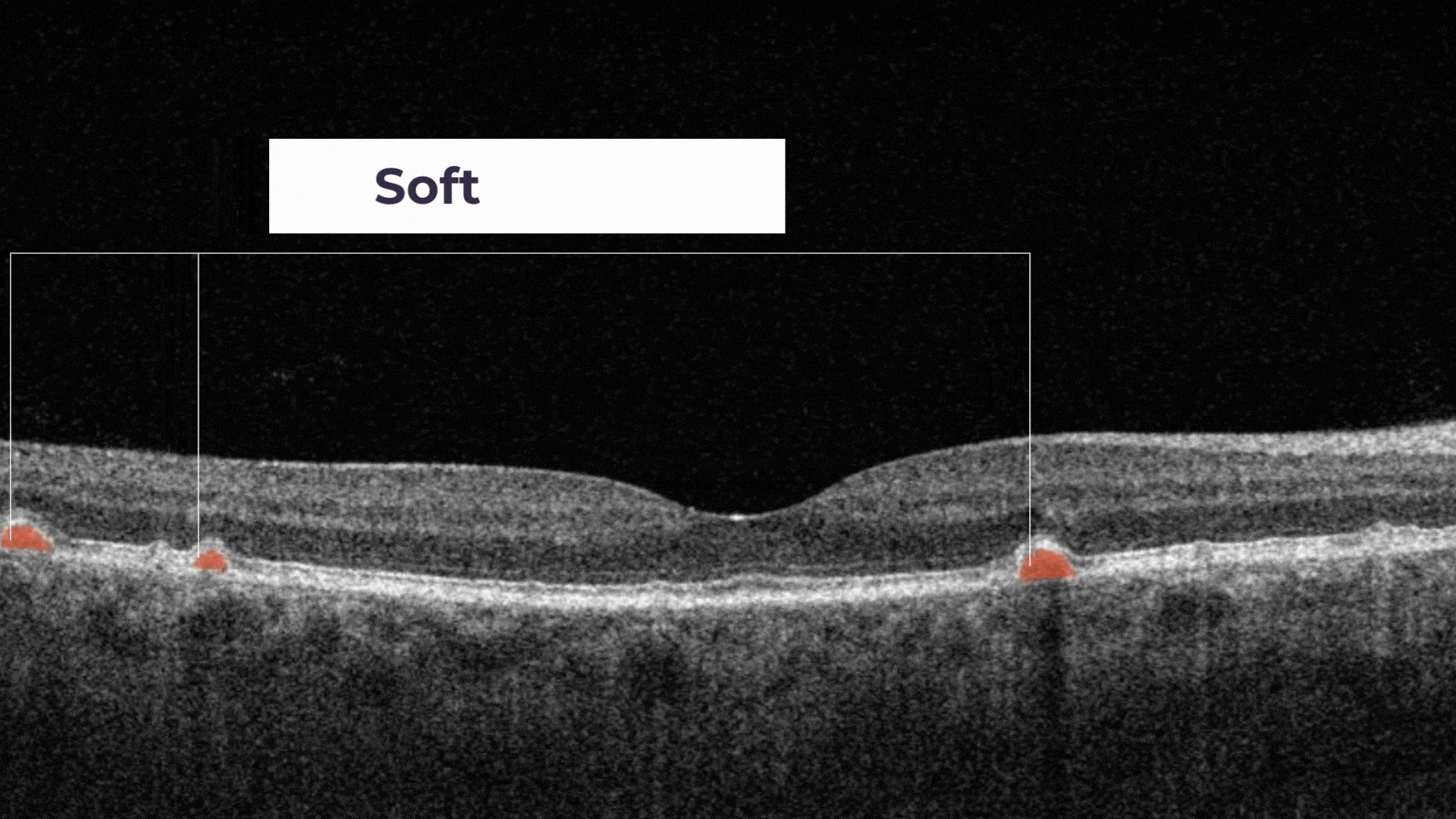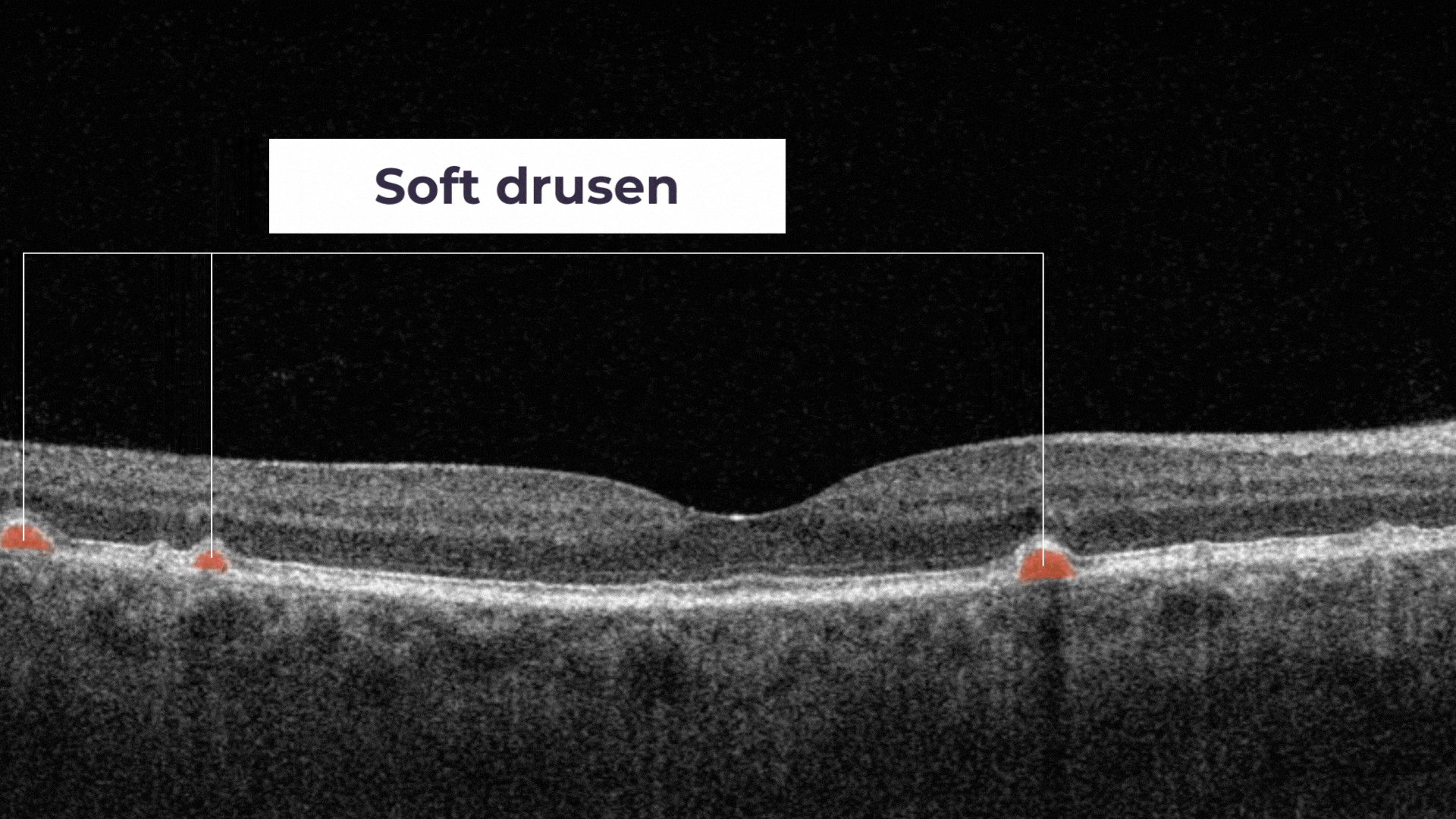
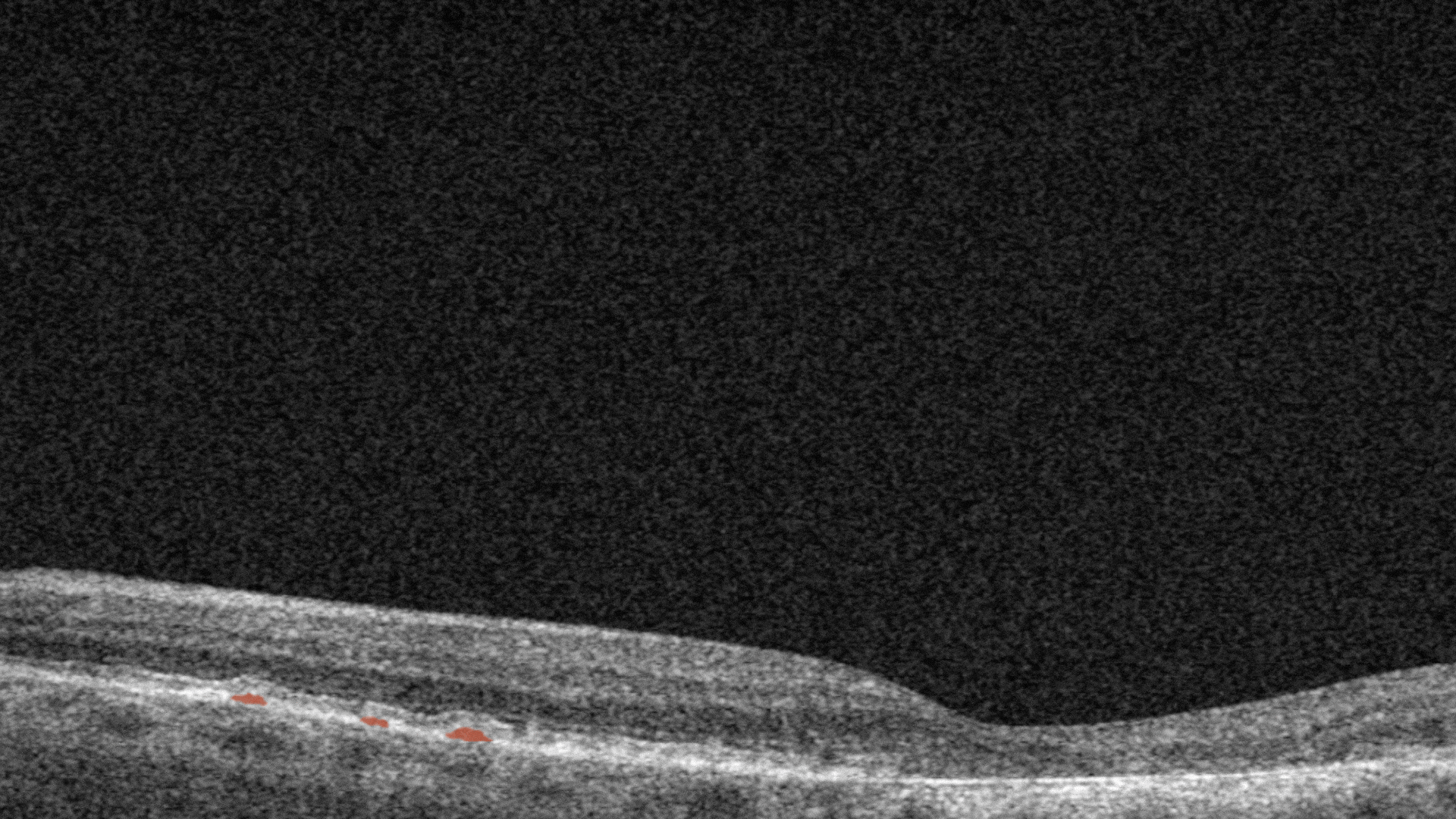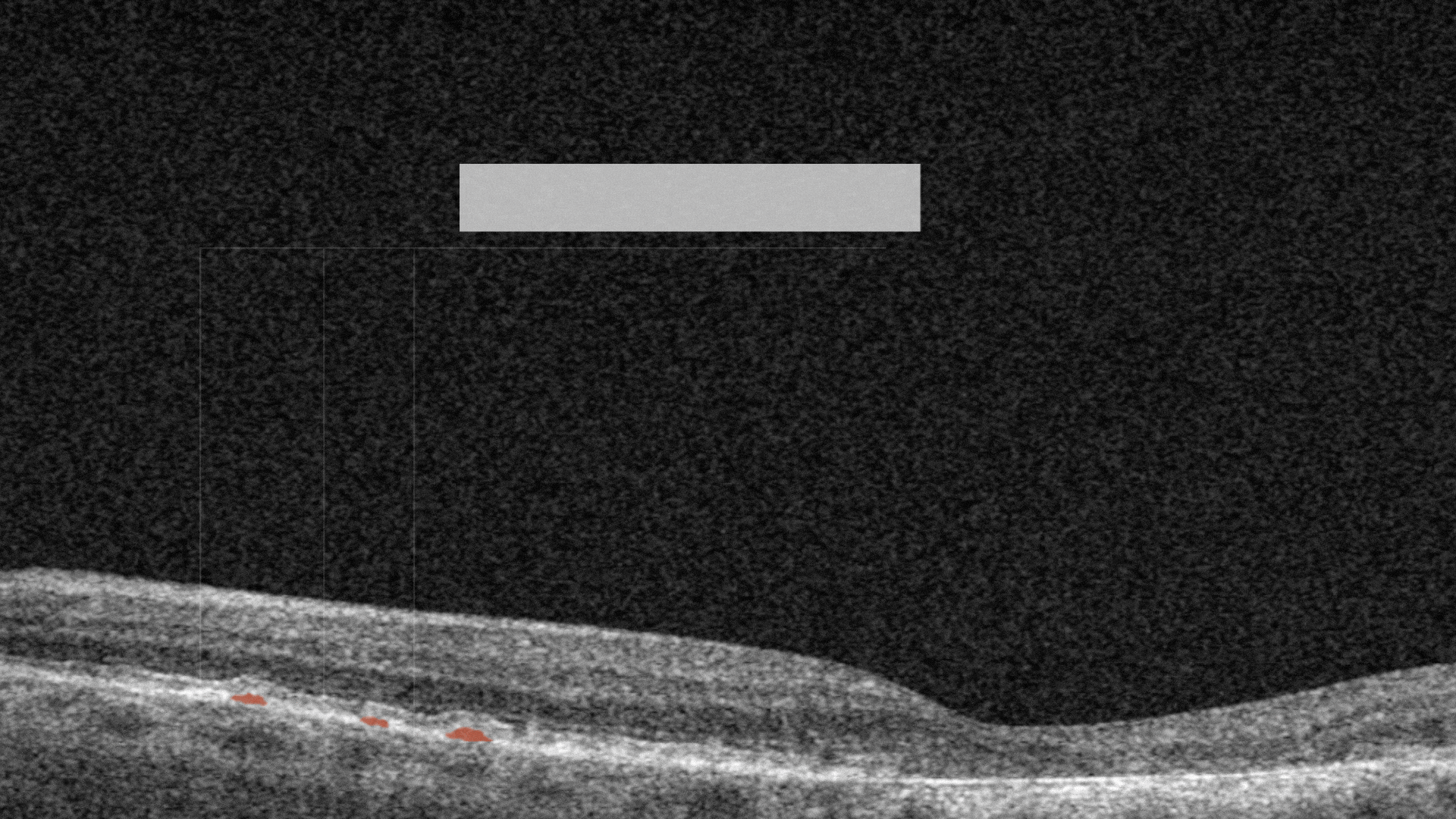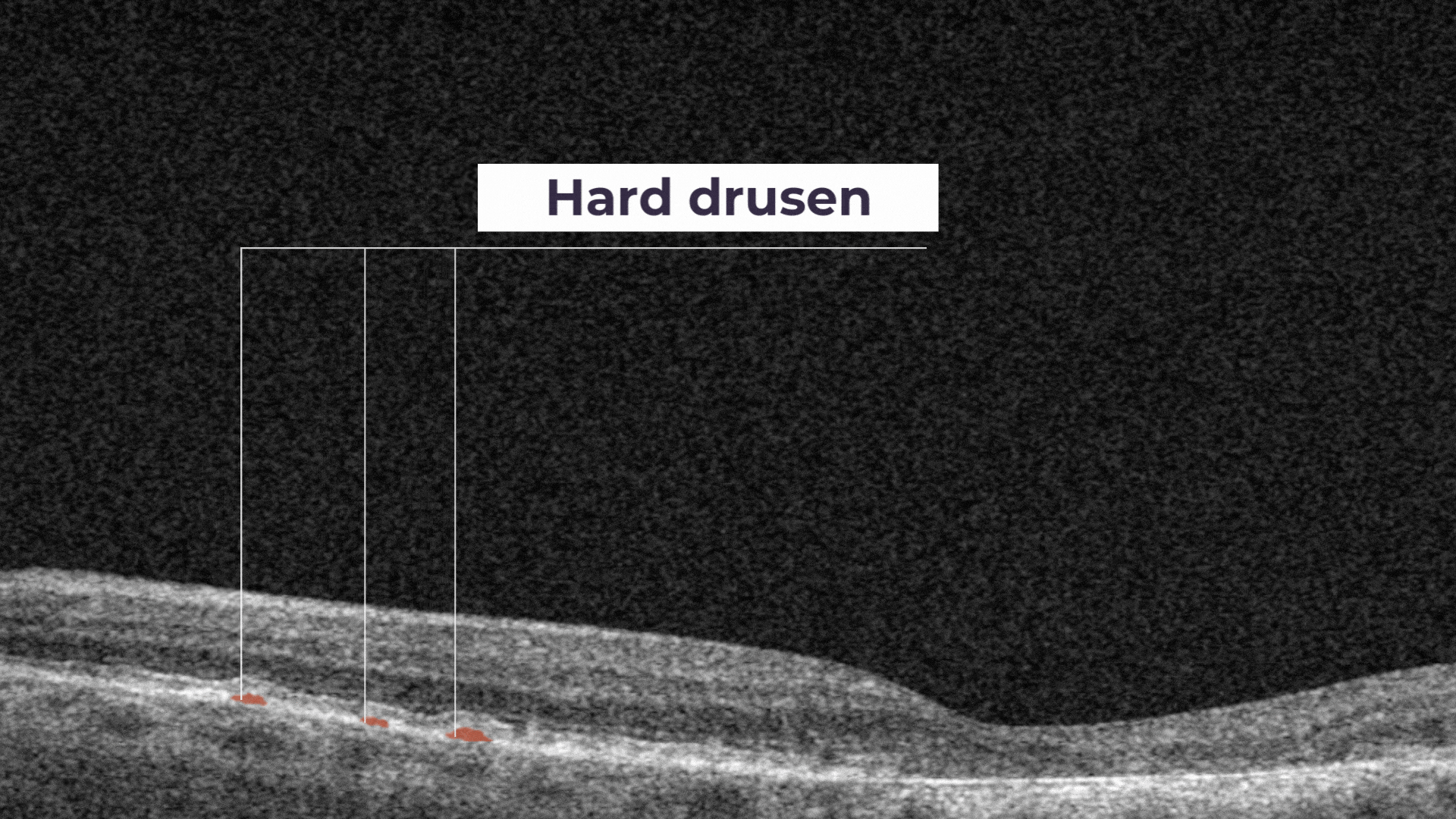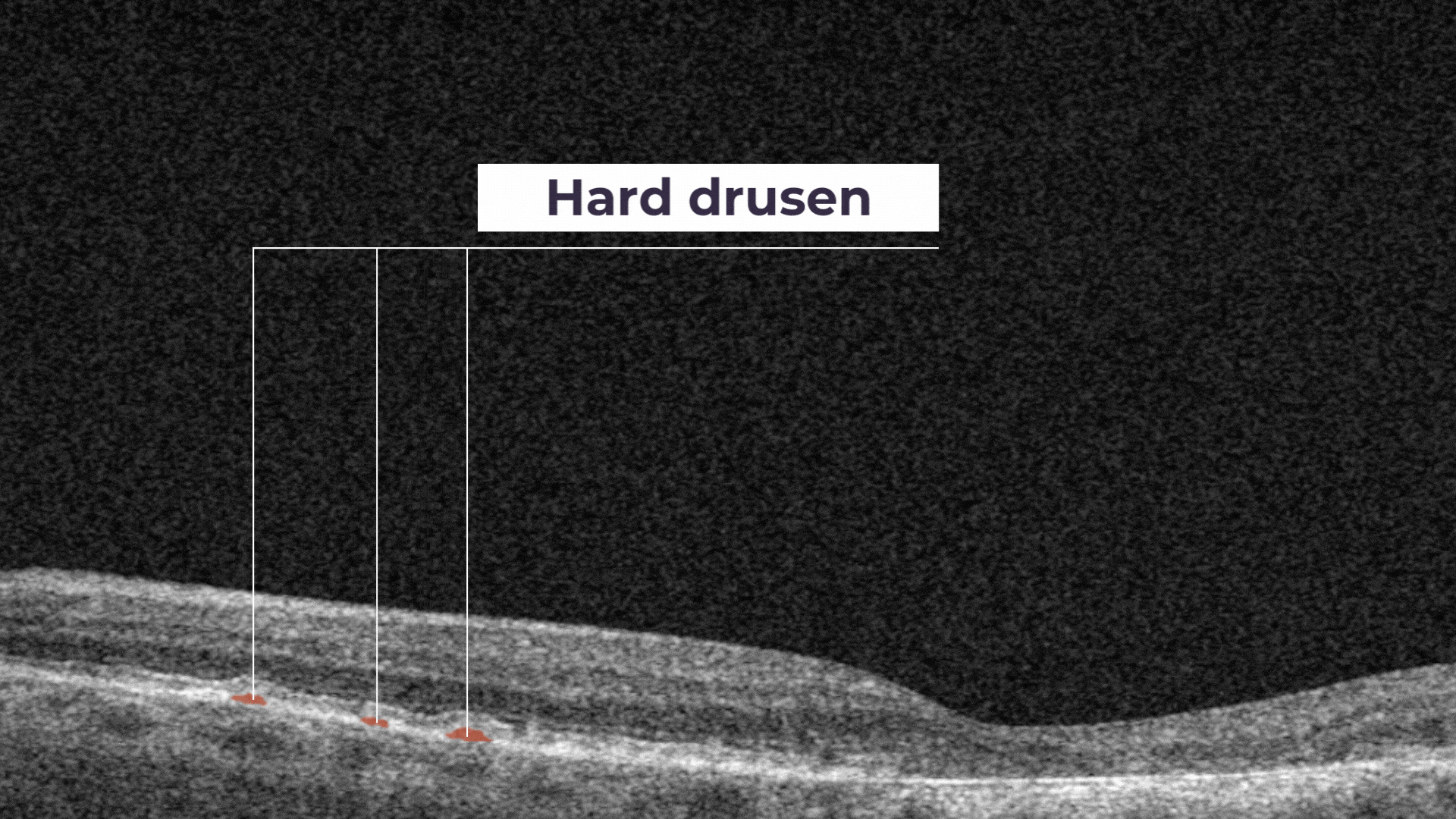
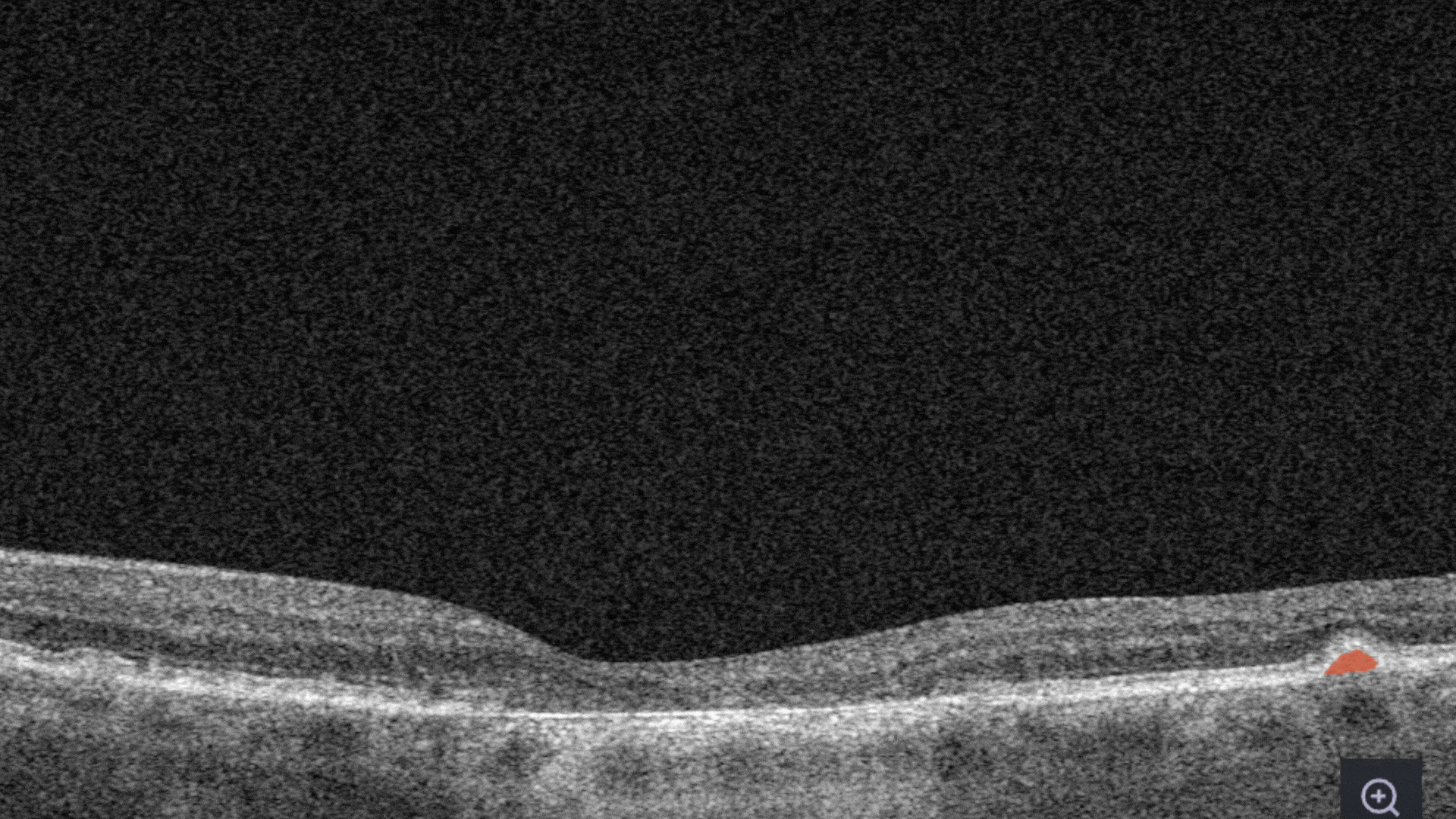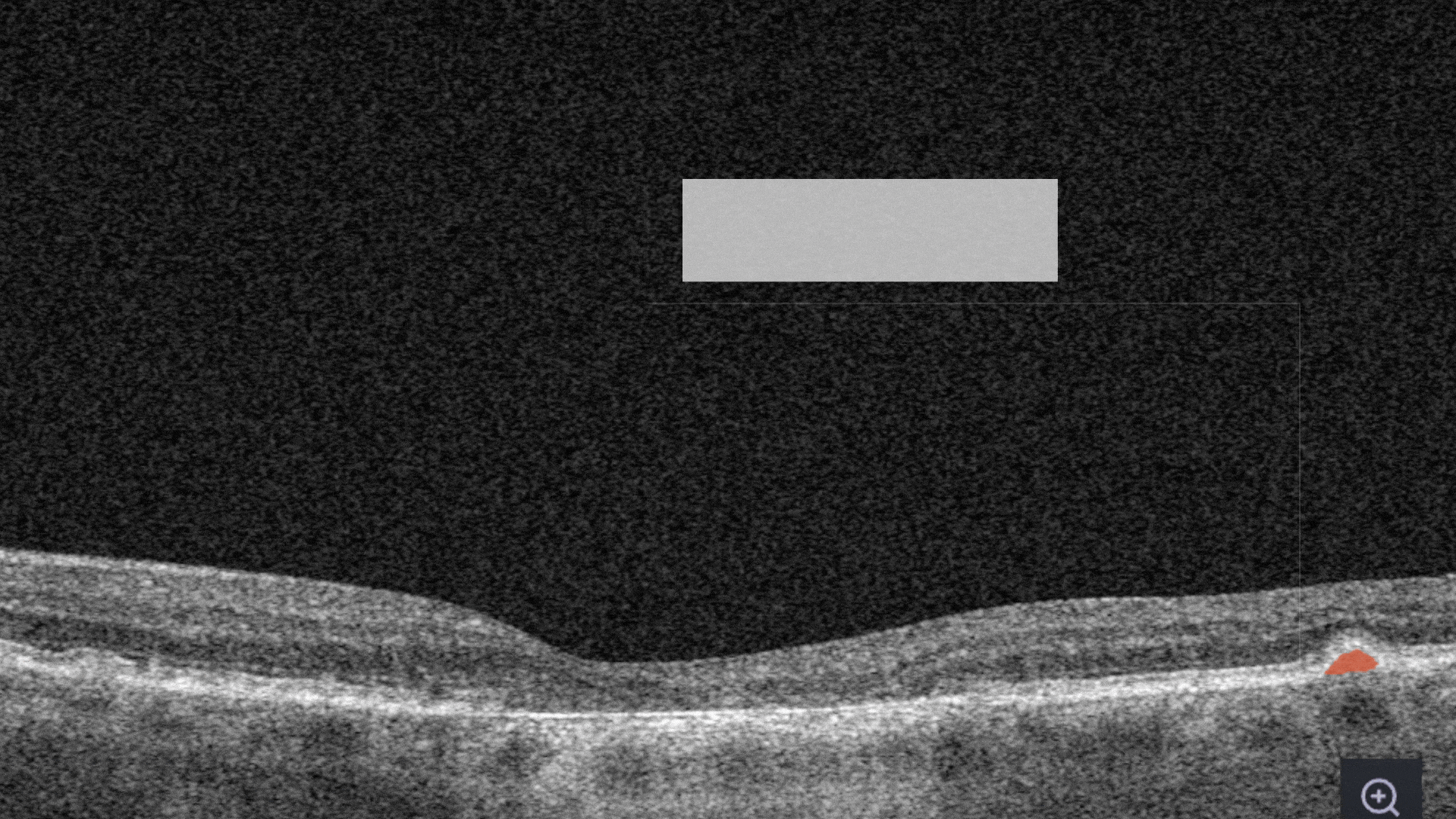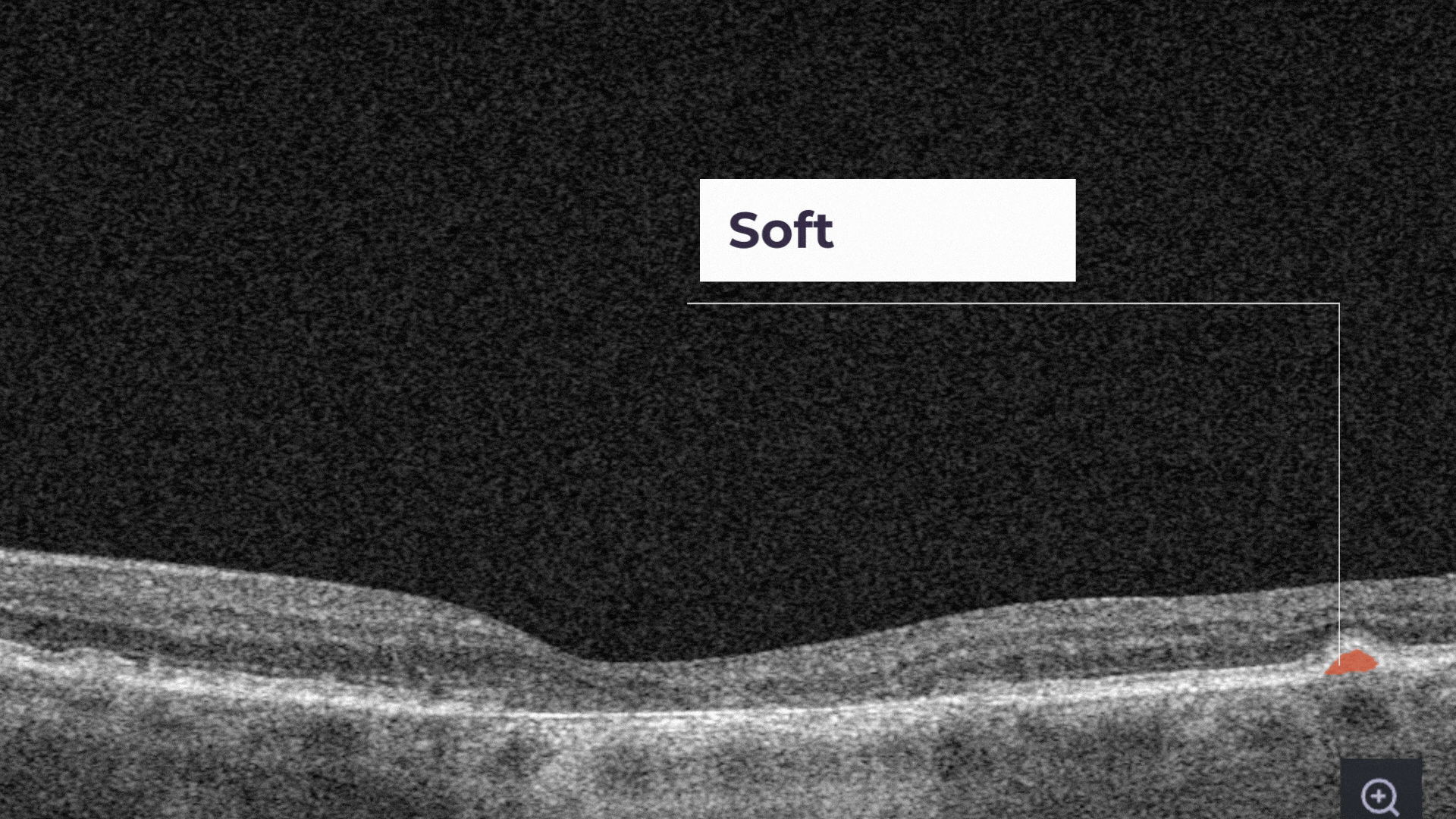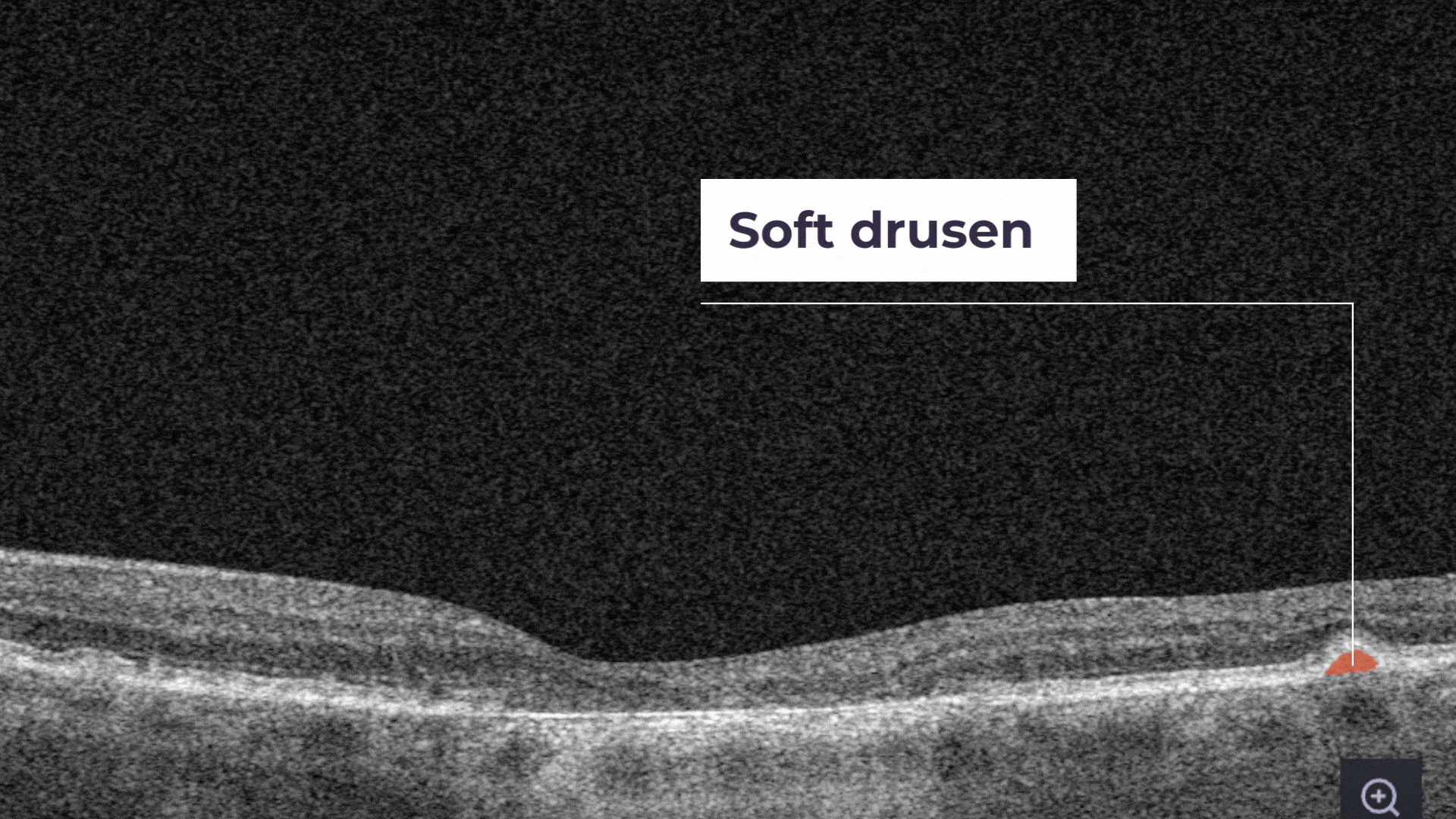
The presence of a large number of larger drusen is an early sign of dry age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
-


Soft drusen are larger, cluster together, and have edges that are not as clearly defined.
-


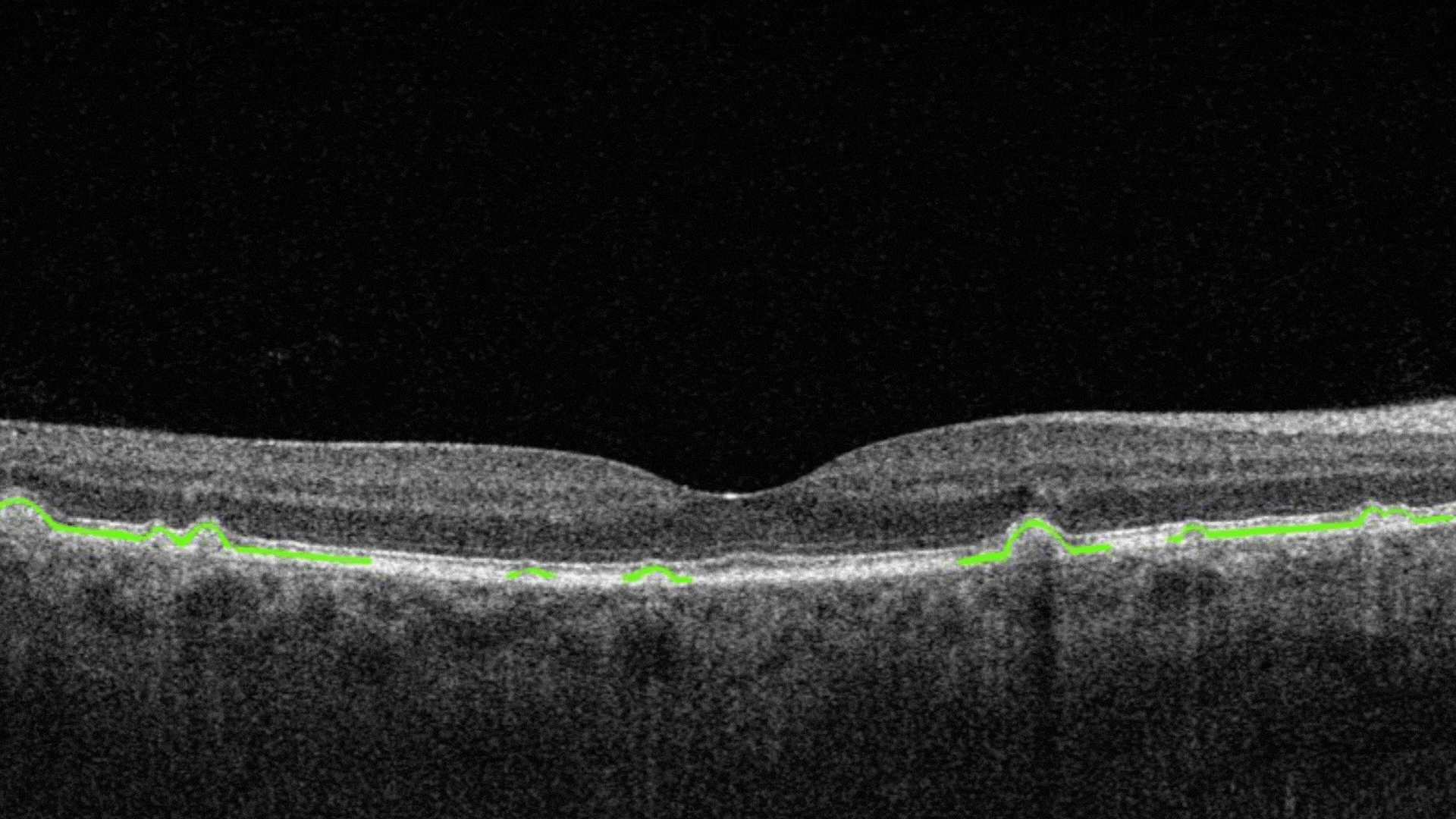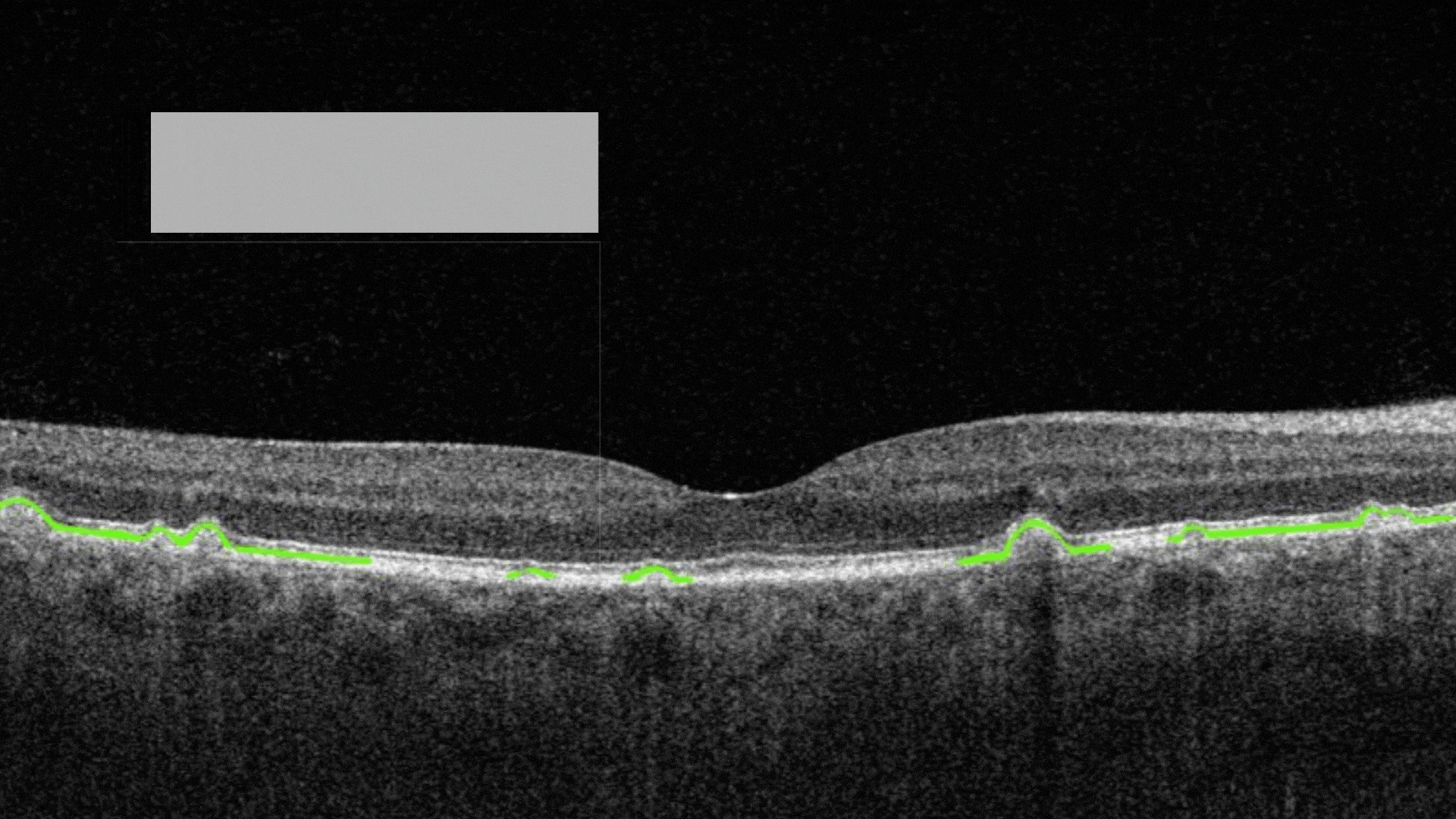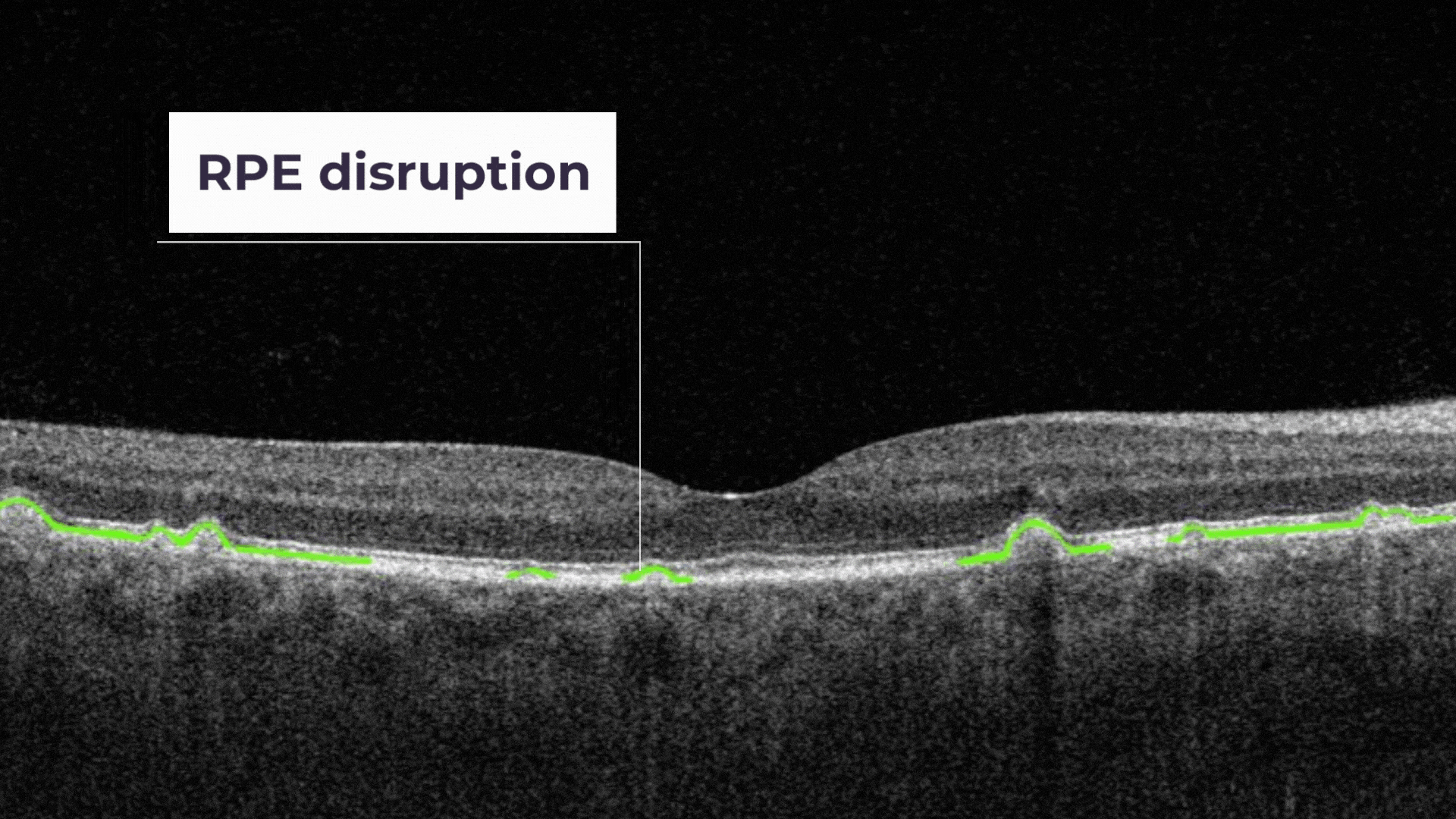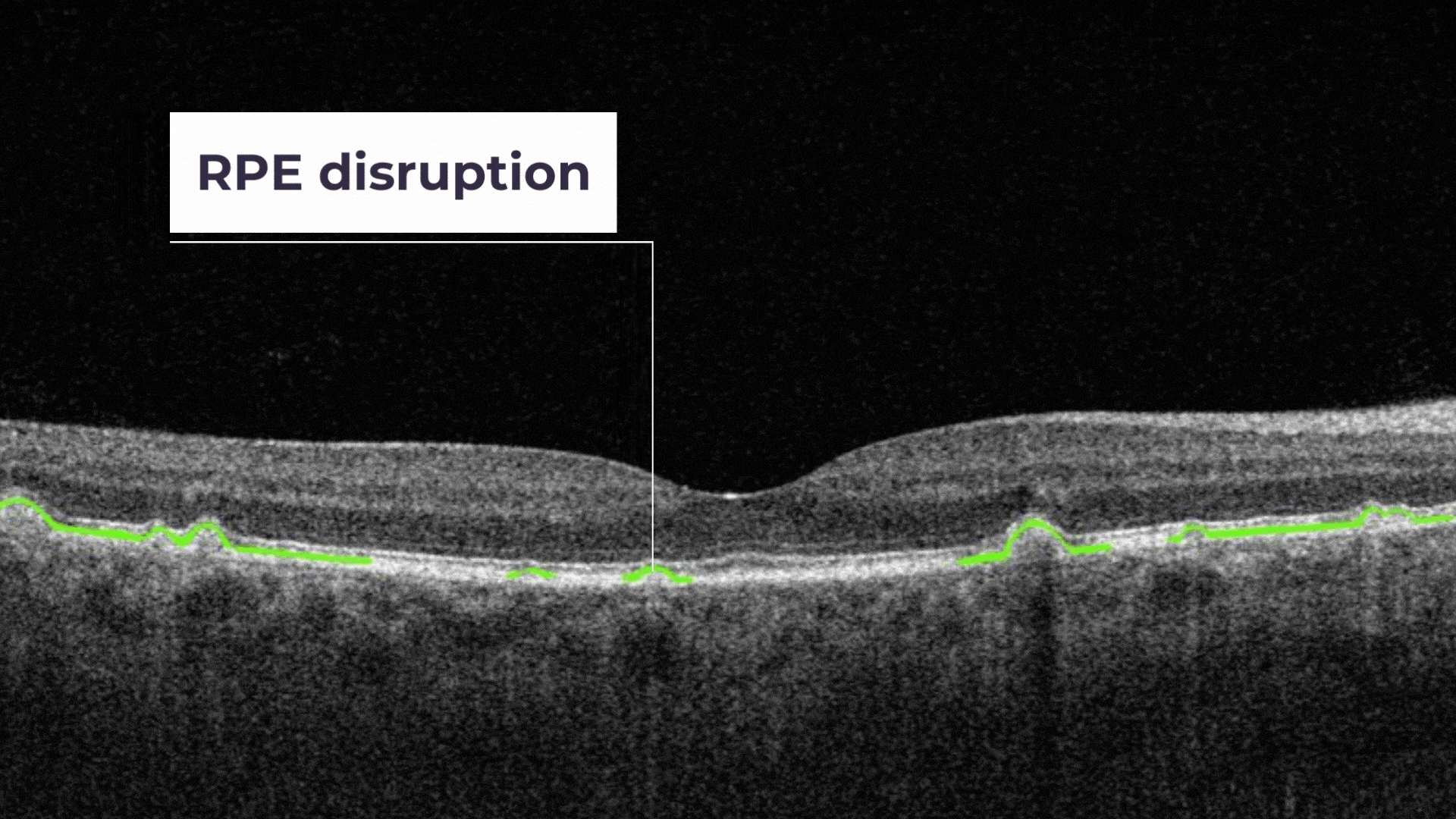
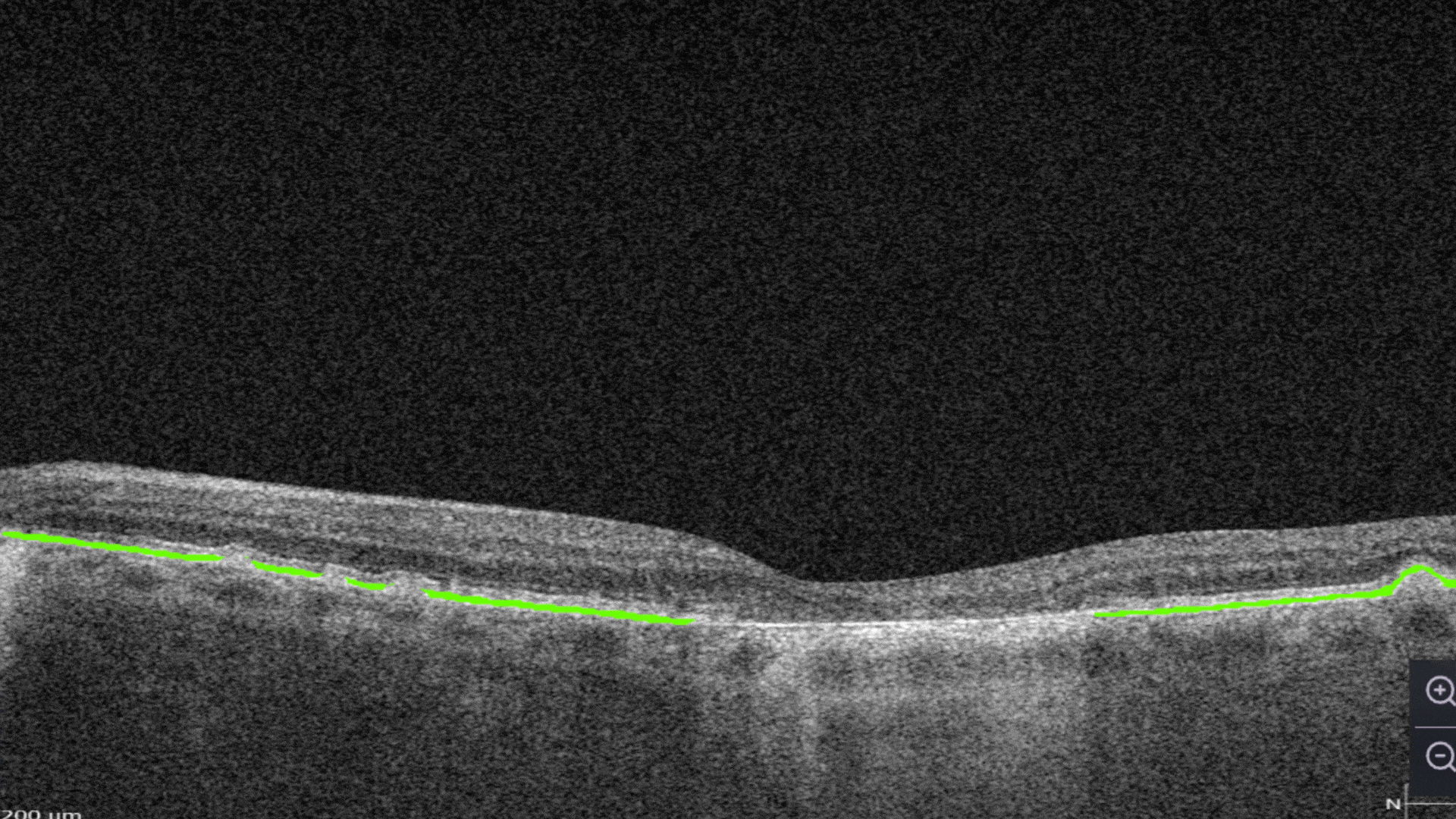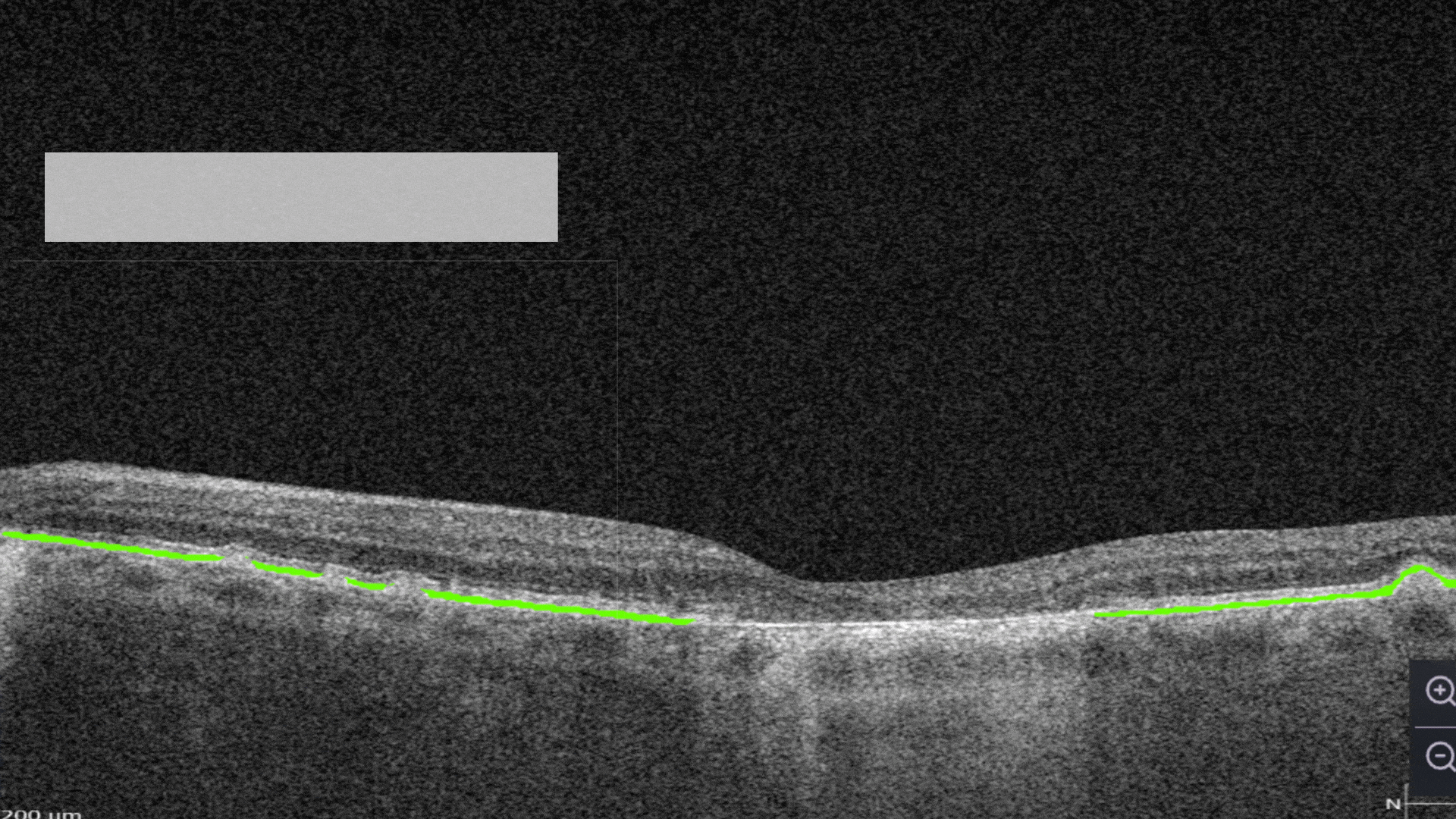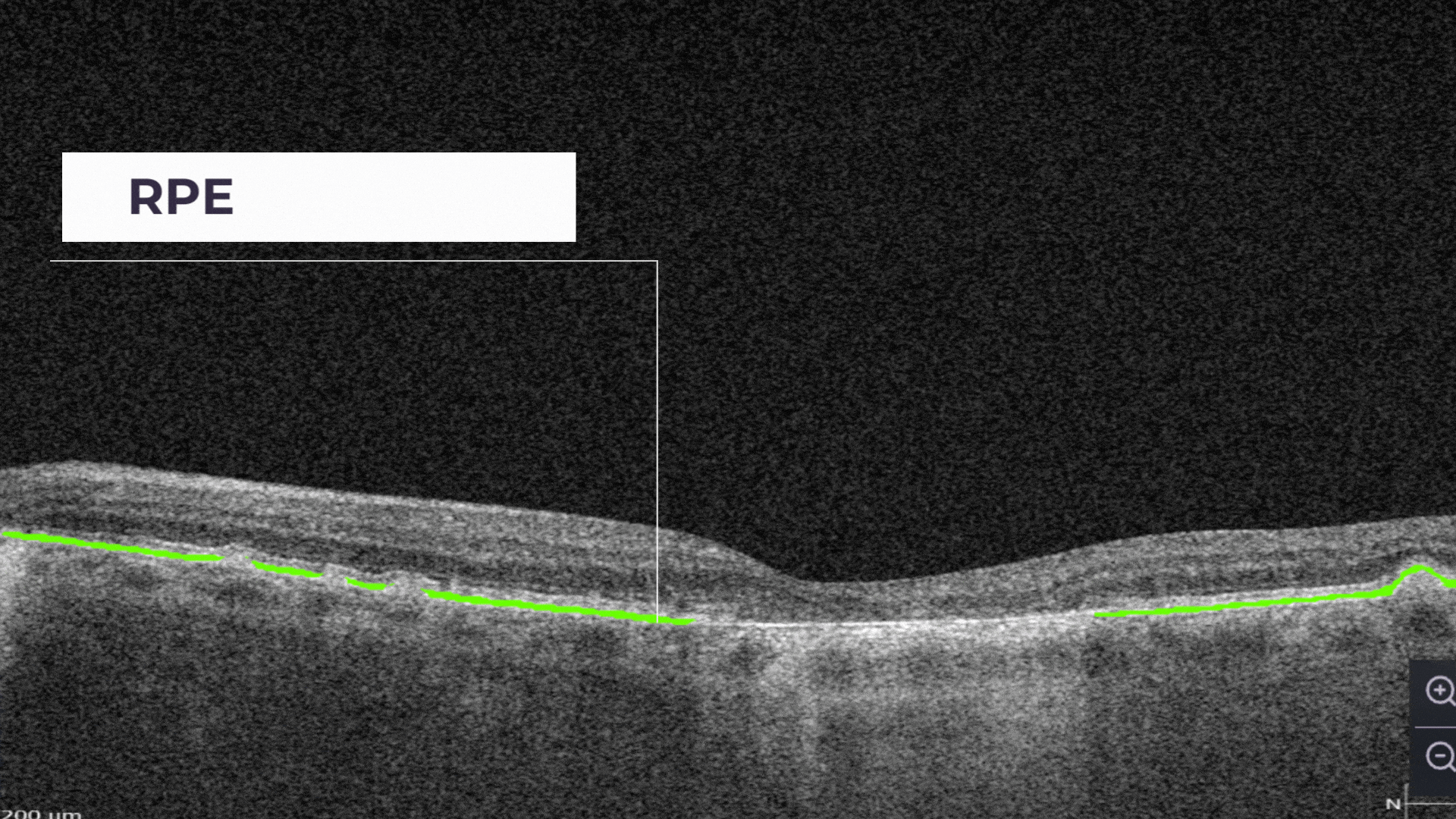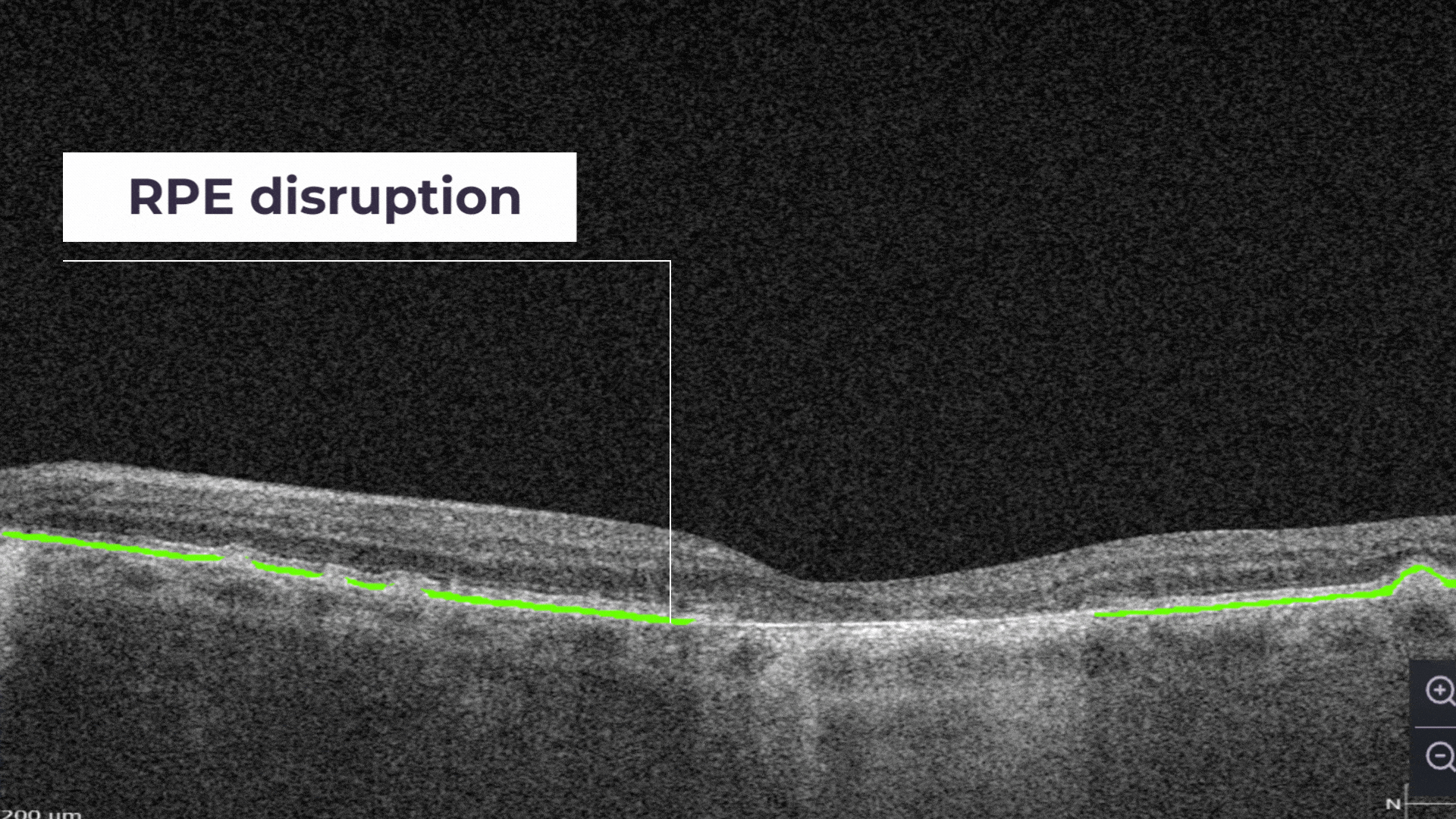
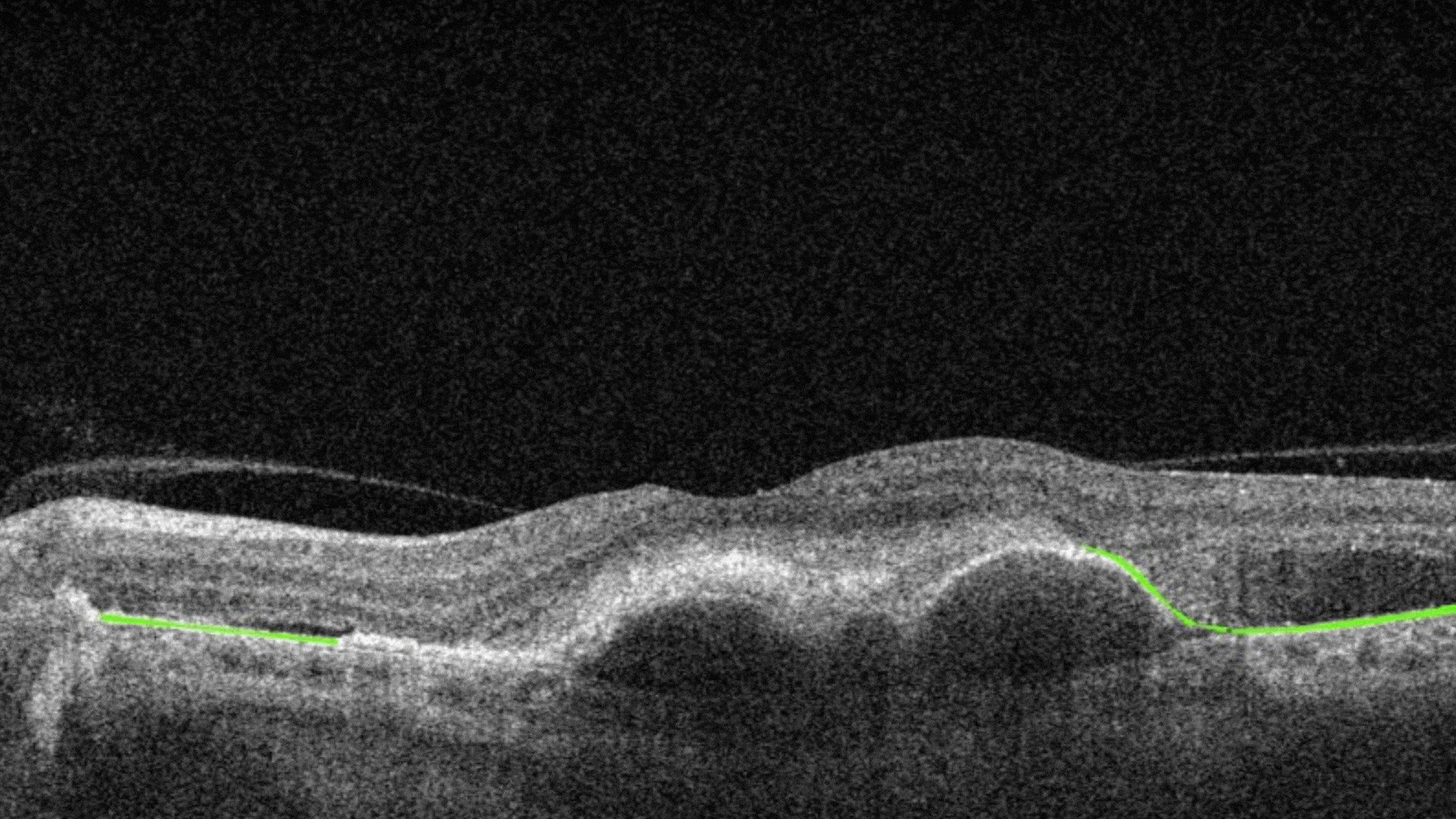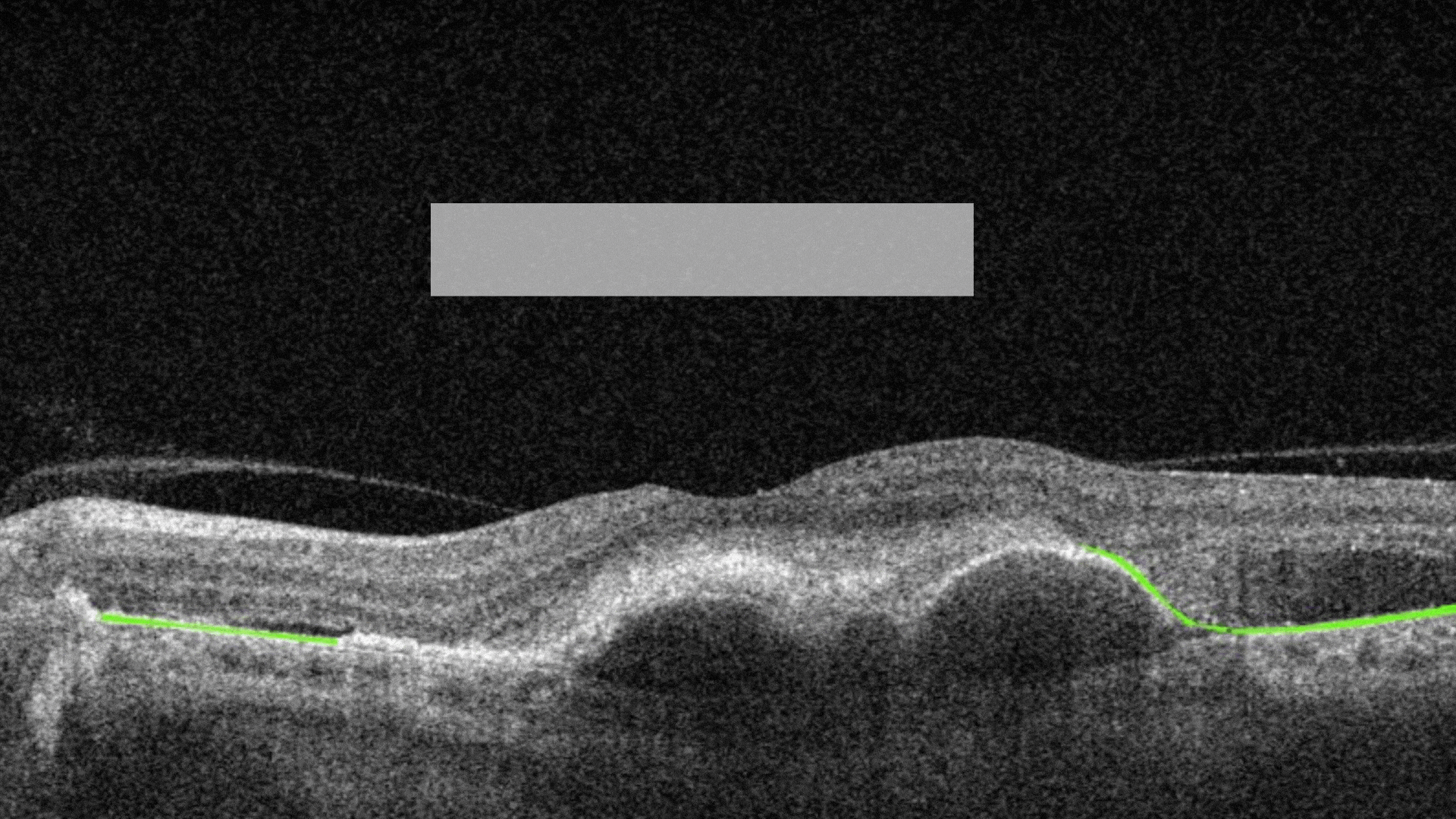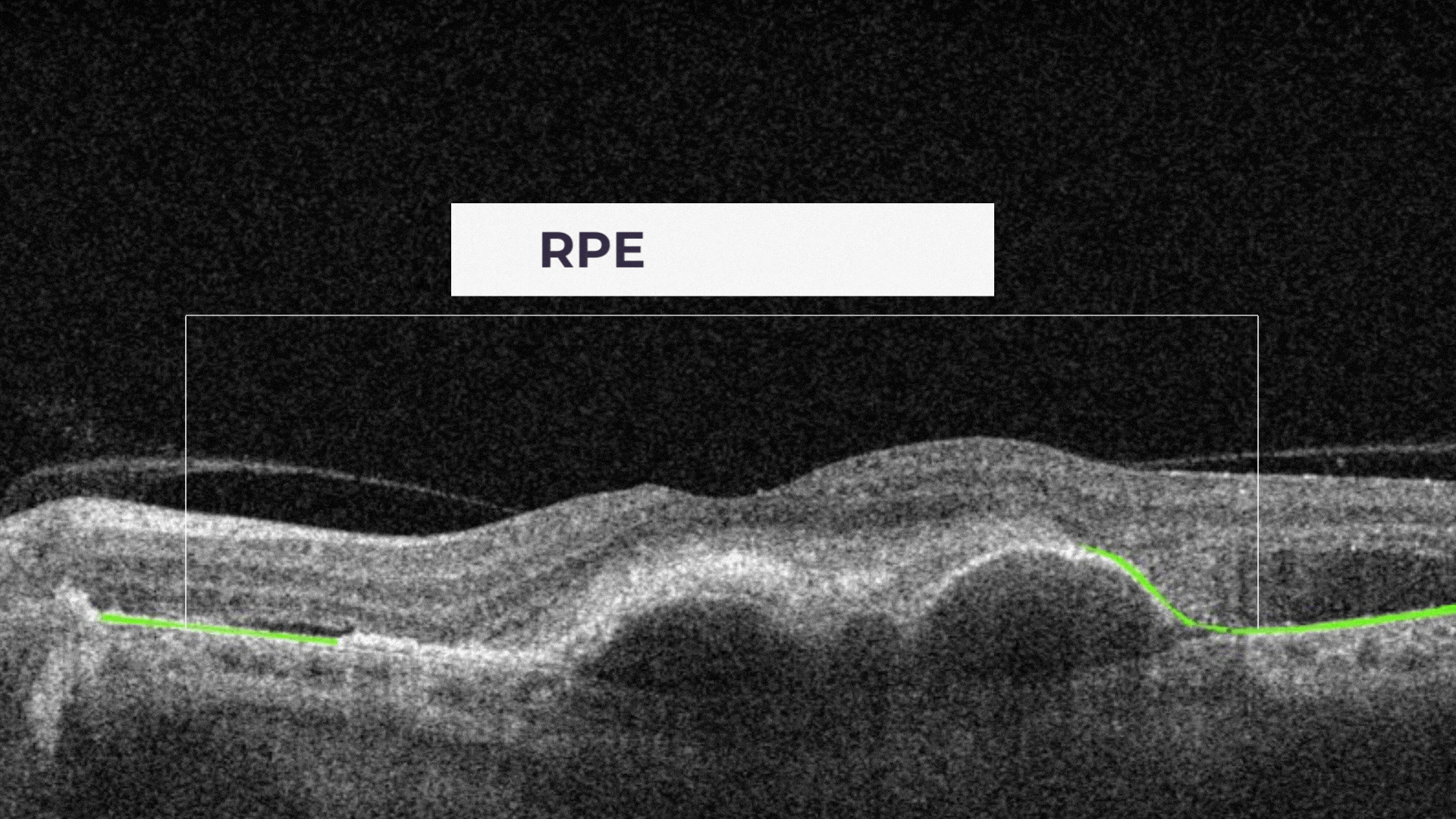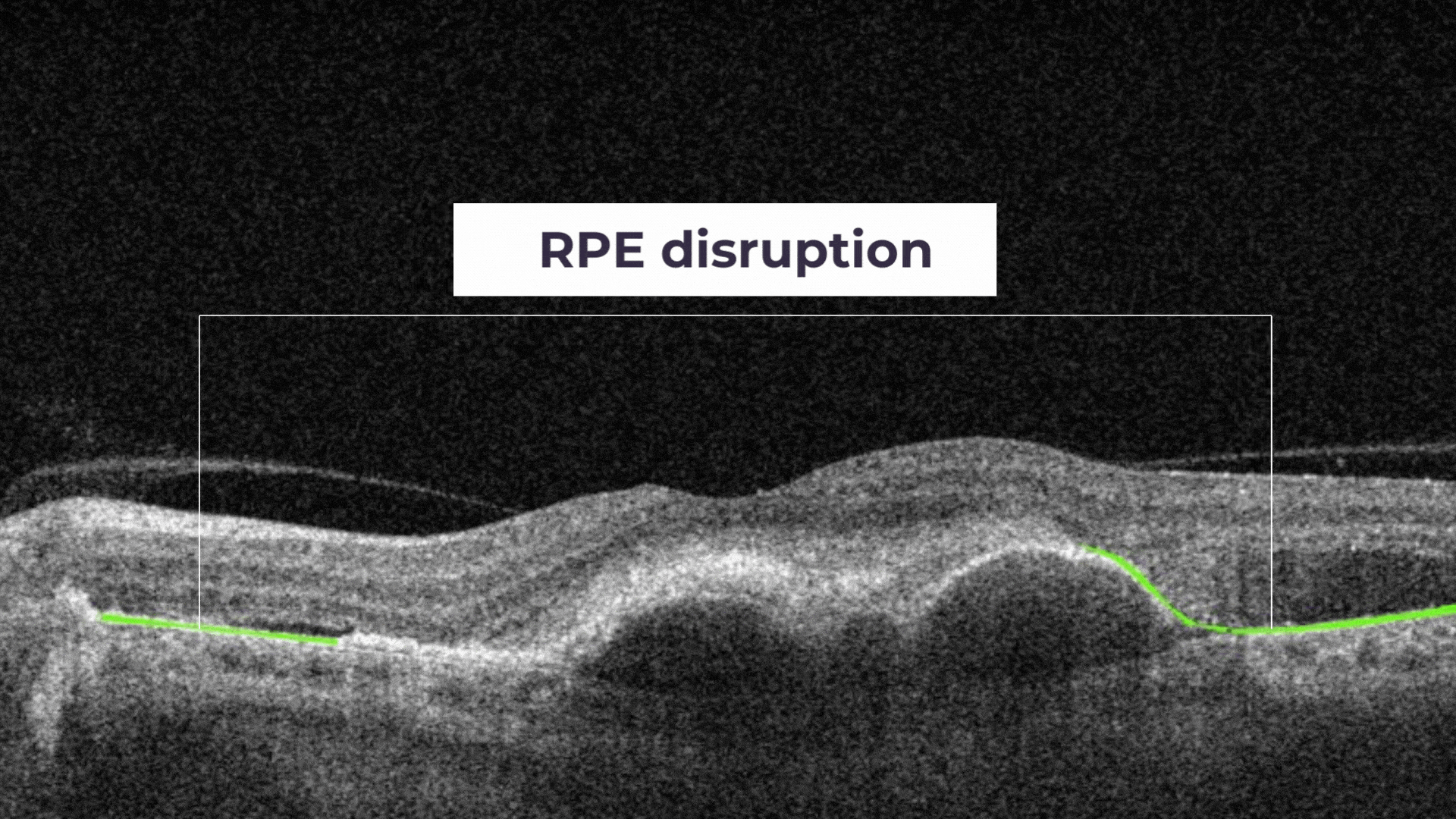
RPE Disruption is the disruption of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium layer
-


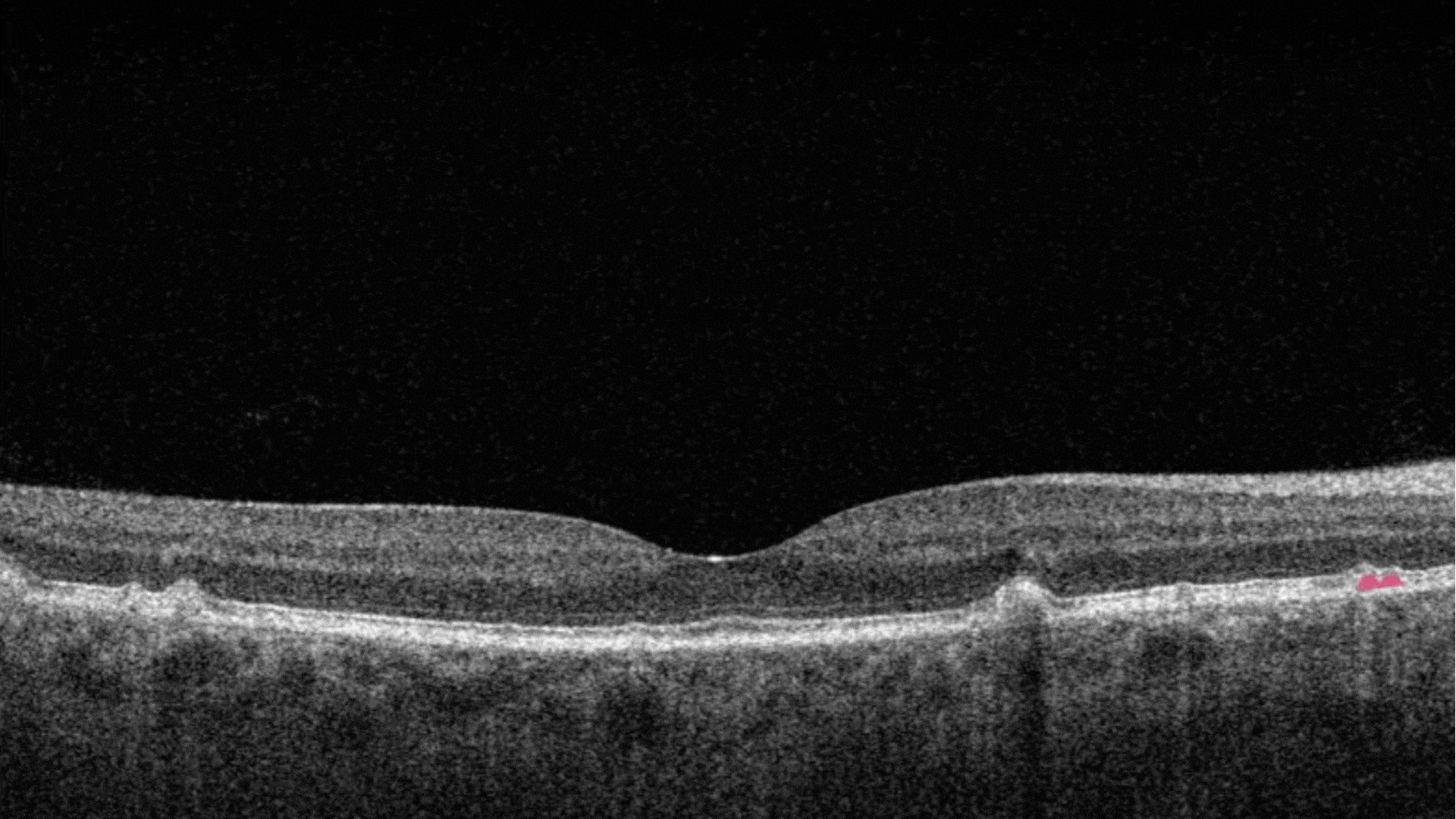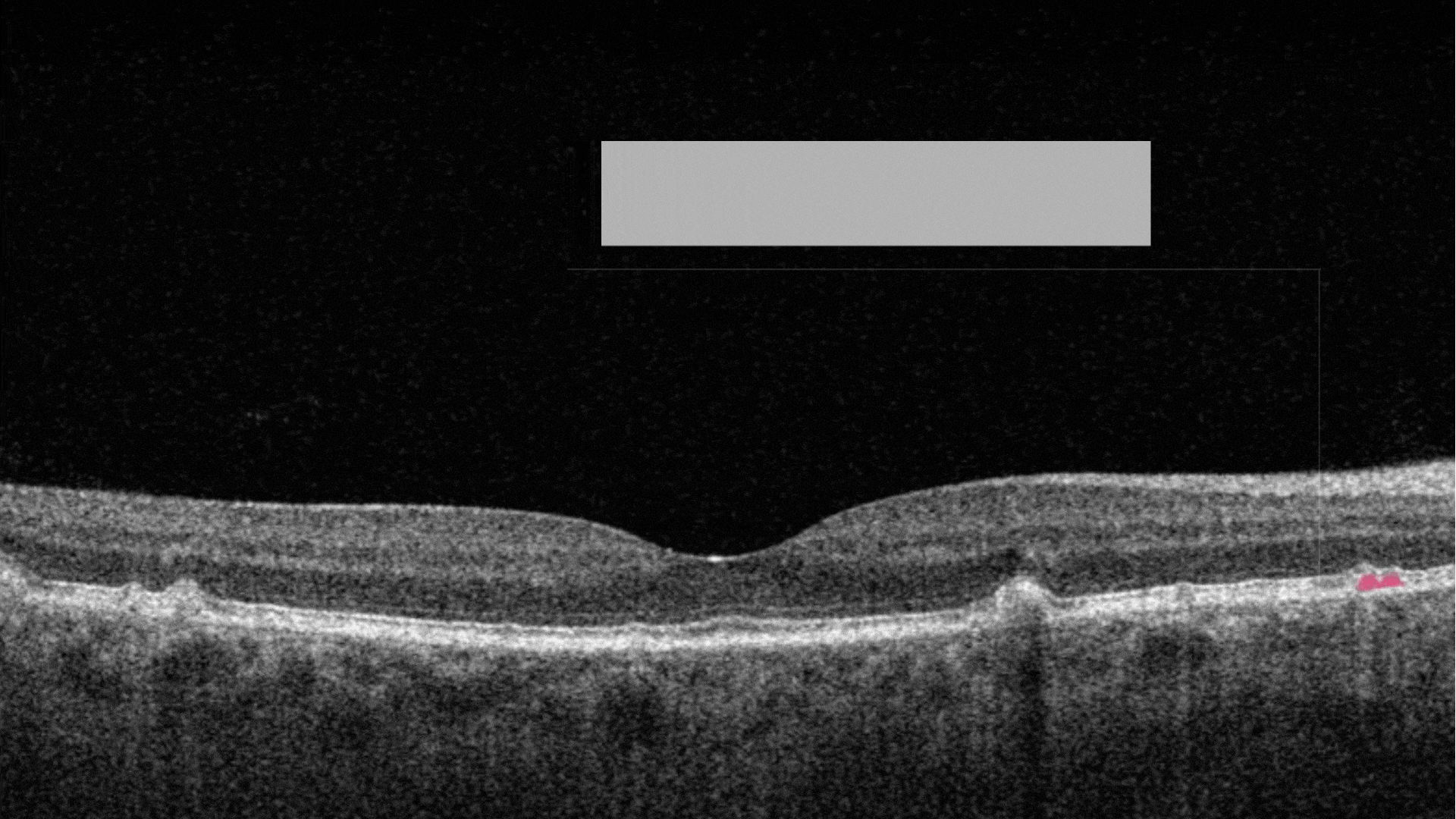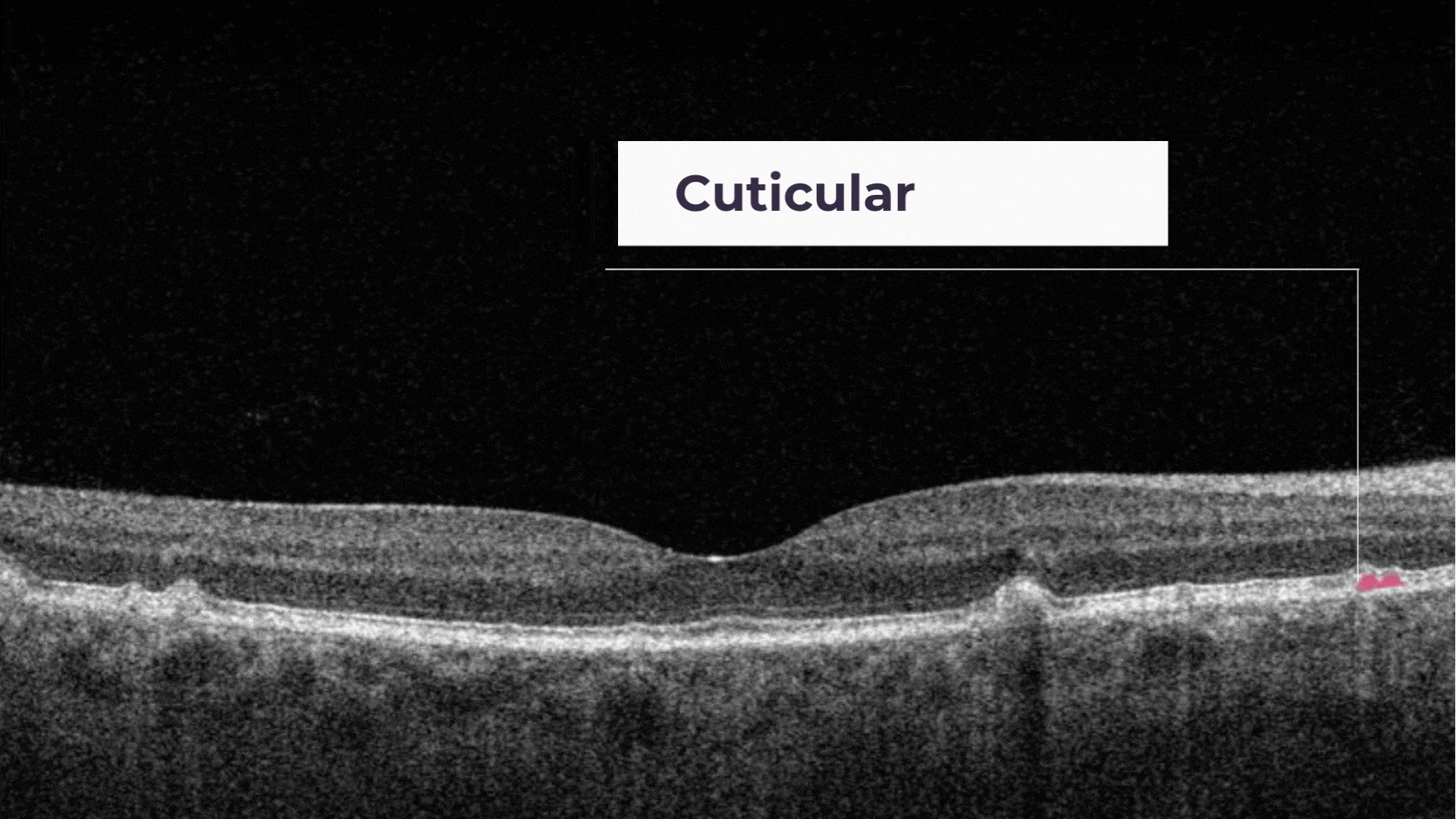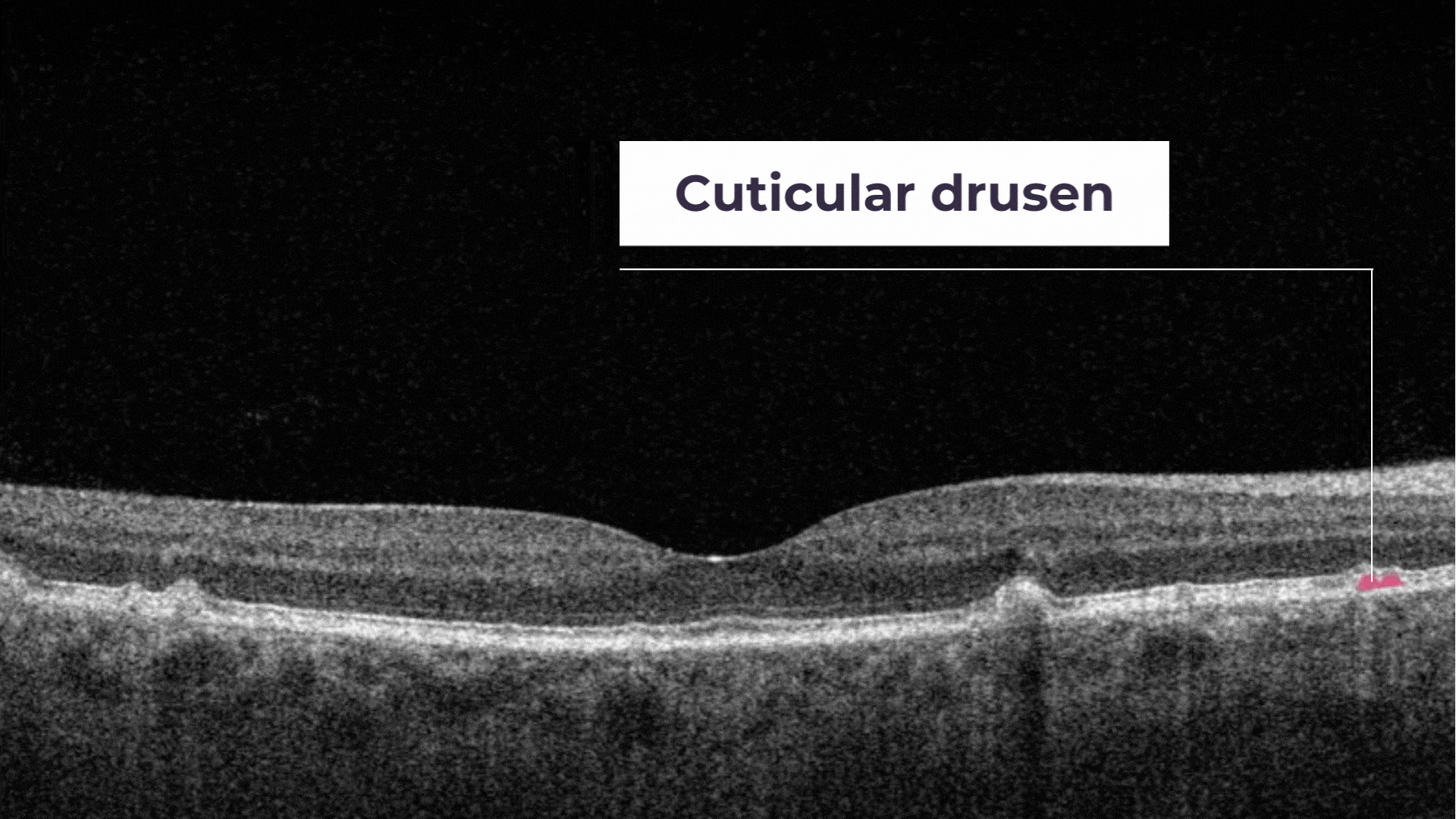
Cuticular drusen are small with steep sides and contain dense hyalinized contents that are identical to small, hard drusen.
-


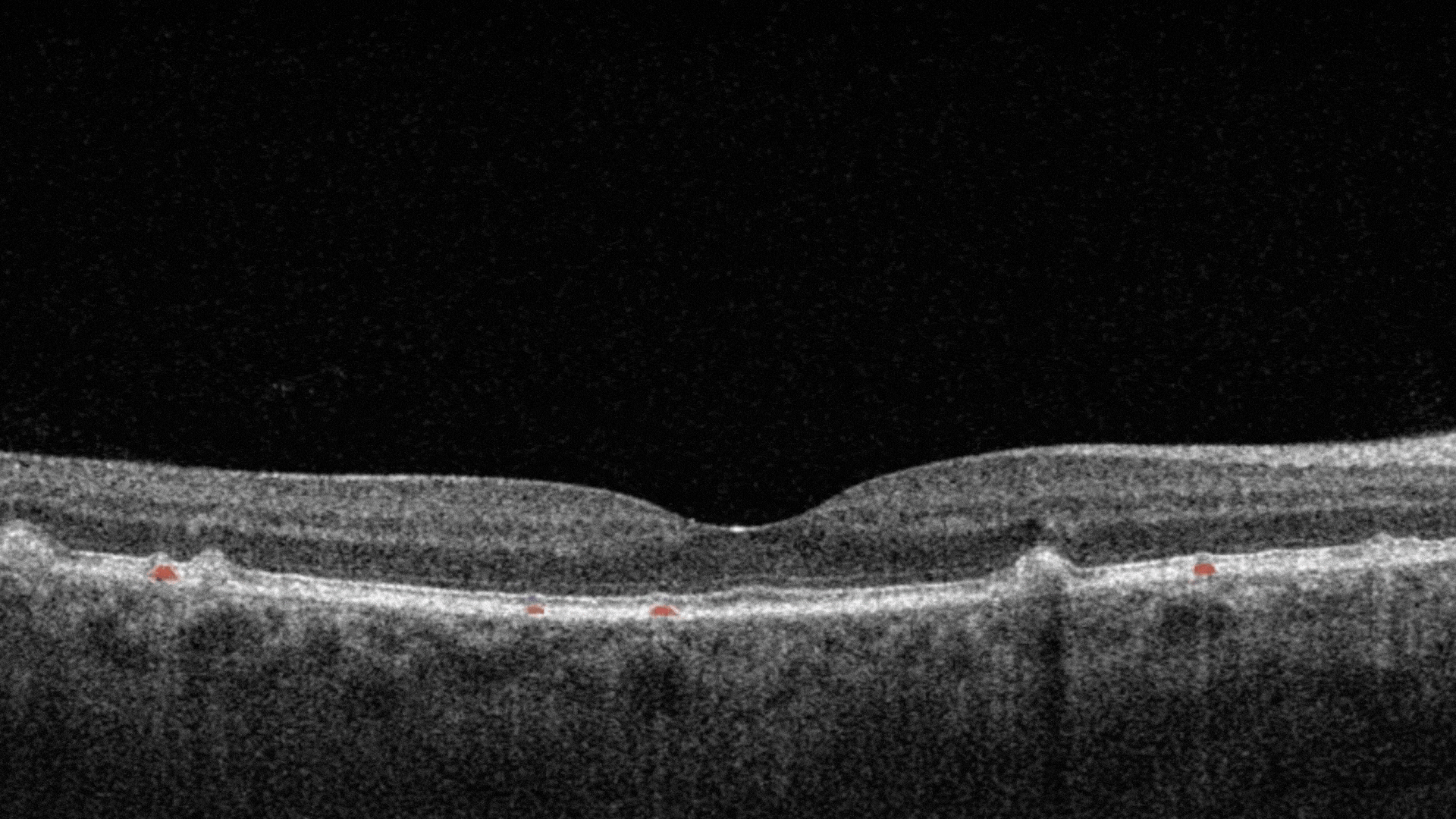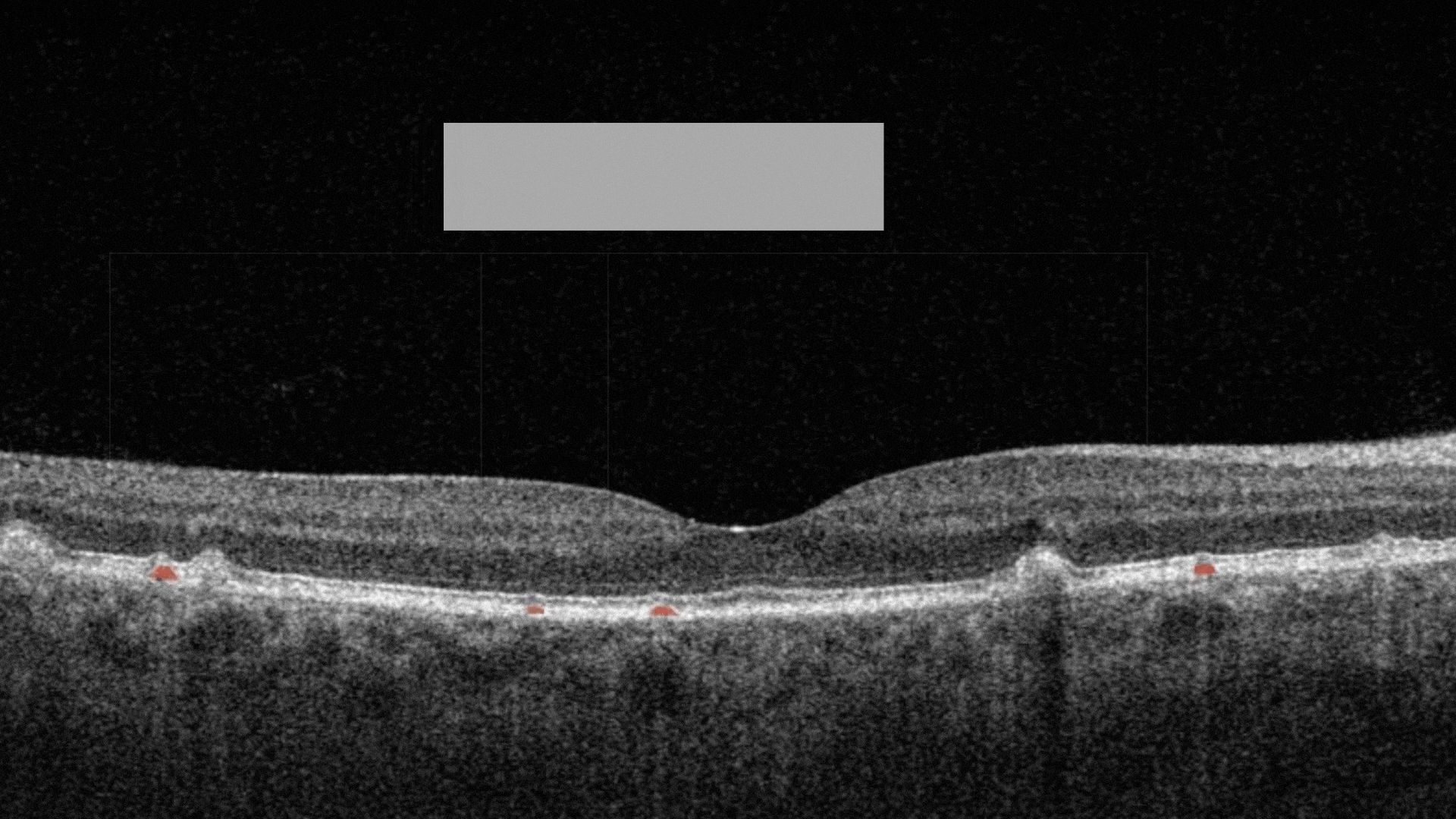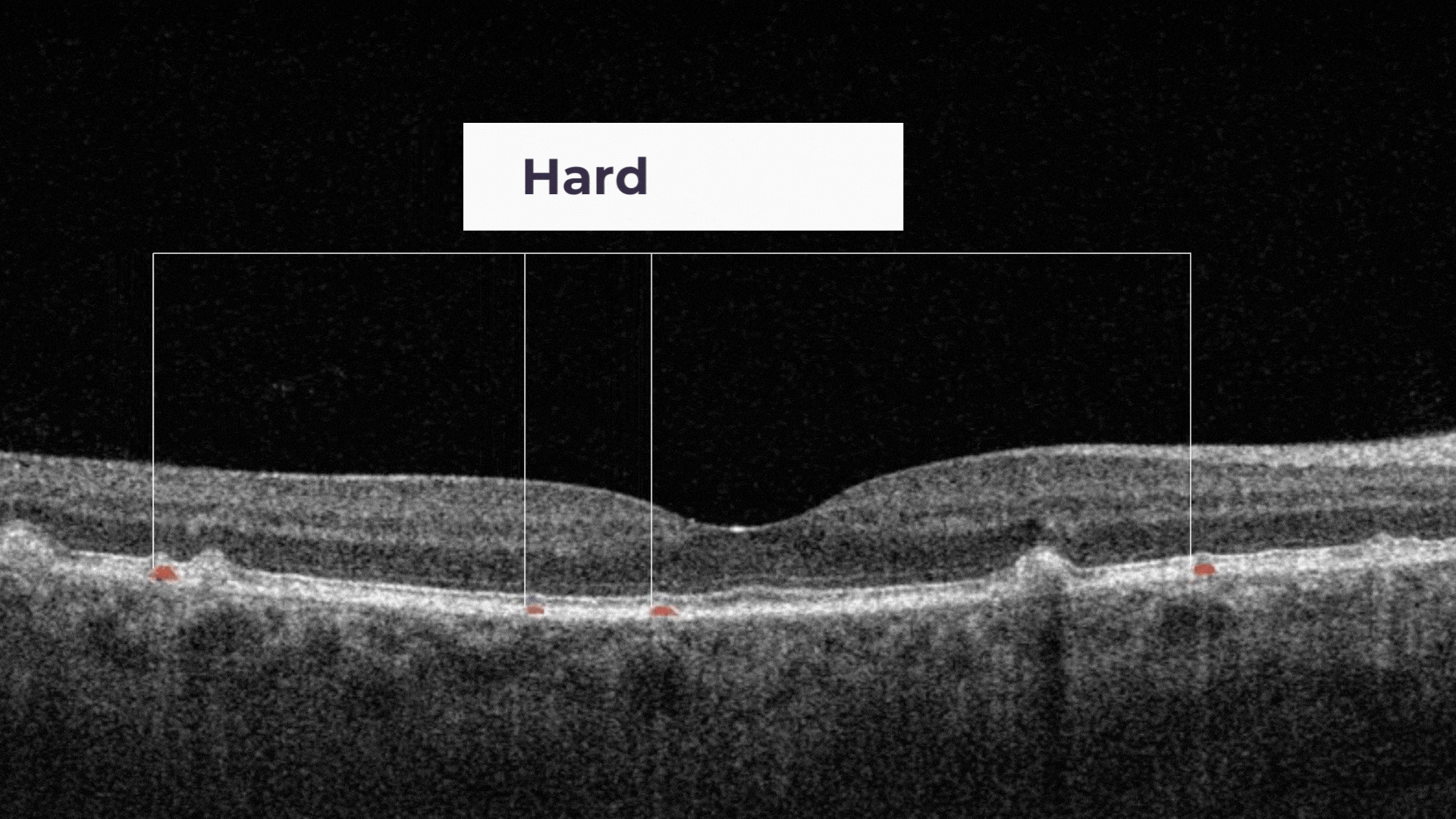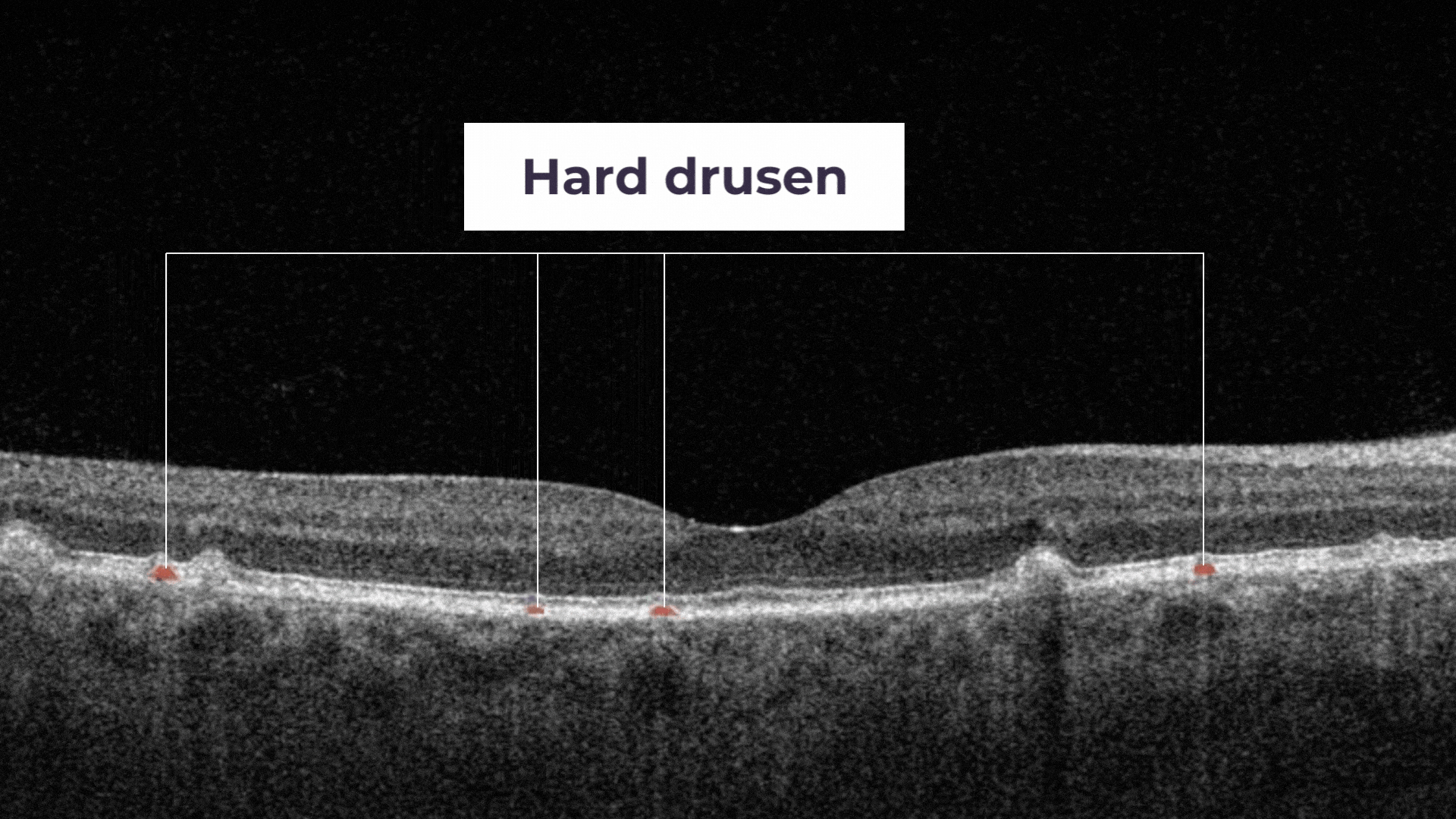
Hard drusen are small, and indicate lower risk of future vision loss.
-


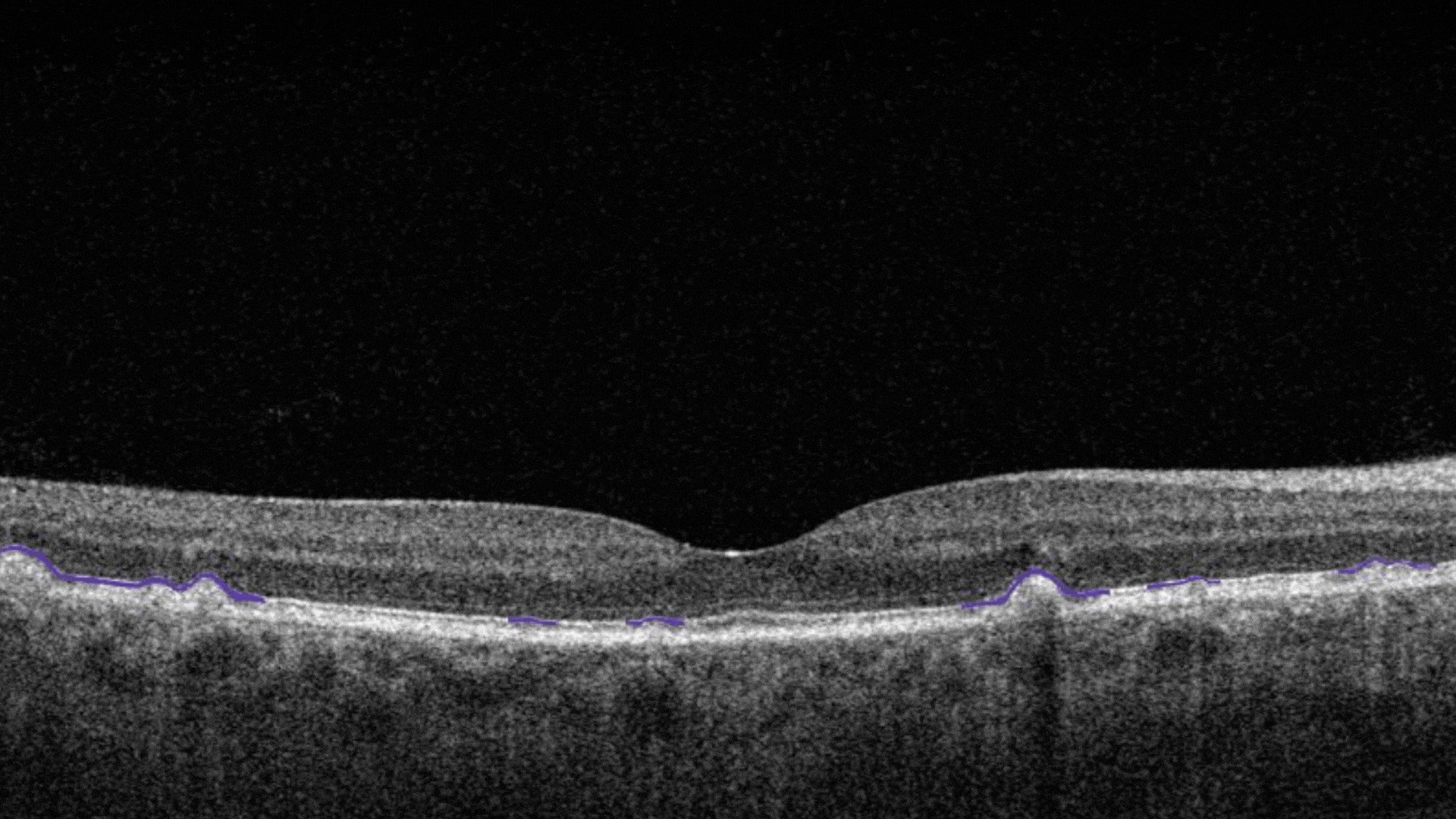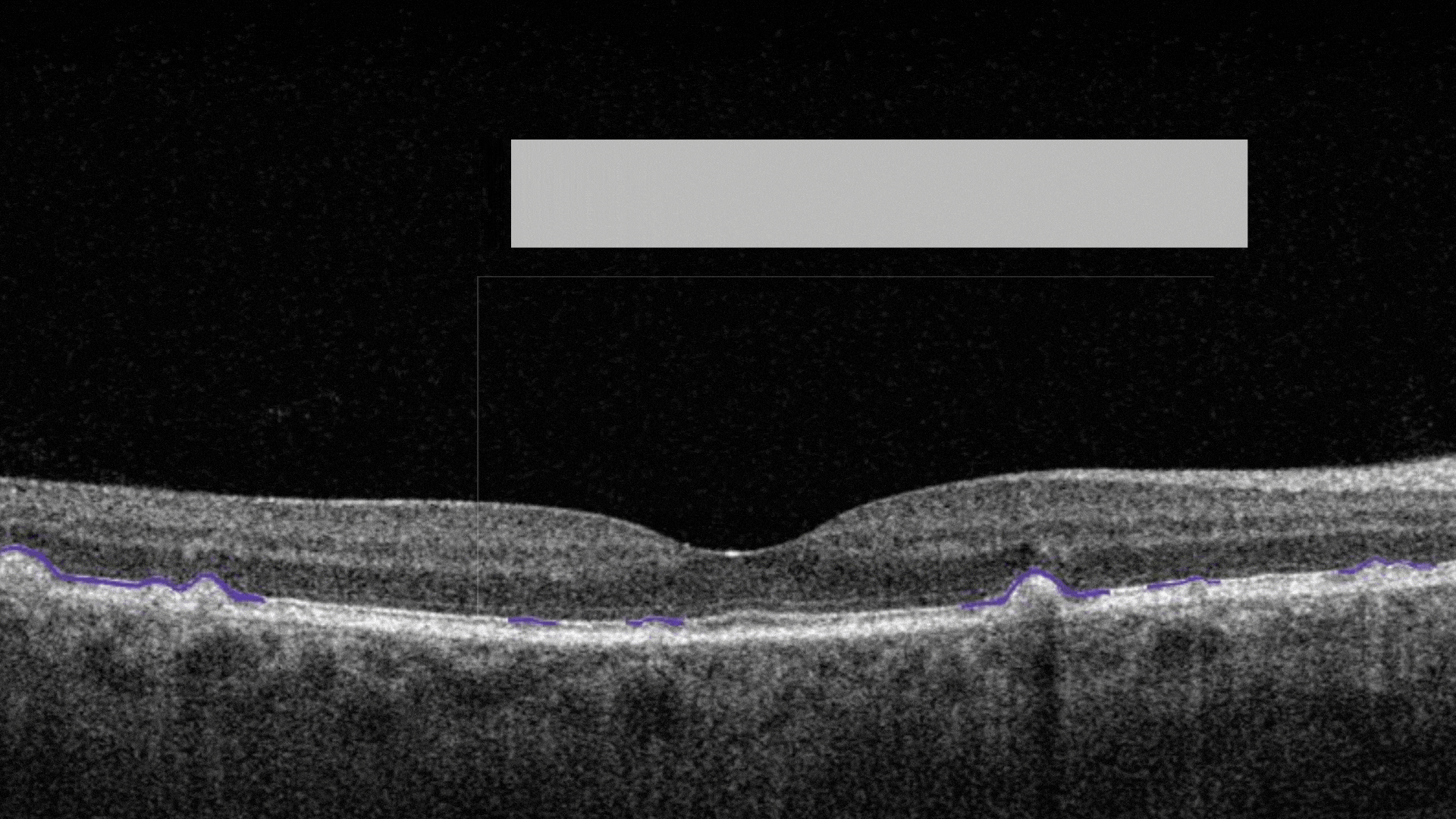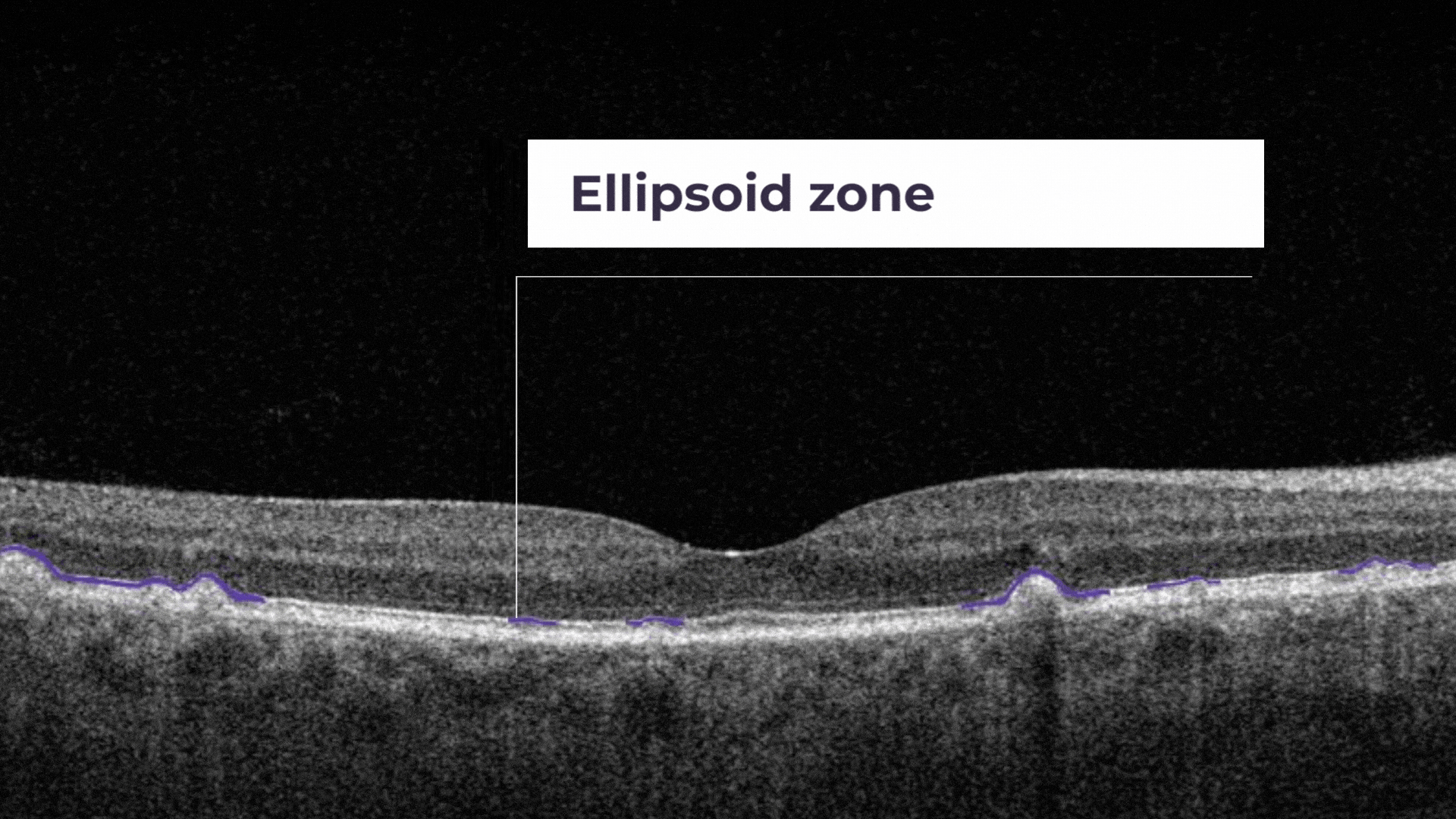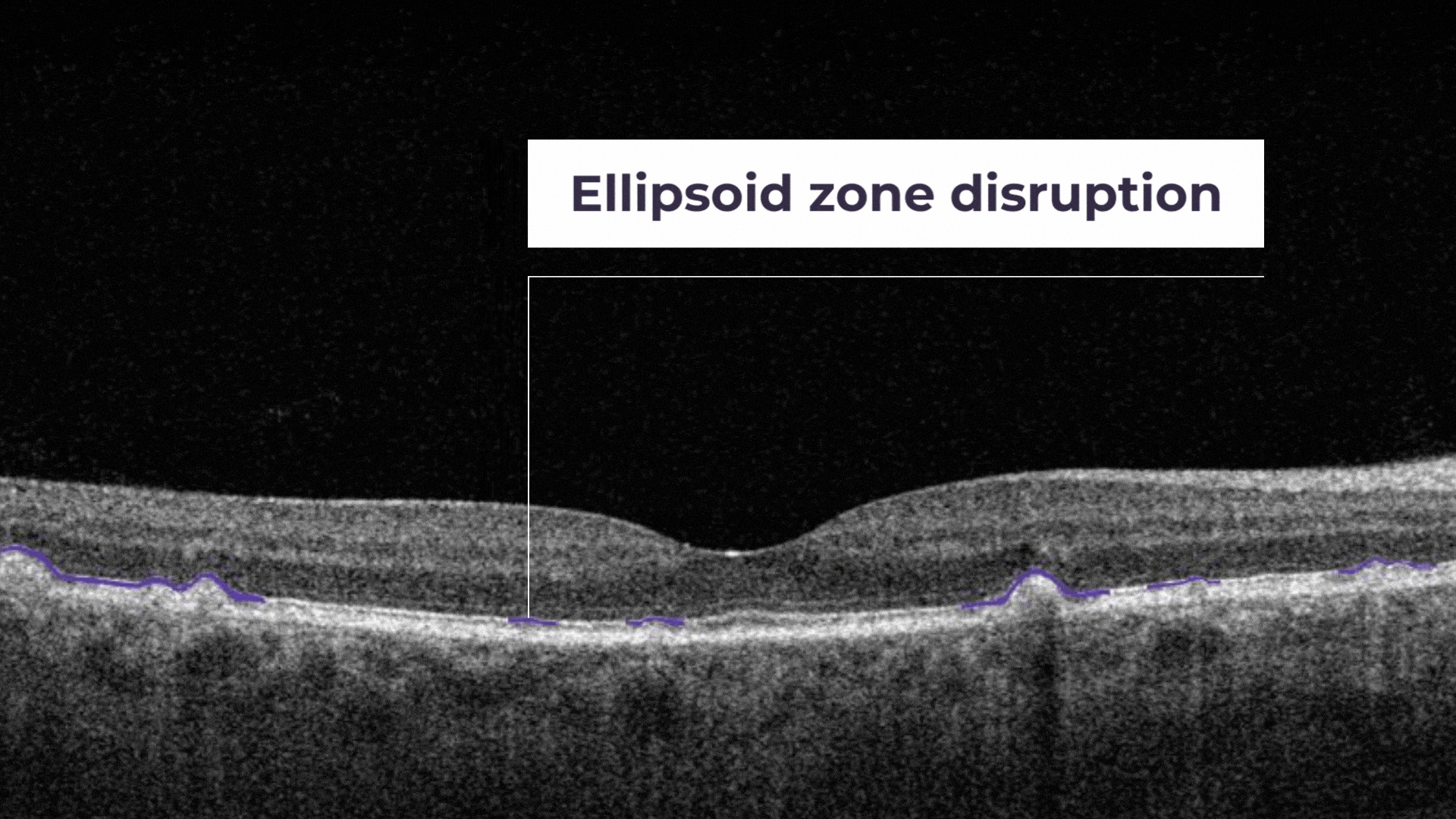
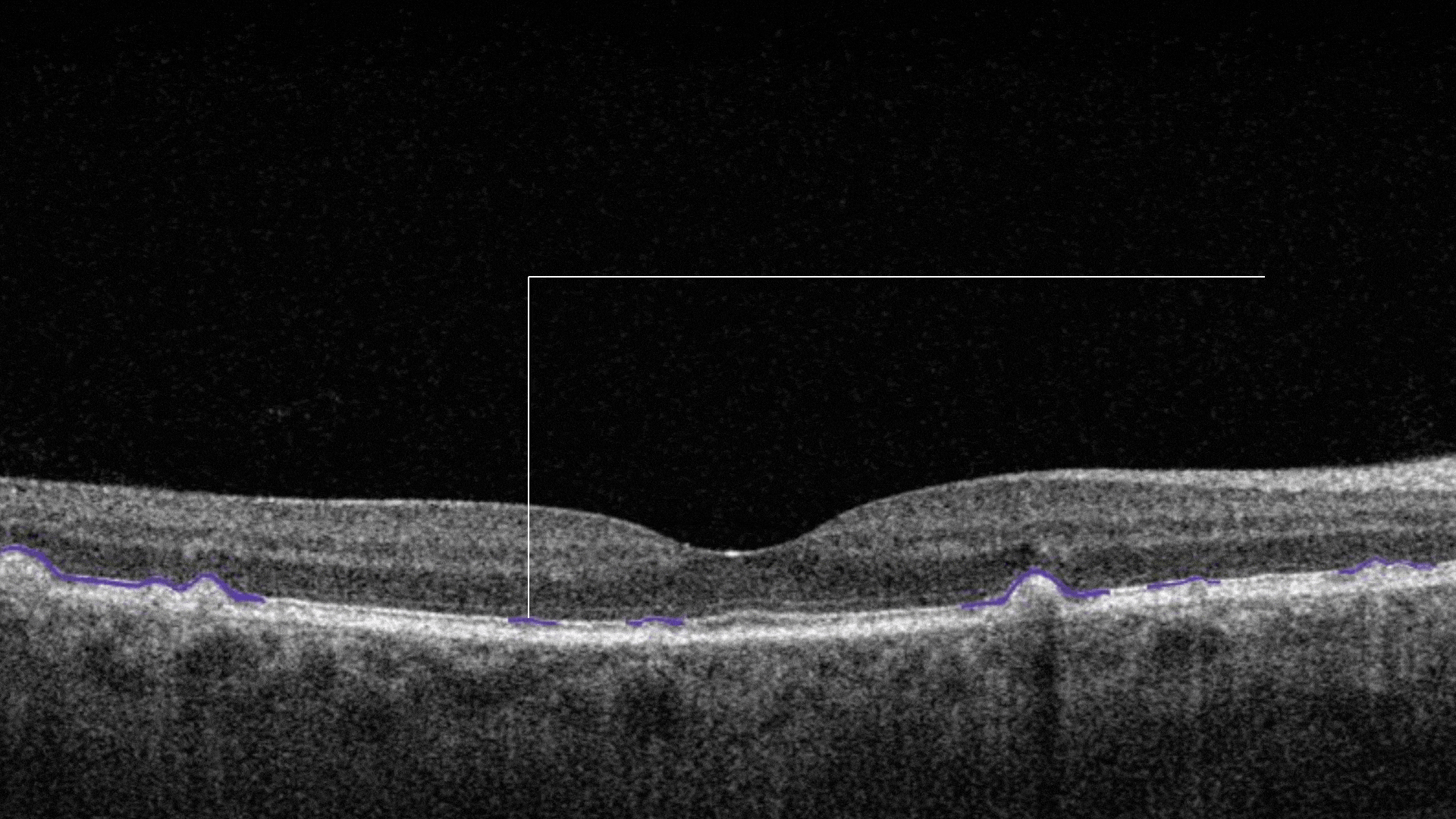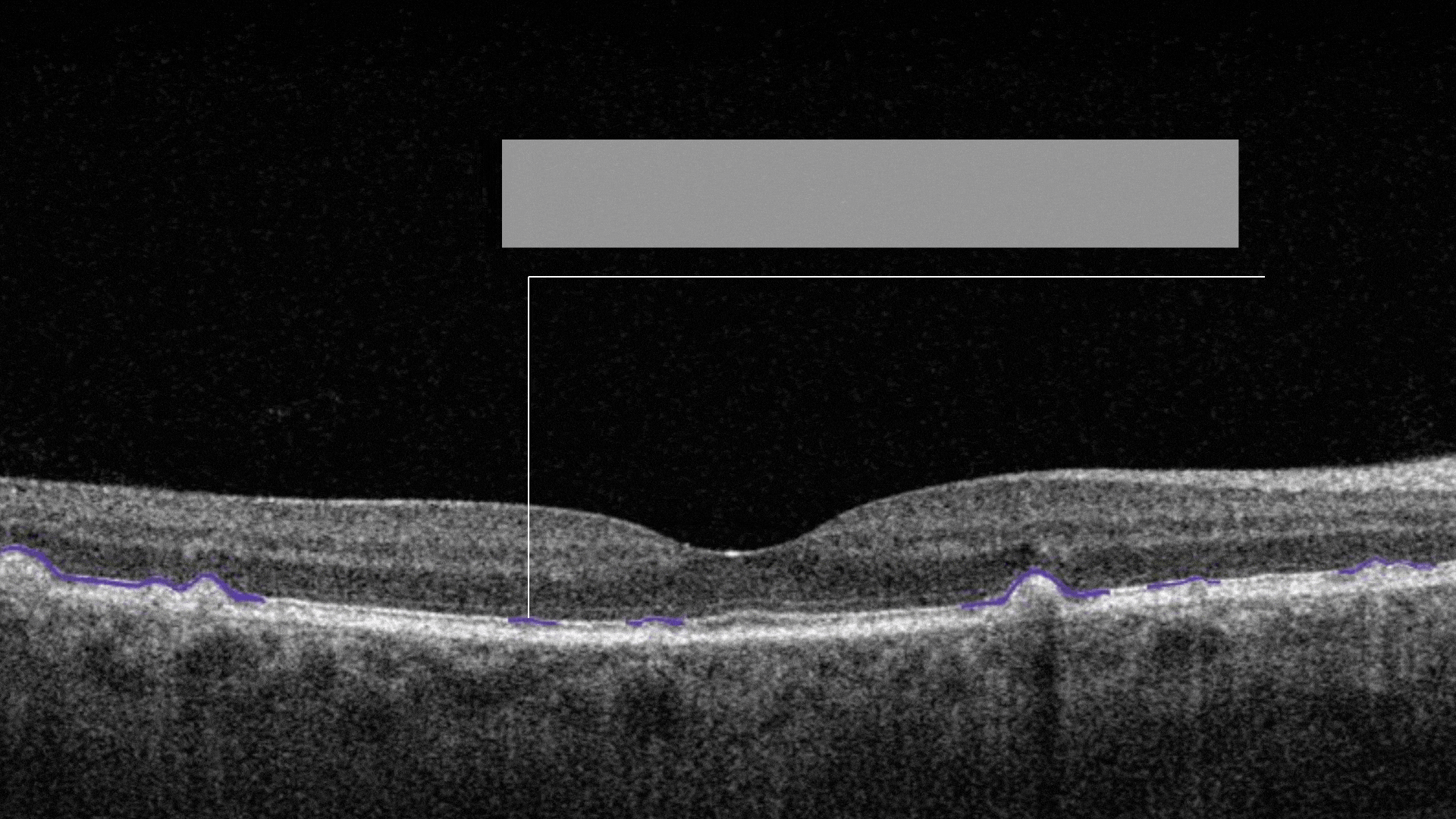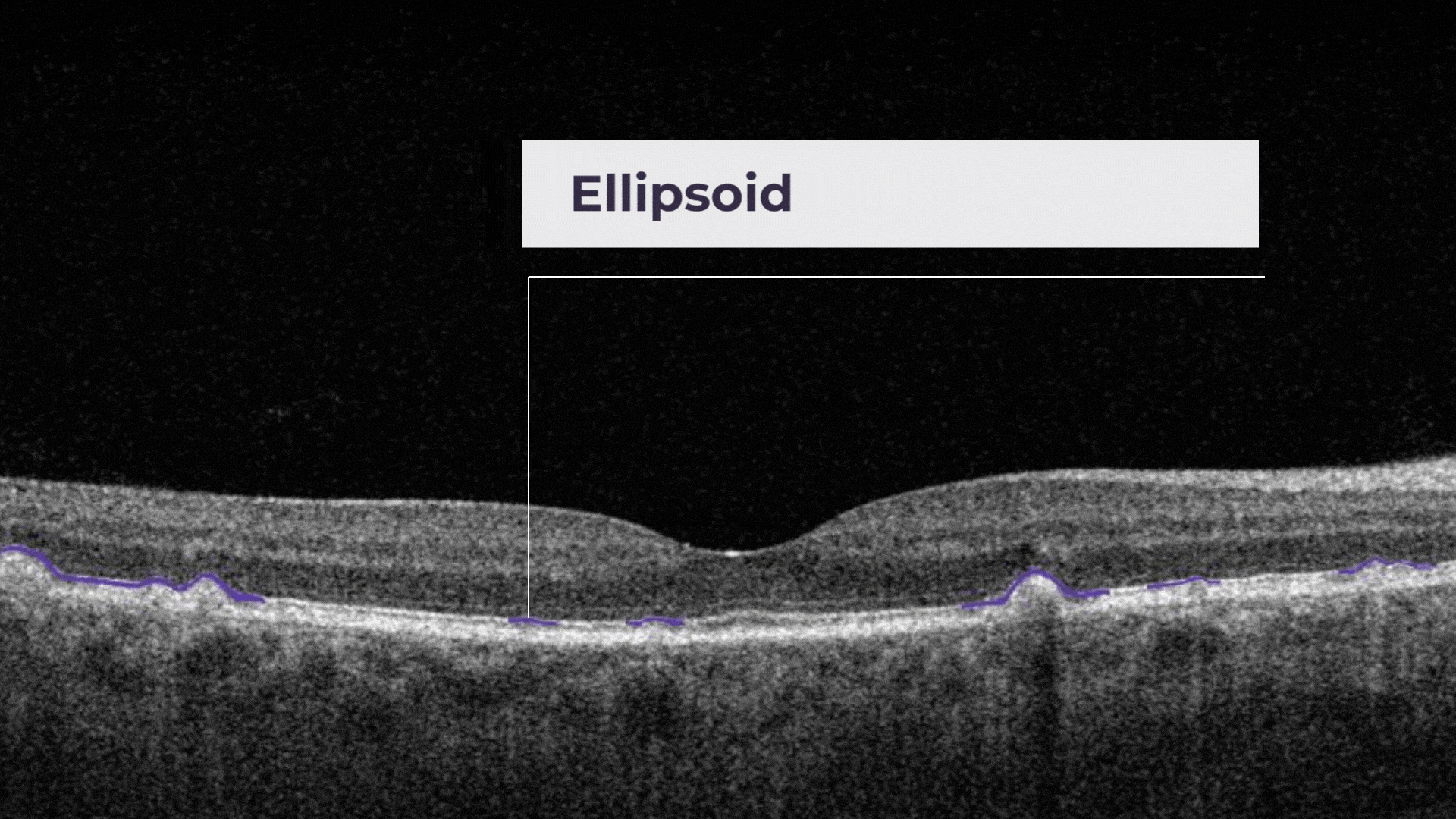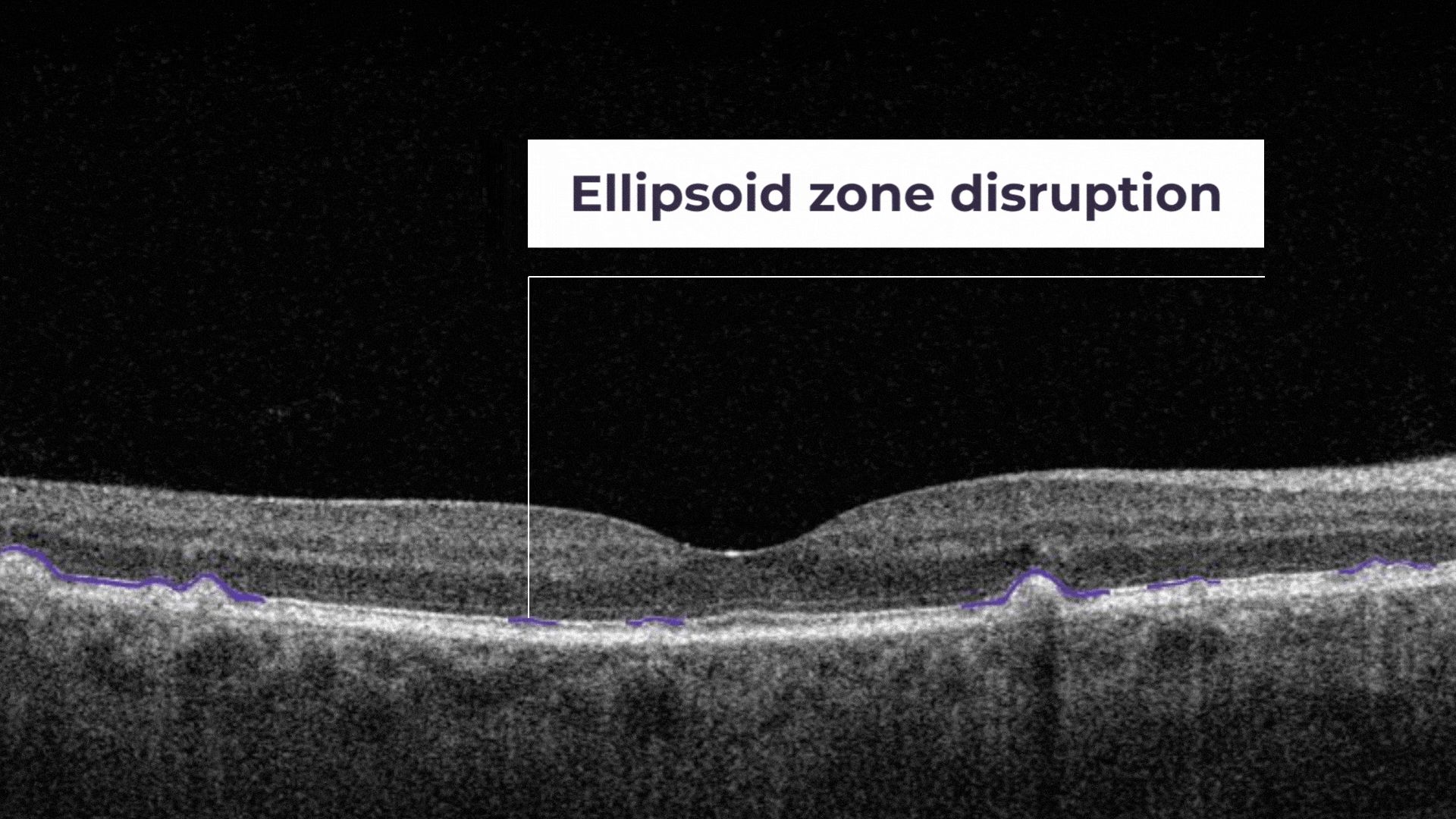
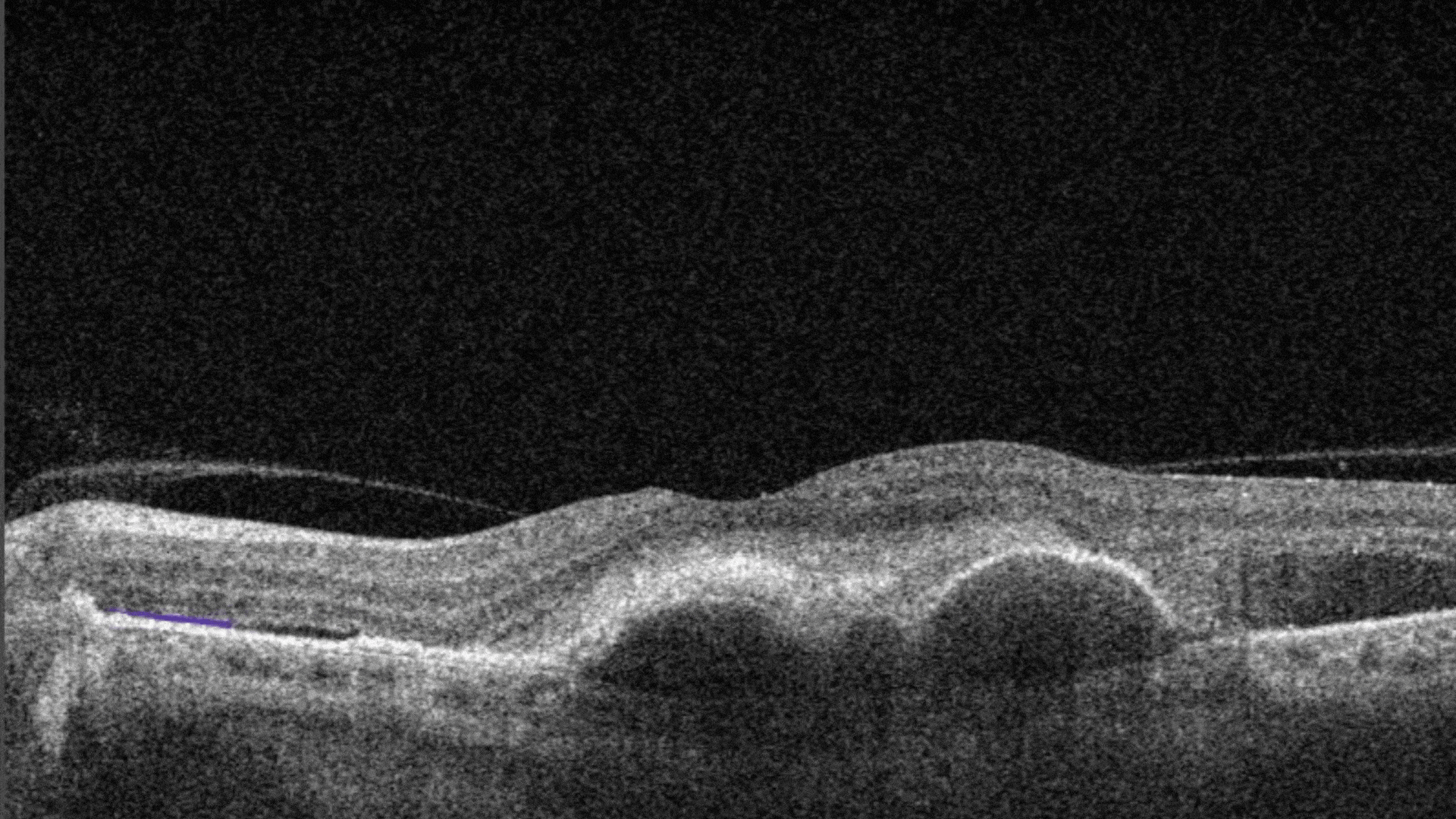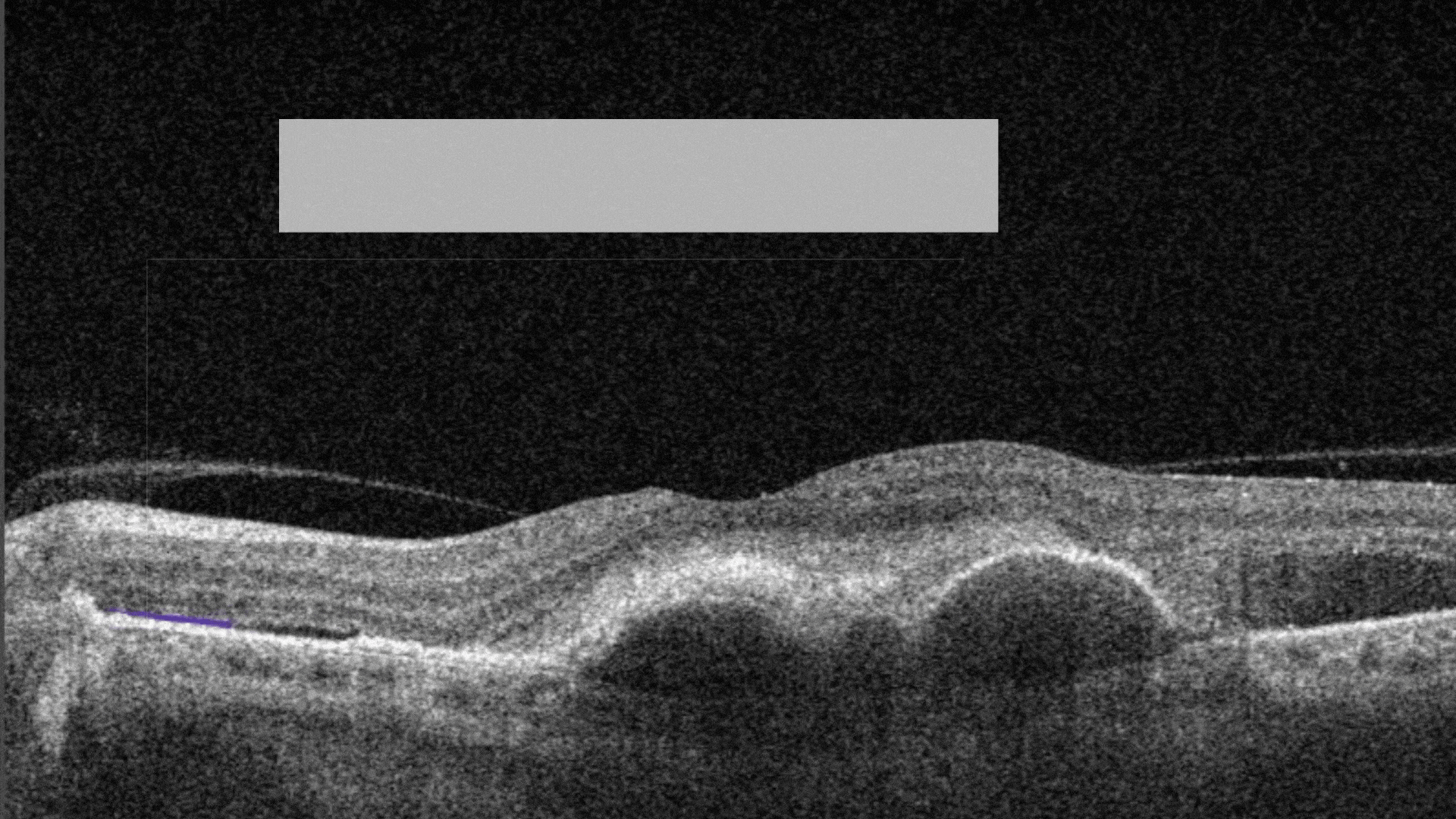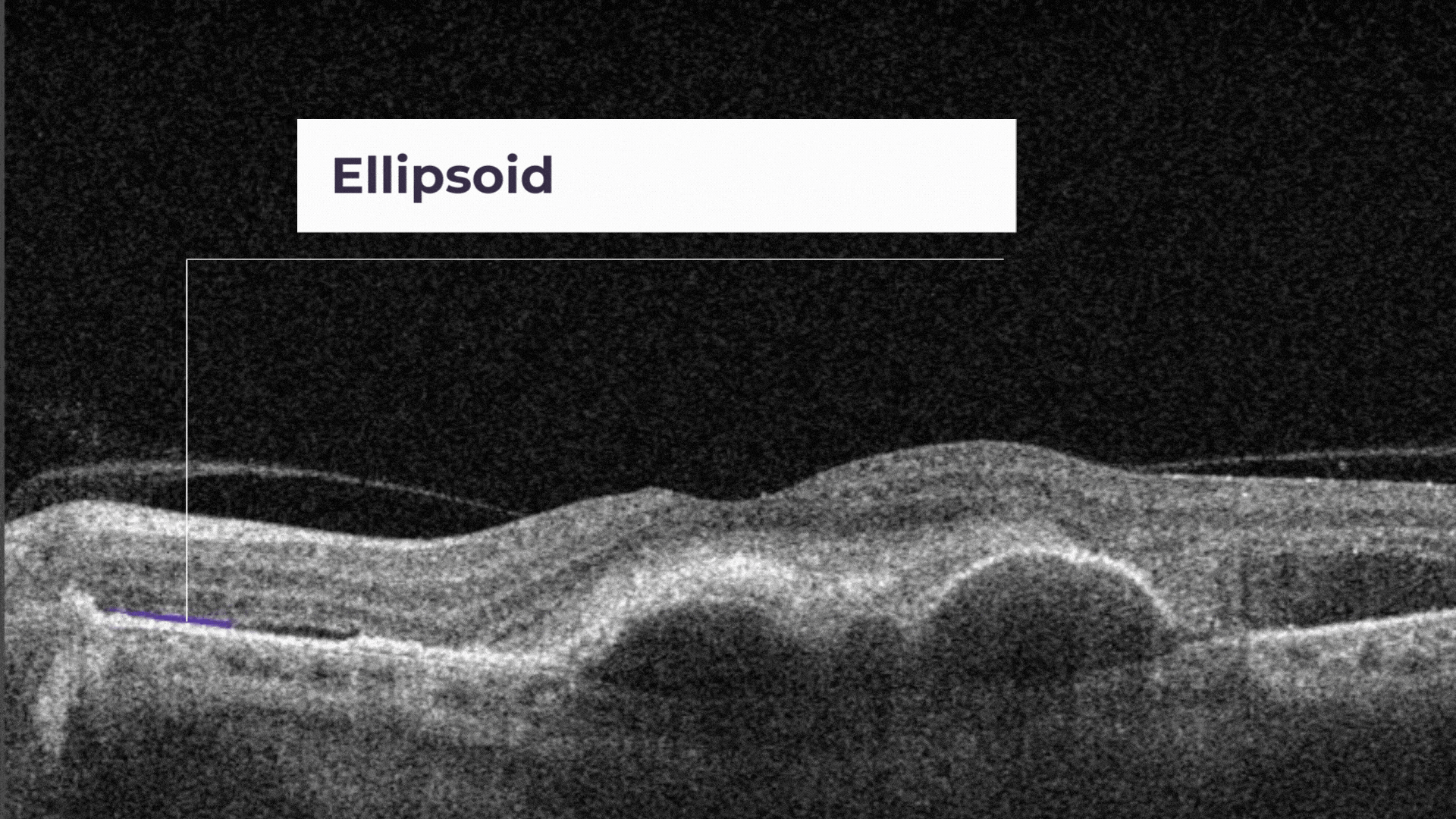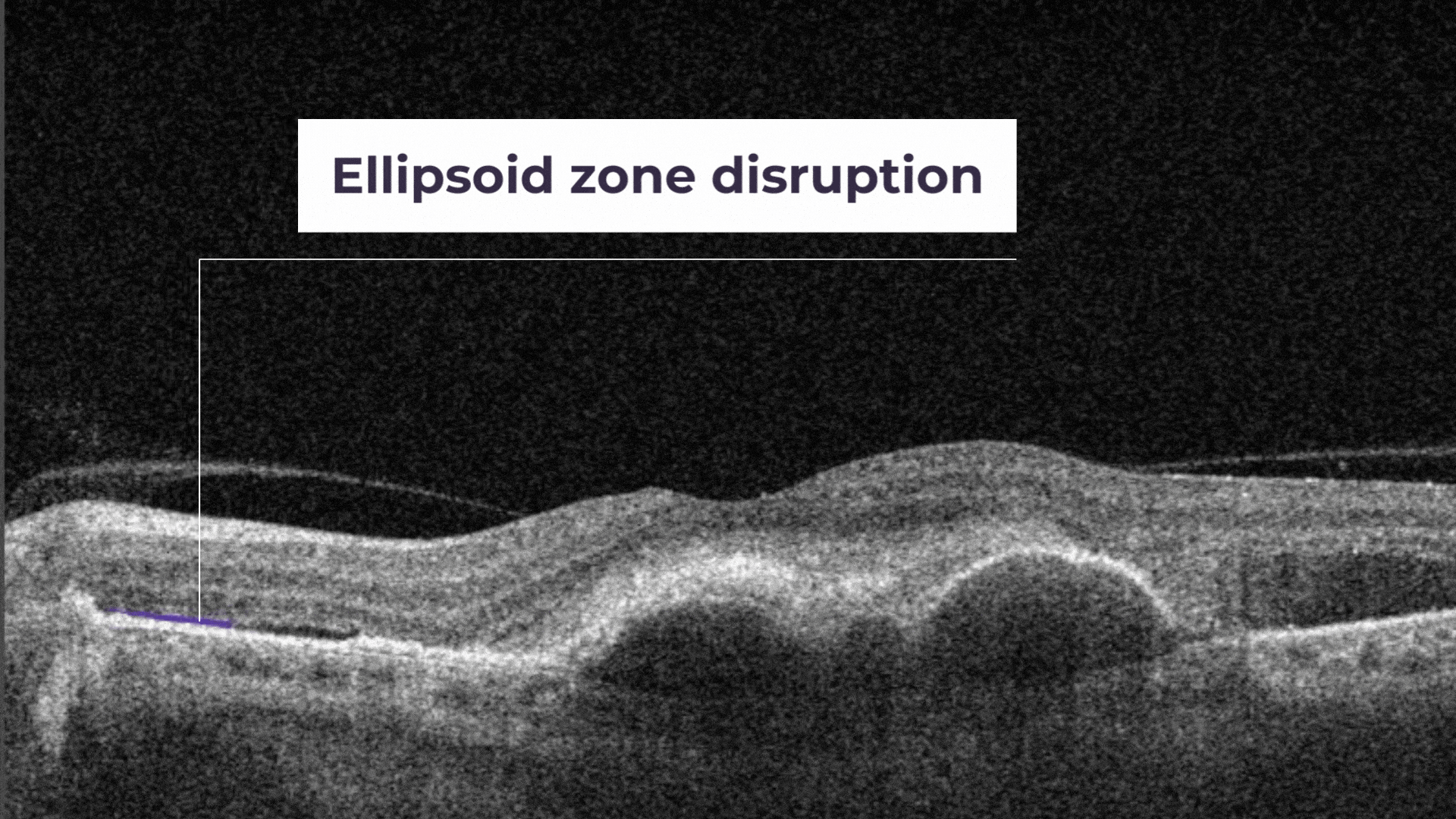
The ellipsoid zone is a hyperreflective outer retinal band just posterior to the external limiting membrane. Its integrity is correlating with visual acuity and other aspects of retinal function.
AI-powered OCT workflow for the patient with dAMD (GA)
Geographic atrophy (GA) is an advanced form of age-related macular degeneration (AMD), characterized by atrophic lesions that first start in the outer retina and progressively expand to cover the macula and the fovea.
-


The platform allows you to analyze Geographic Atrophy (GA) using each of its biomarkers individually. You can also use a dedicated feature to calculate the total GA area and track its progression over time.
-


Hypertransmission can be one of the biomarkers of GA.
-


Hard drusen are small, and indicate lower risk of future vision loss.
-


Soft drusen are larger, cluster together, and have edges that are not as clearly defined.
-


Ellipsoid zone disruption is a hyperreflective outer retinal band just posterior to the external limiting membrane. Its integrity is correlating with visual acuity and other aspects of retinal function.
-


Neurosensory retina atrophy – the atrophy of the inner layer.
-


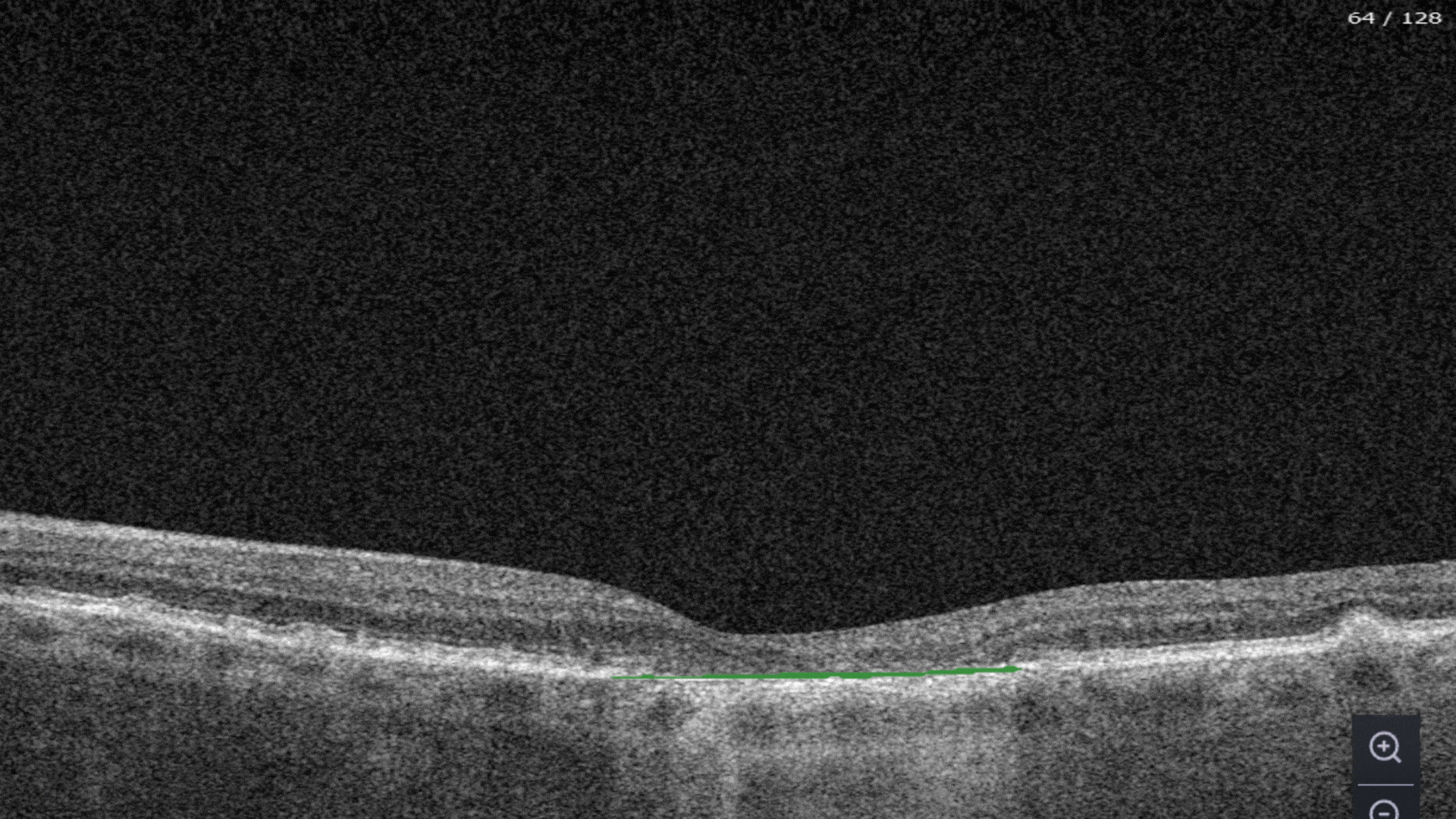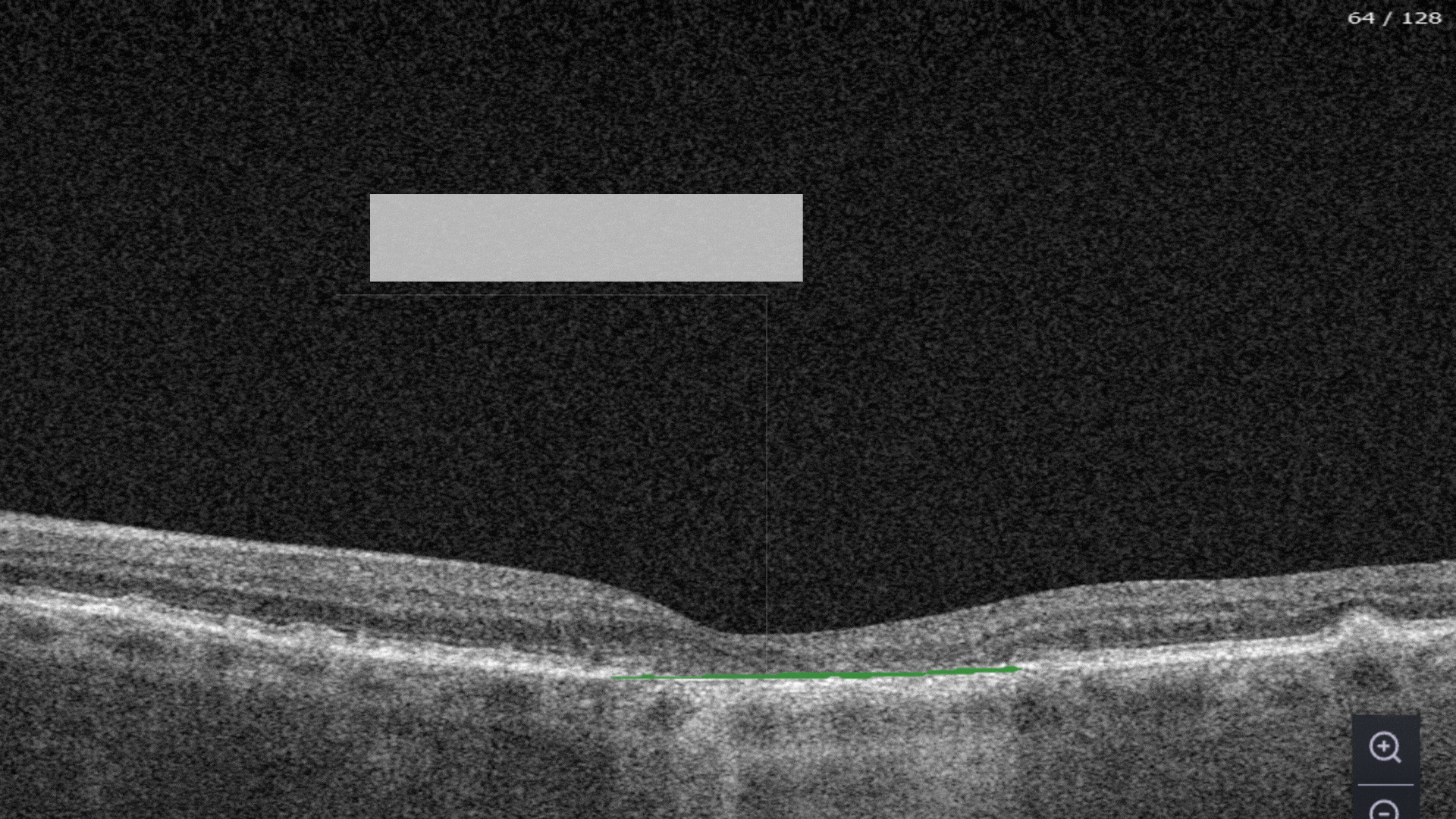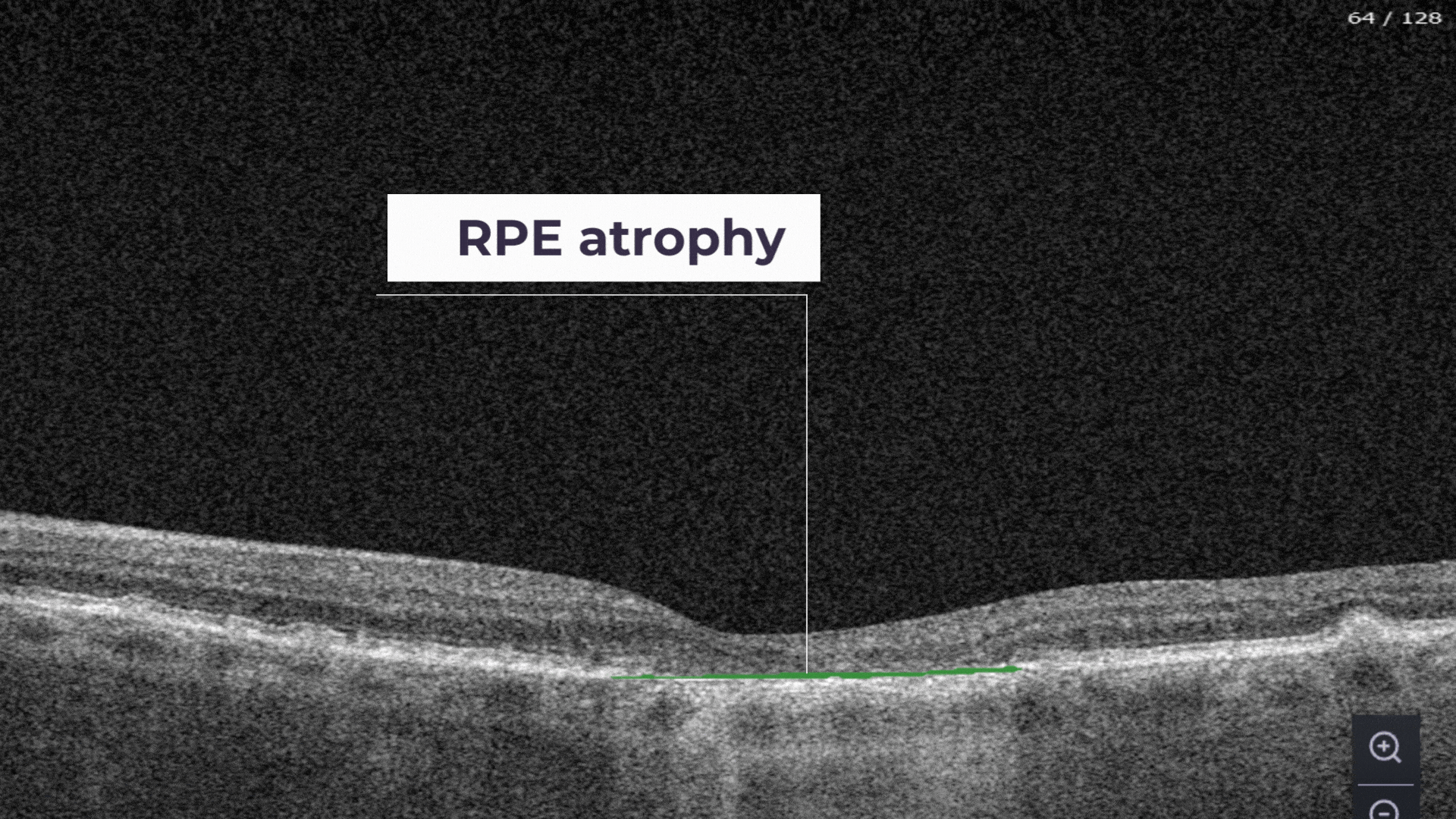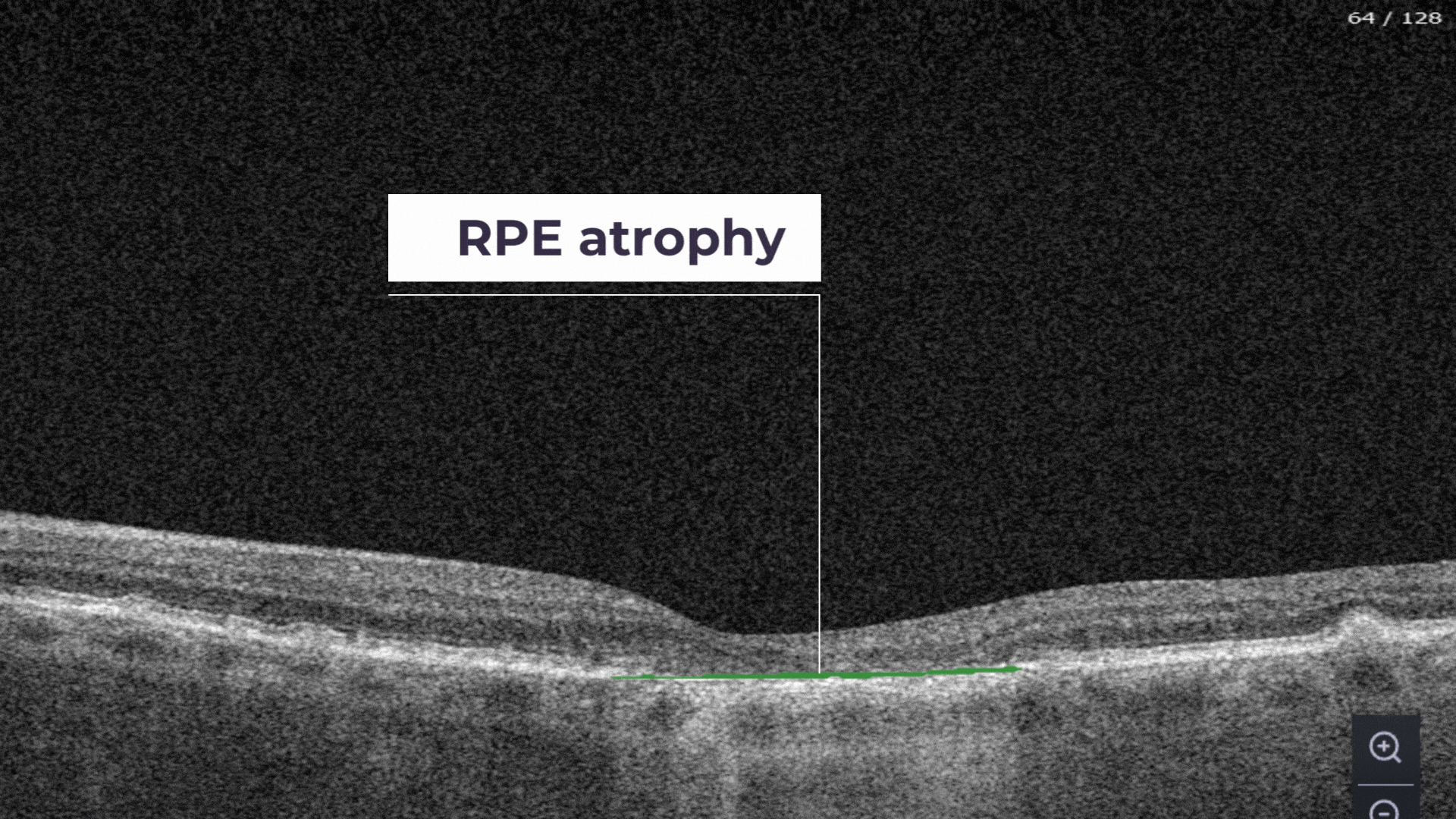
RPE Atrophy – the atrophy of Retinal Pigment Epithelium layer.
-


RPE Disruption – the disruption of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium layer.
nAMD(CNV)
-


Ellipsoid Zone Disruption is a hyperreflective outer retinal band just posterior to the external limiting membrane. Its integrity is correlating with visual acuity and other aspects of retinal function.
-


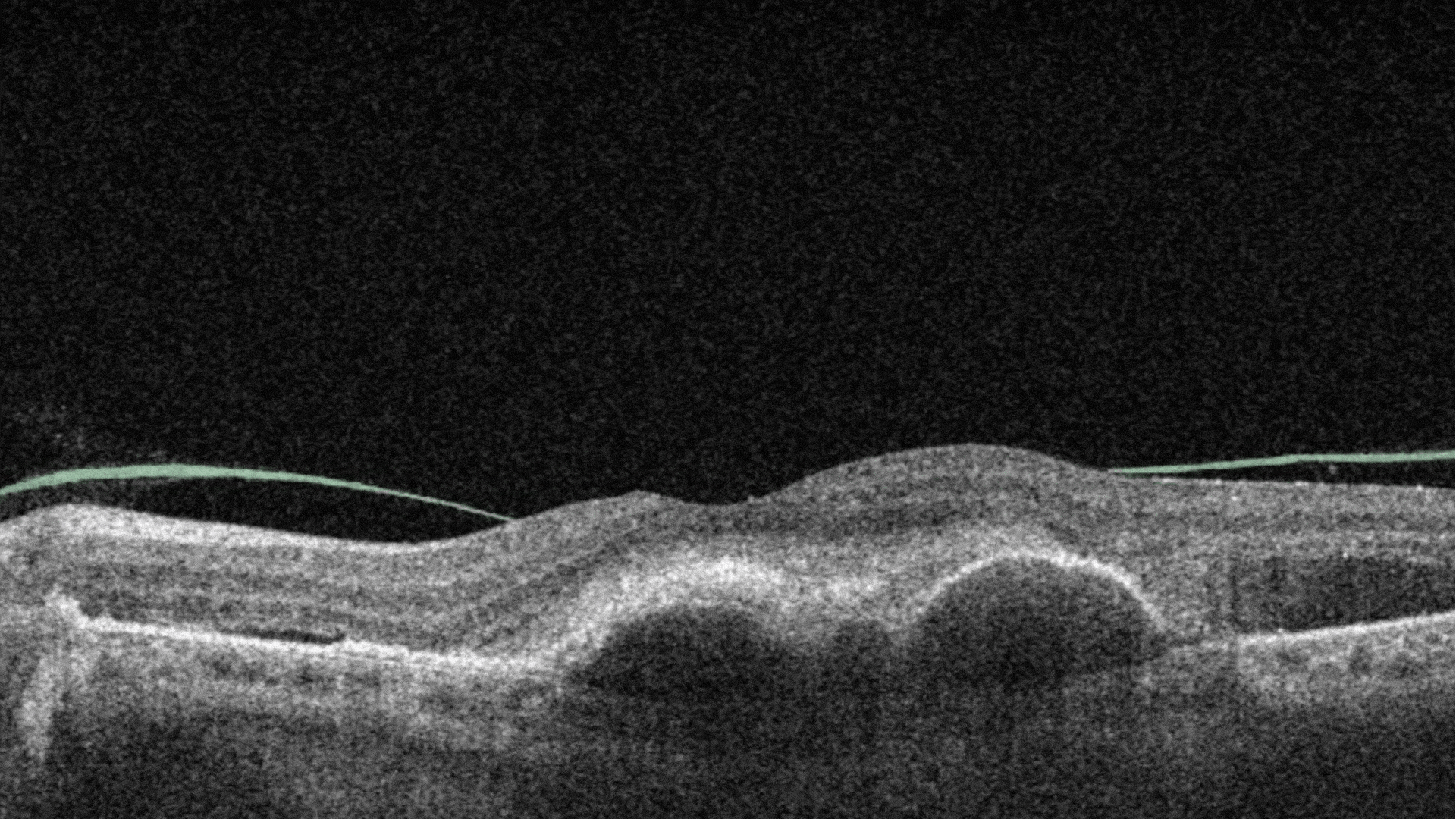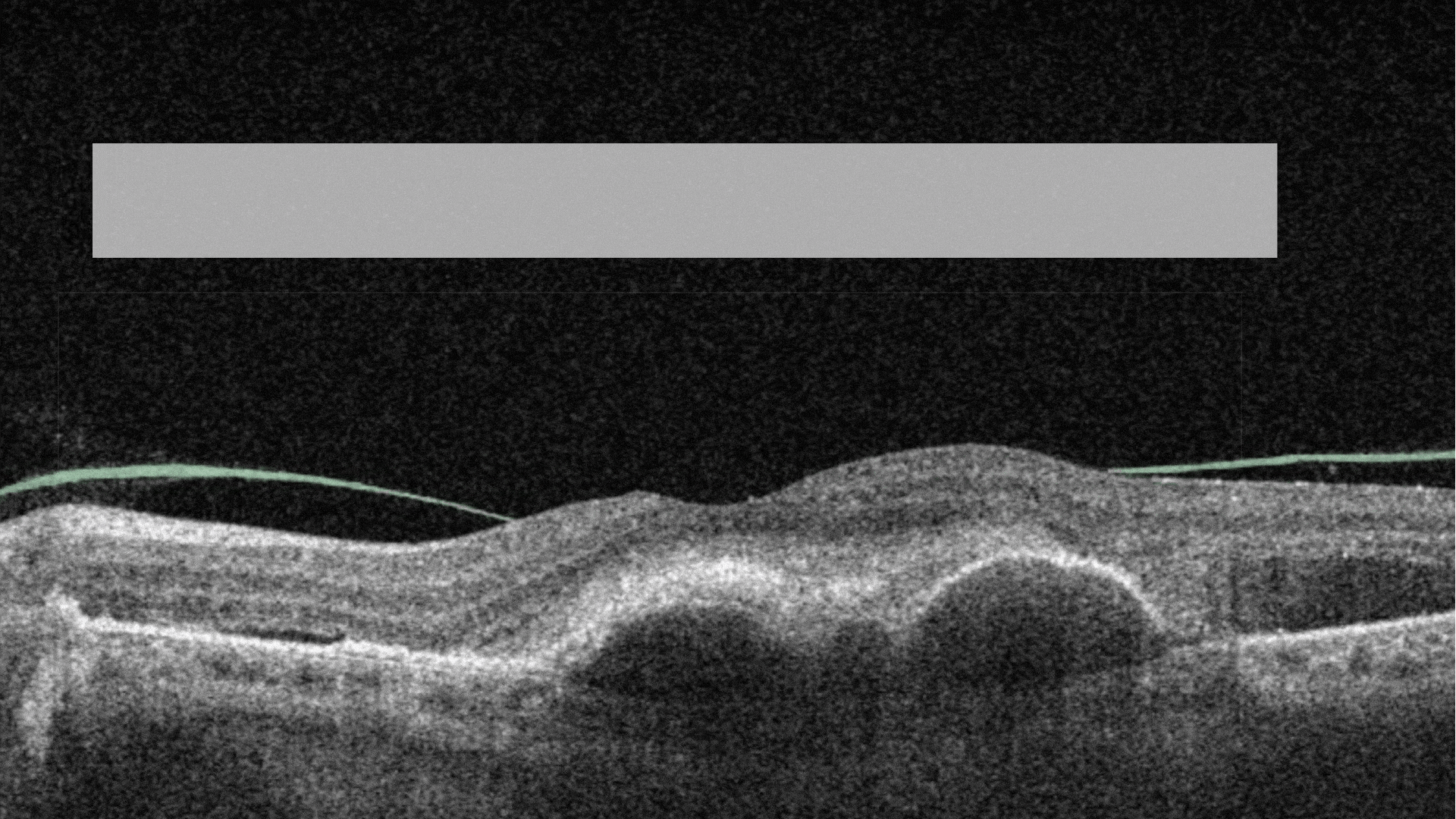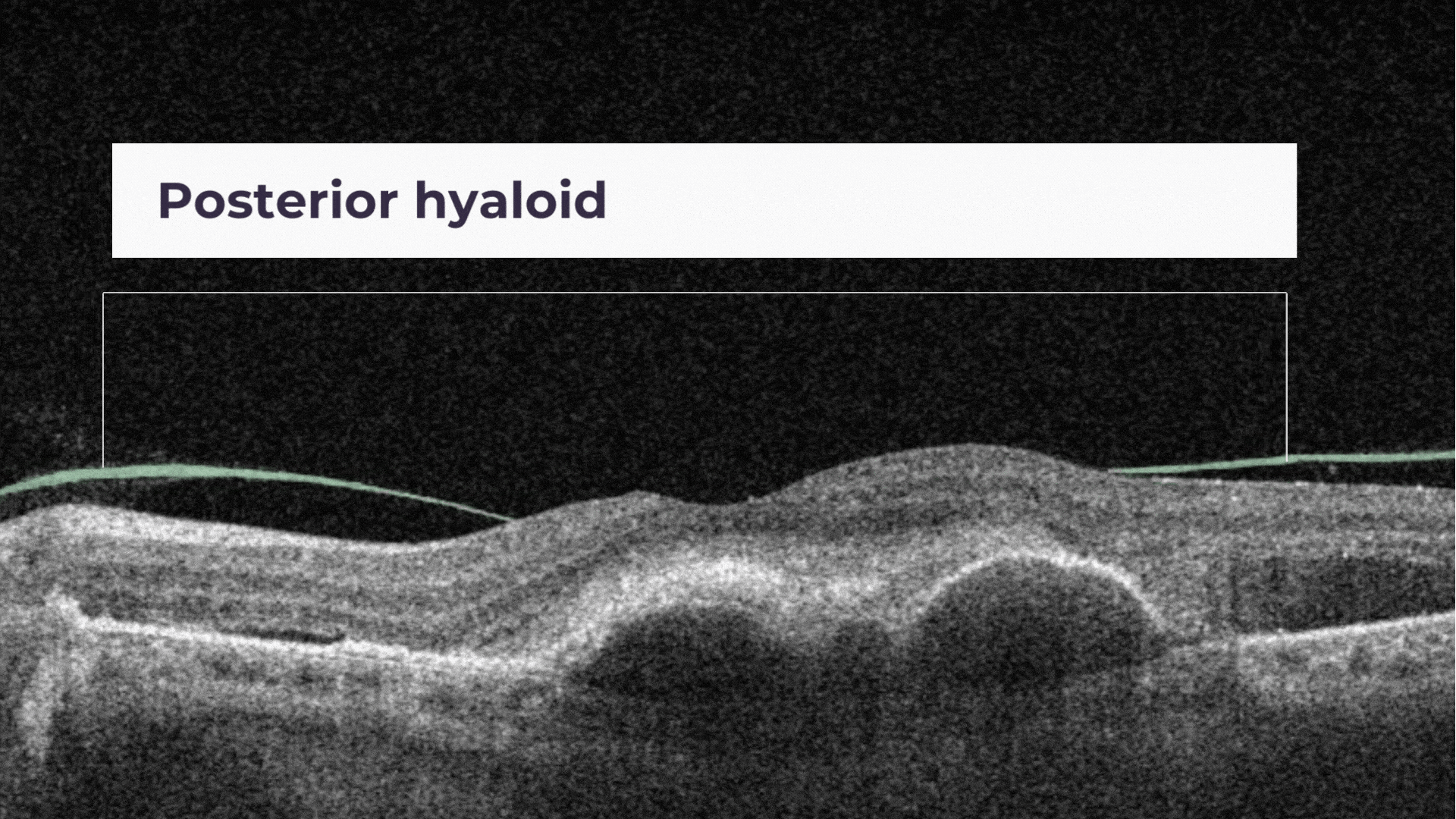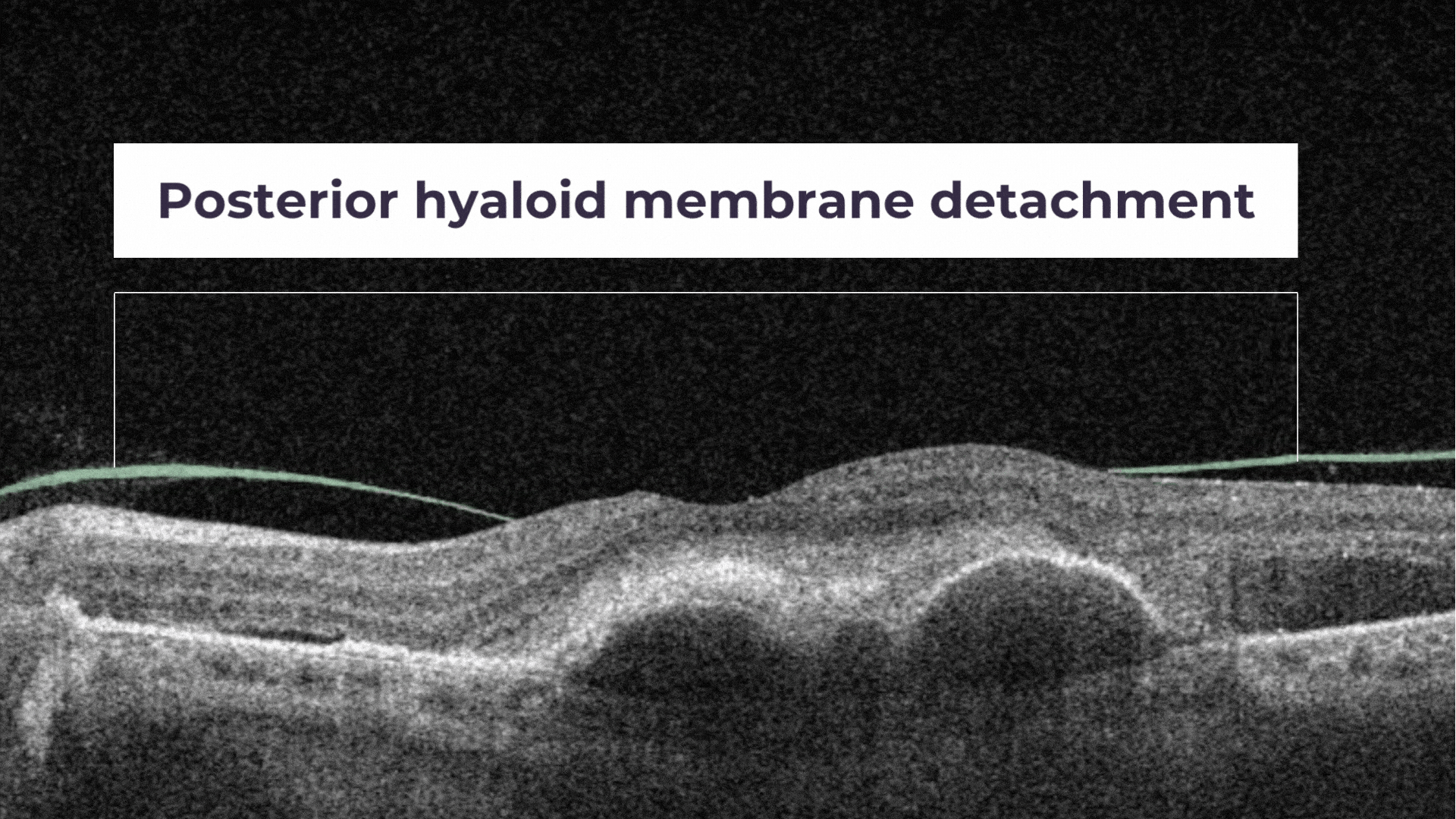
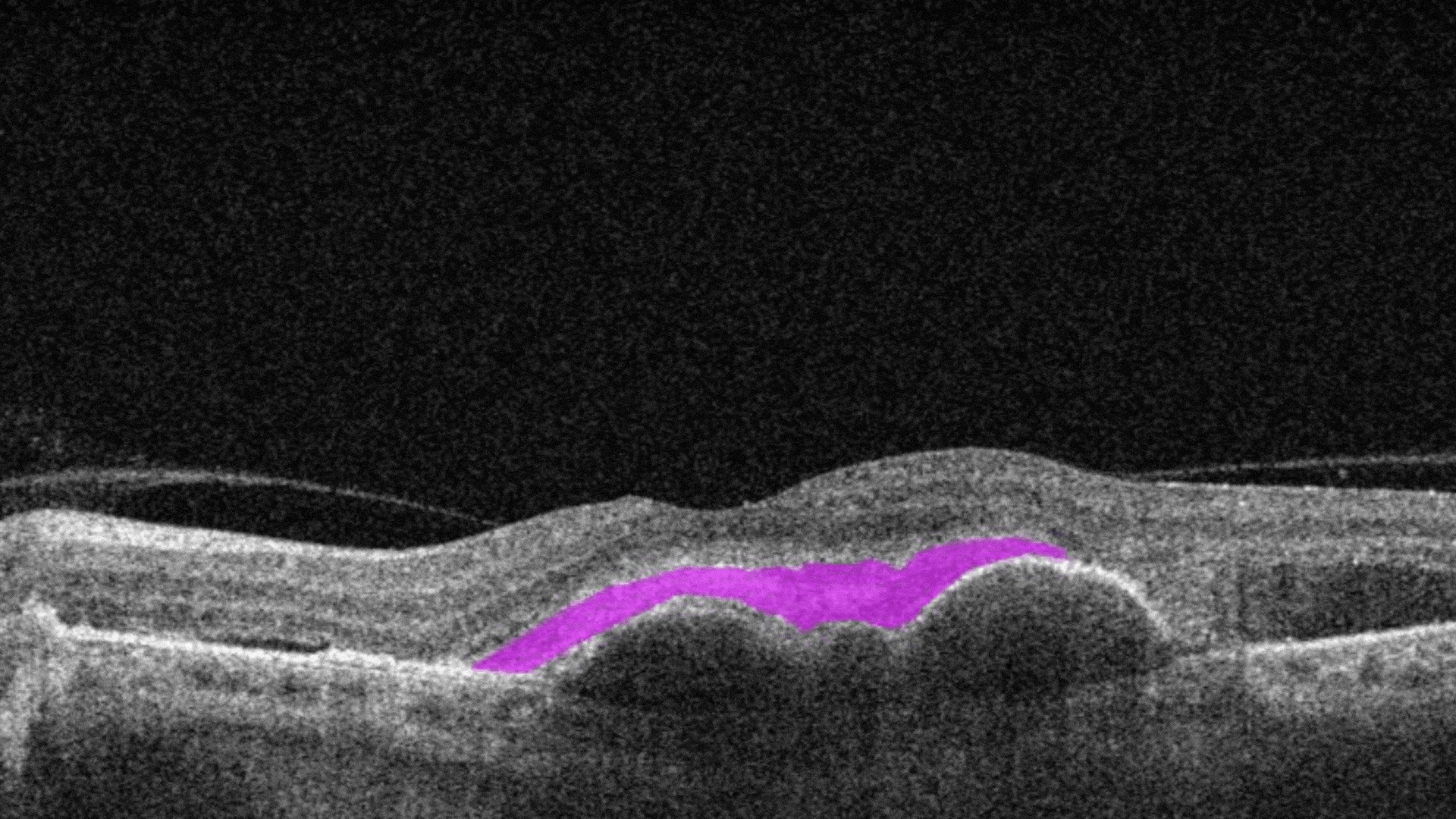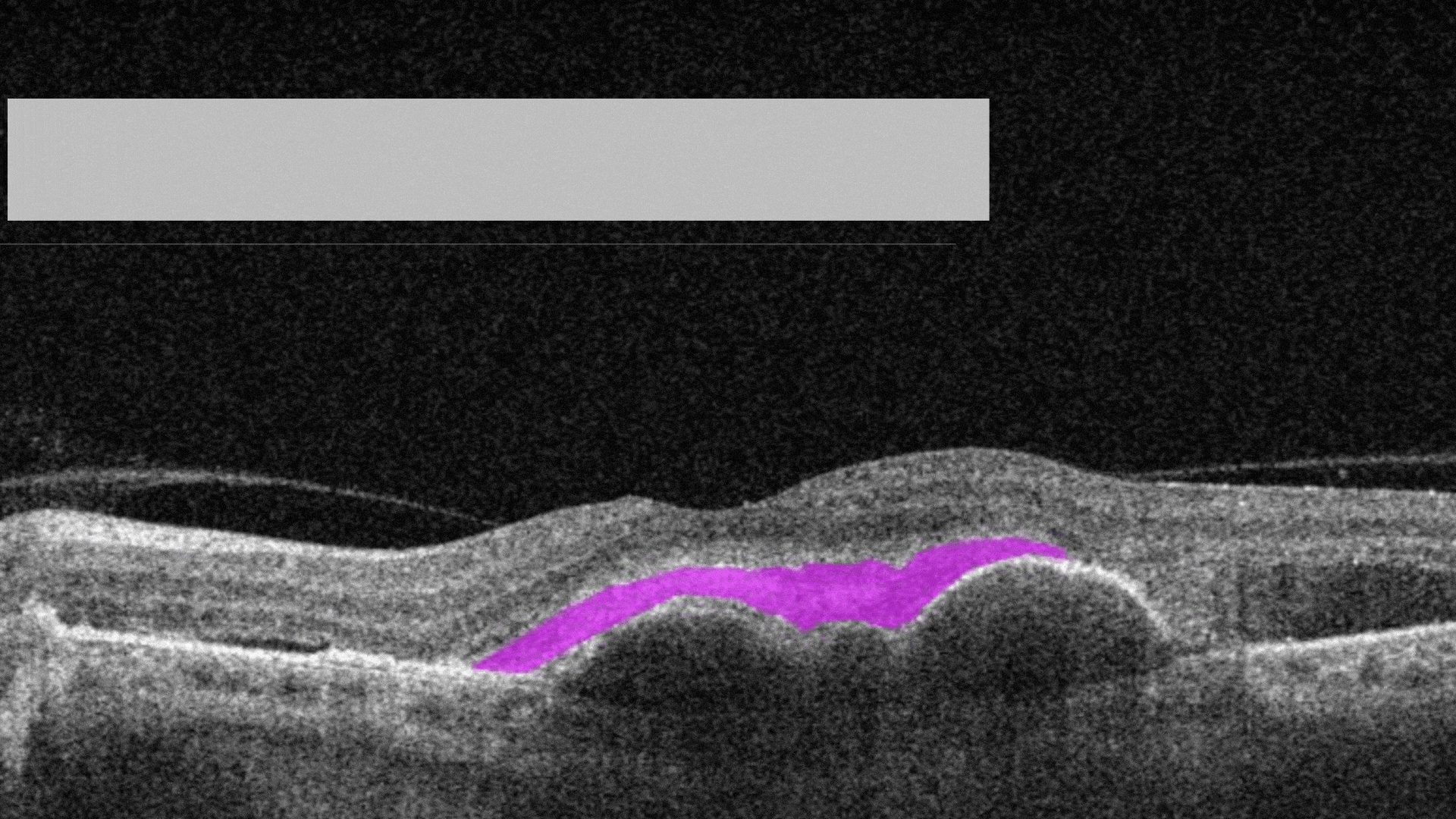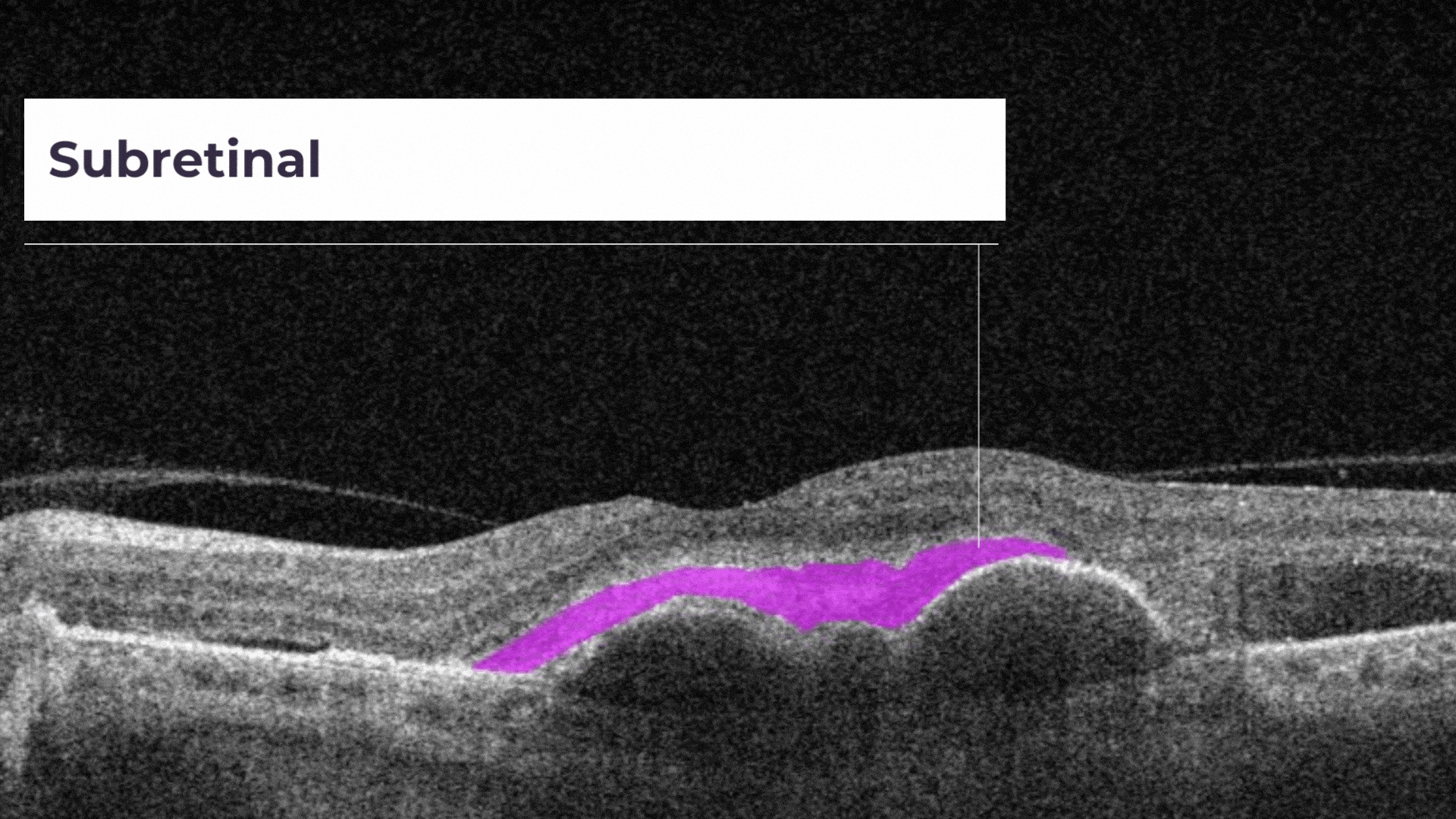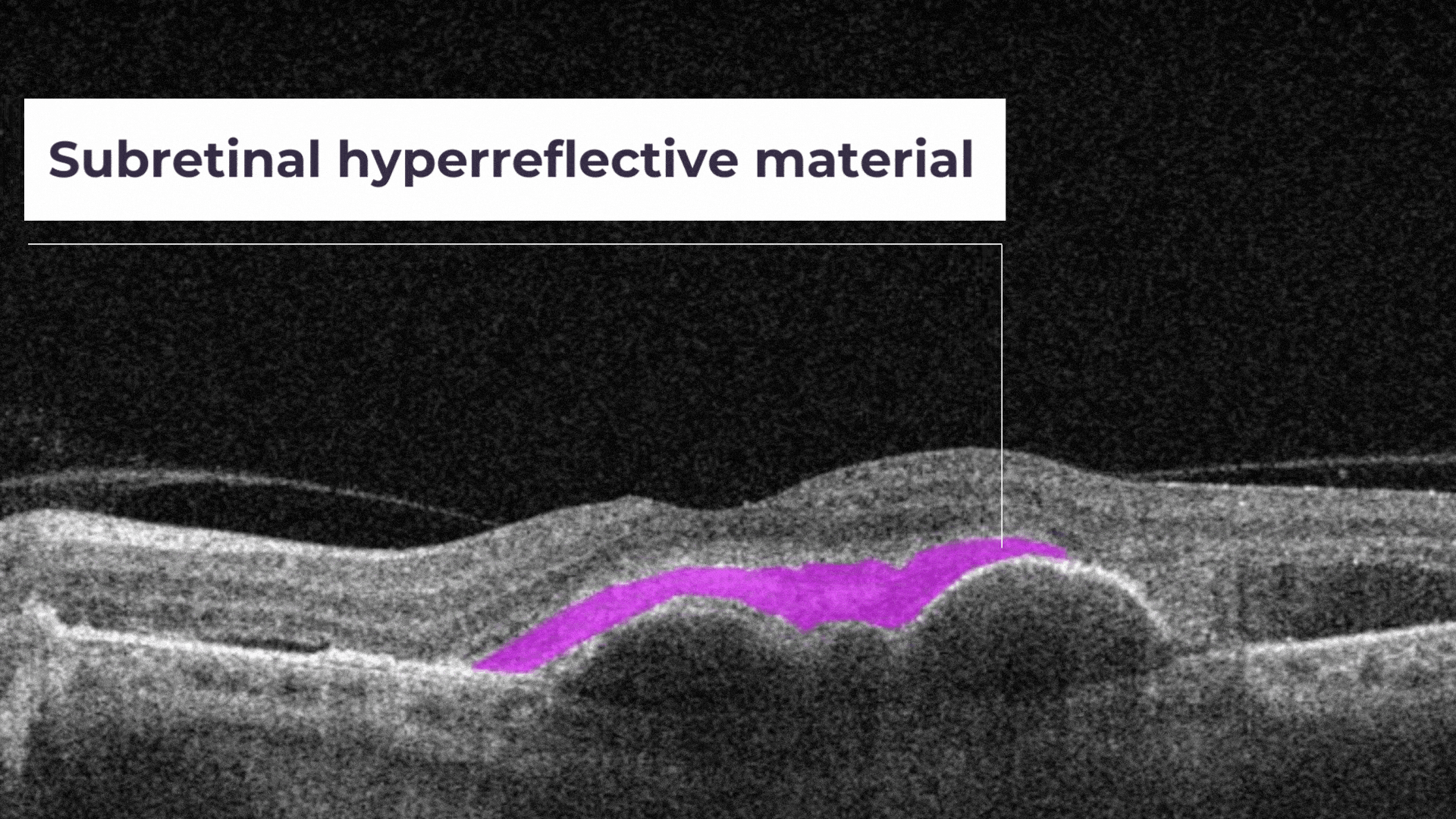
Posterior Hyaloid Membrane Detachment occurs when the retinal layer and vitreous body/posterior hyaloid membrane dissociate, with an intervening fluid collection forming in the subhyaloid space.
-


SHRM is a morphologic component seen as hyperreflective material that is external to the retina and internal to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).
-


Diffuse Edema is a thickened area of lower reflectivity in the outer retina but specifically without cystoid spaces.
-


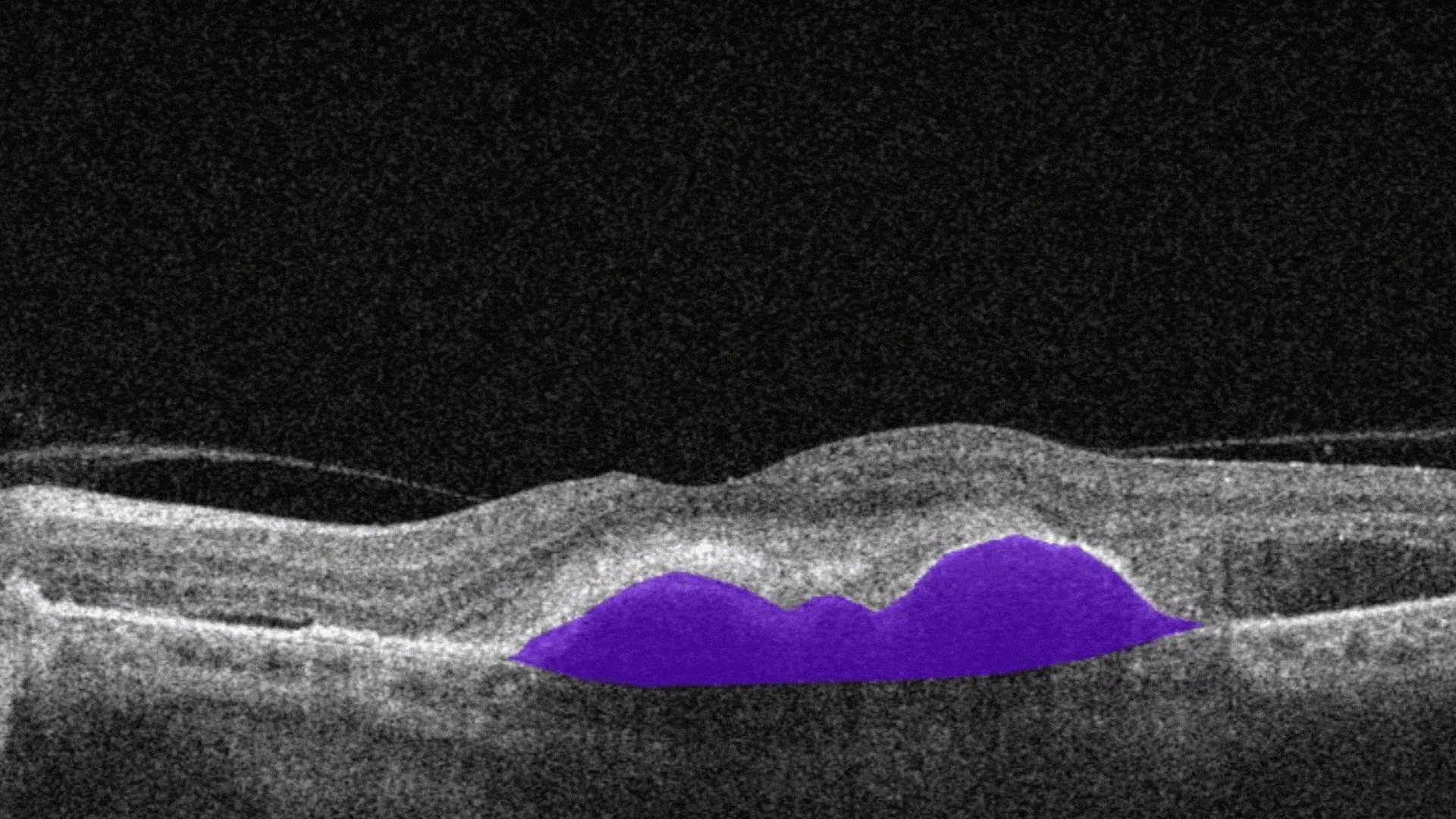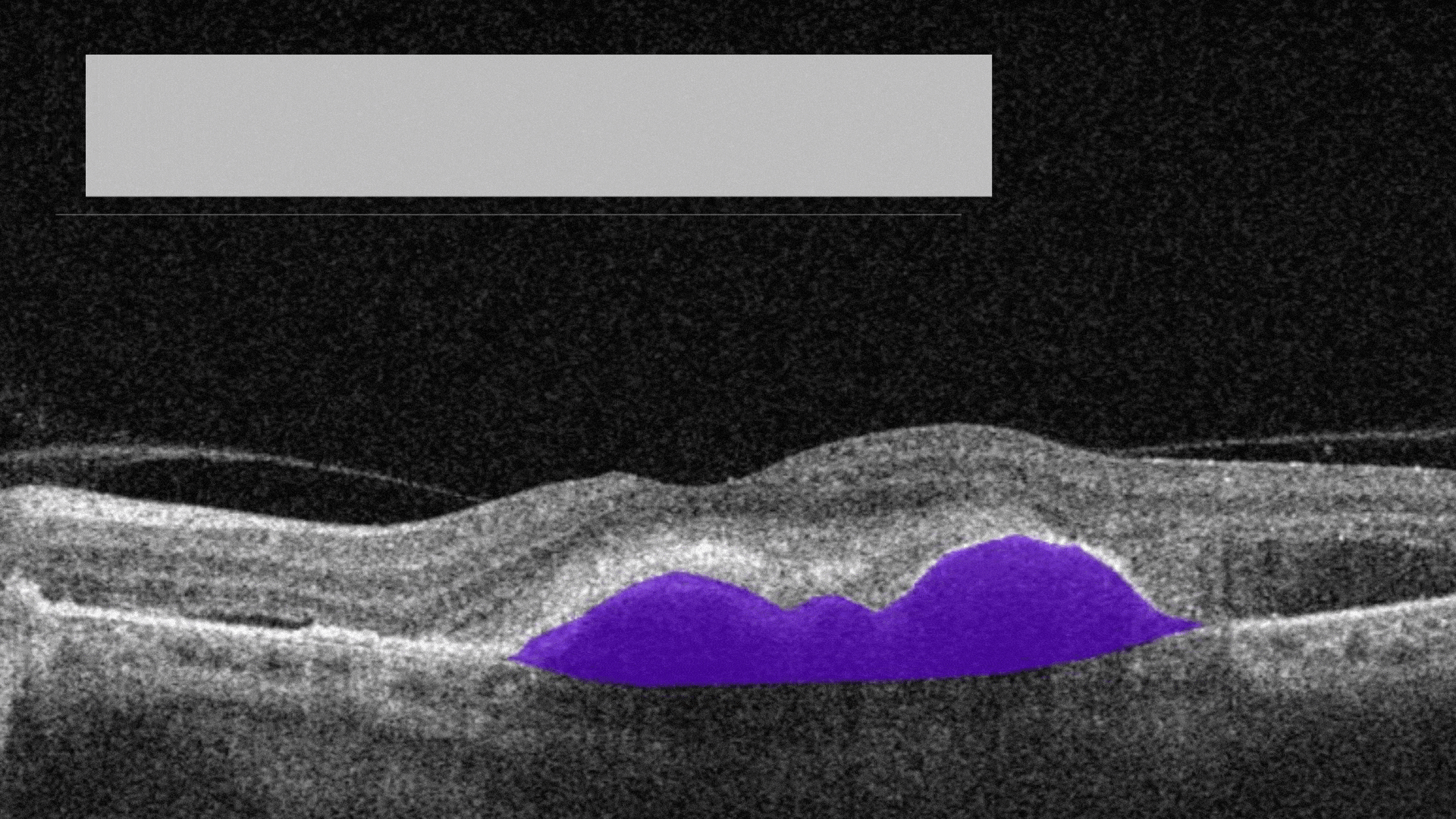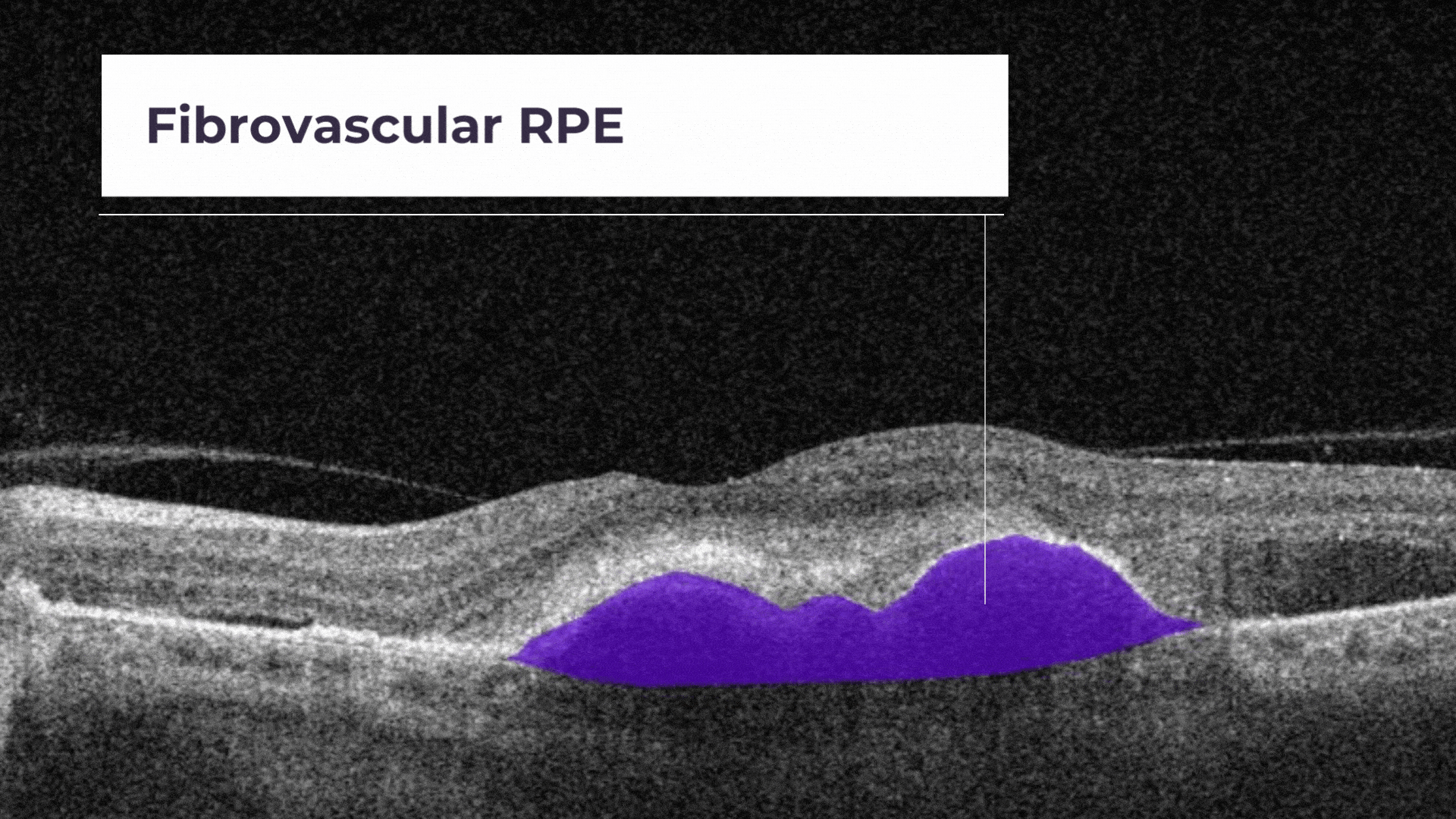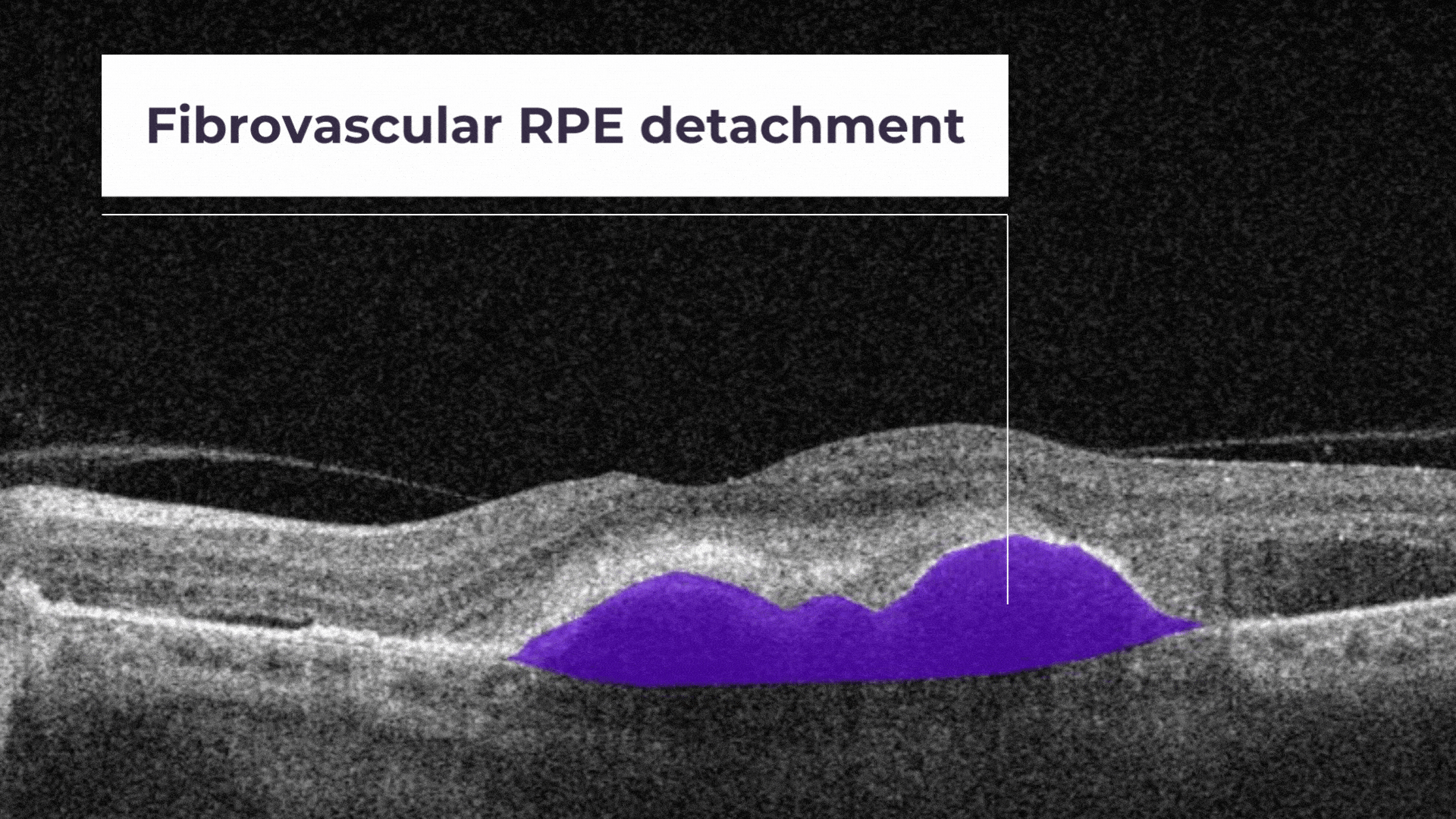
Fibrovascular RPE detachment. Delamination of the pigment epithelium of the retina is caused by the presence of newly formed vessels (fibrovascular membrane) under the RPE.
-


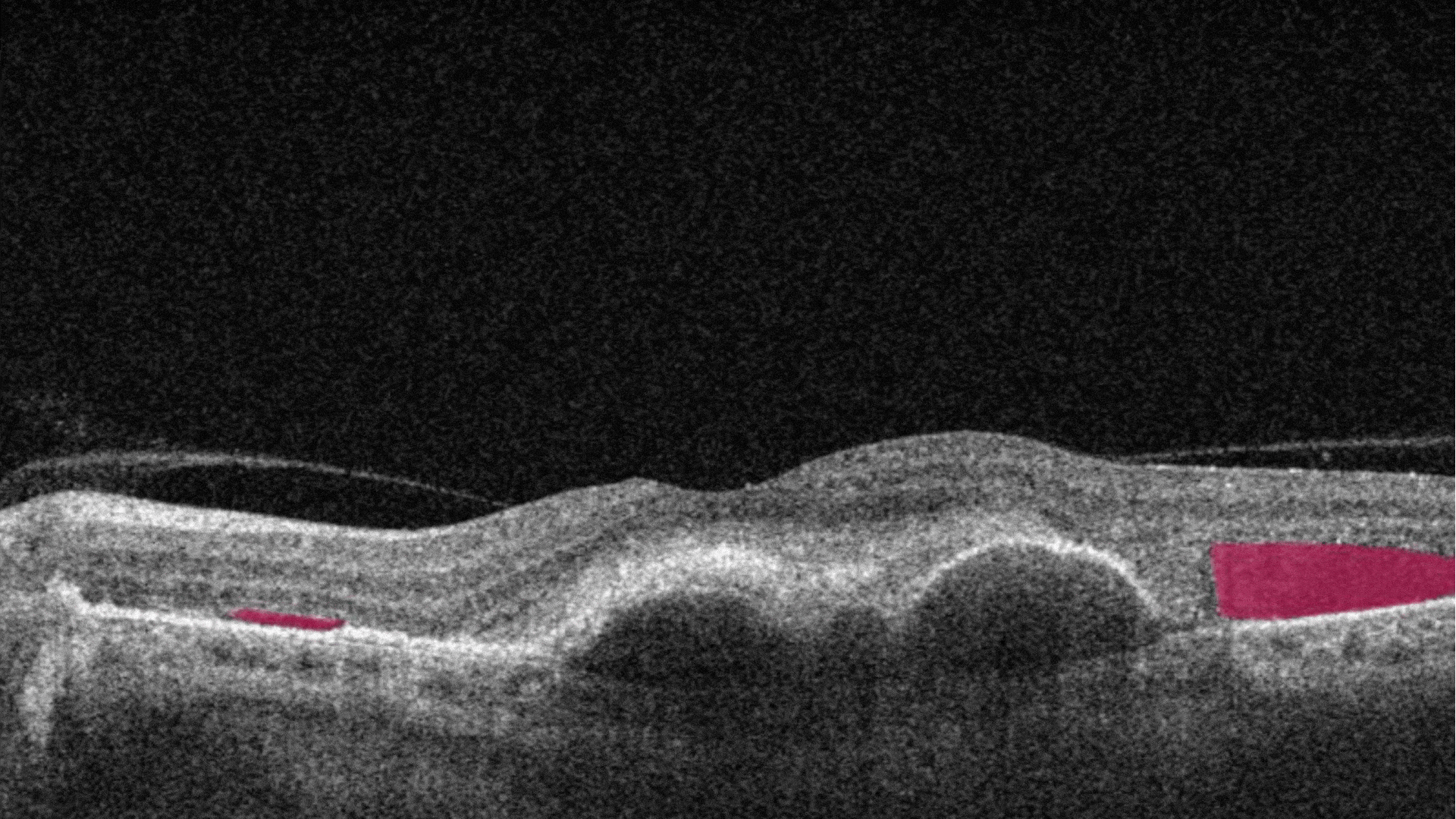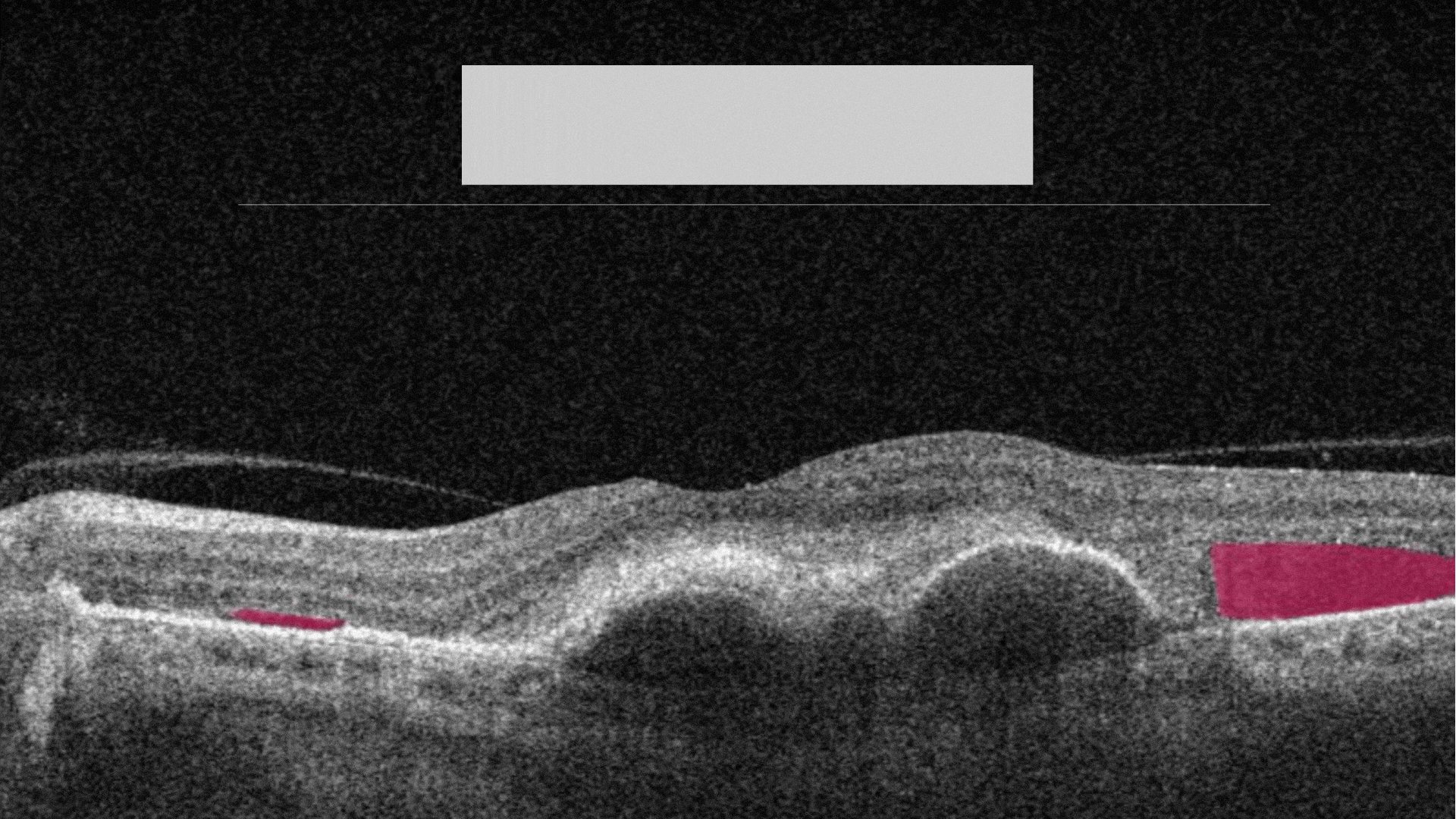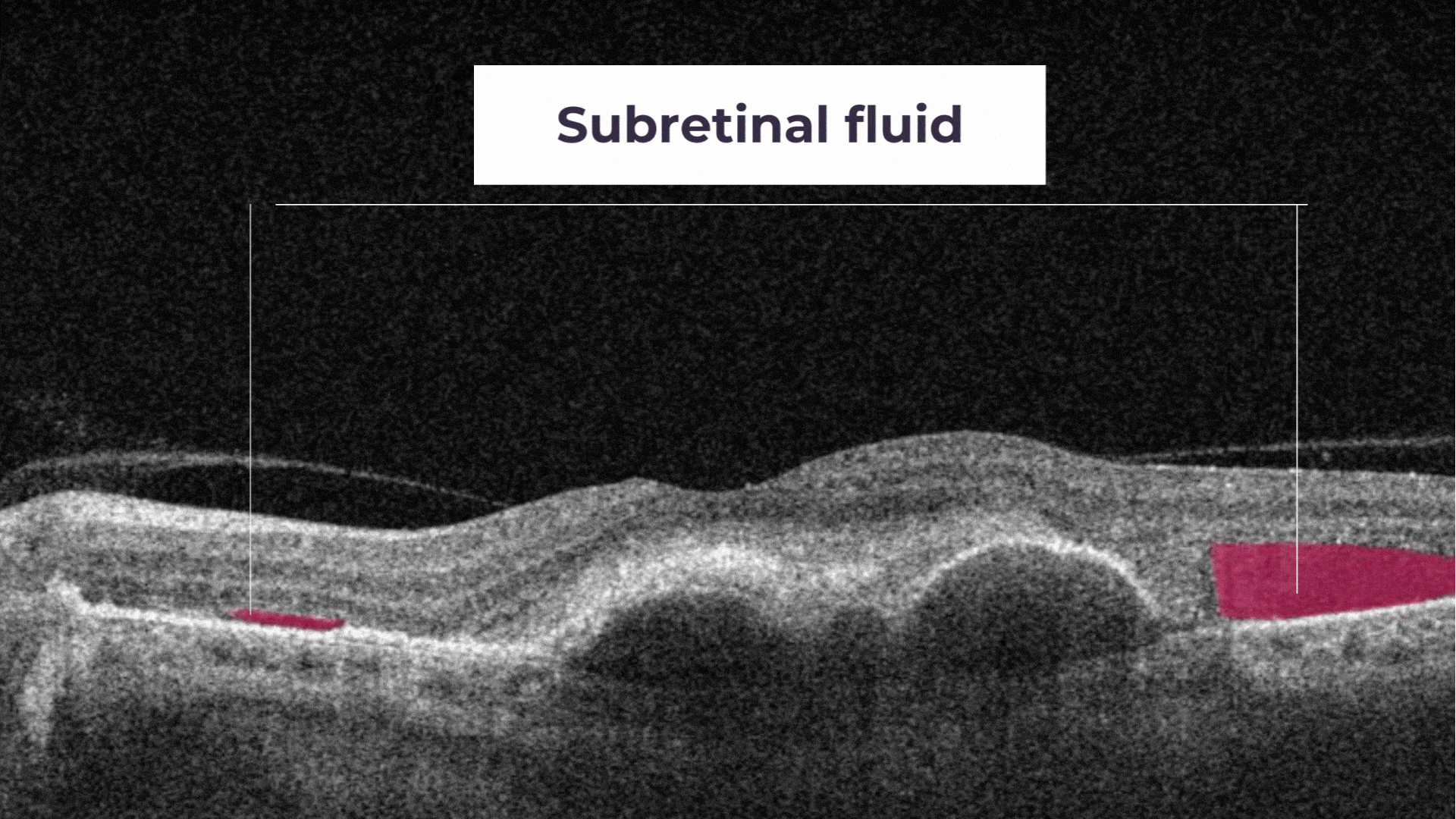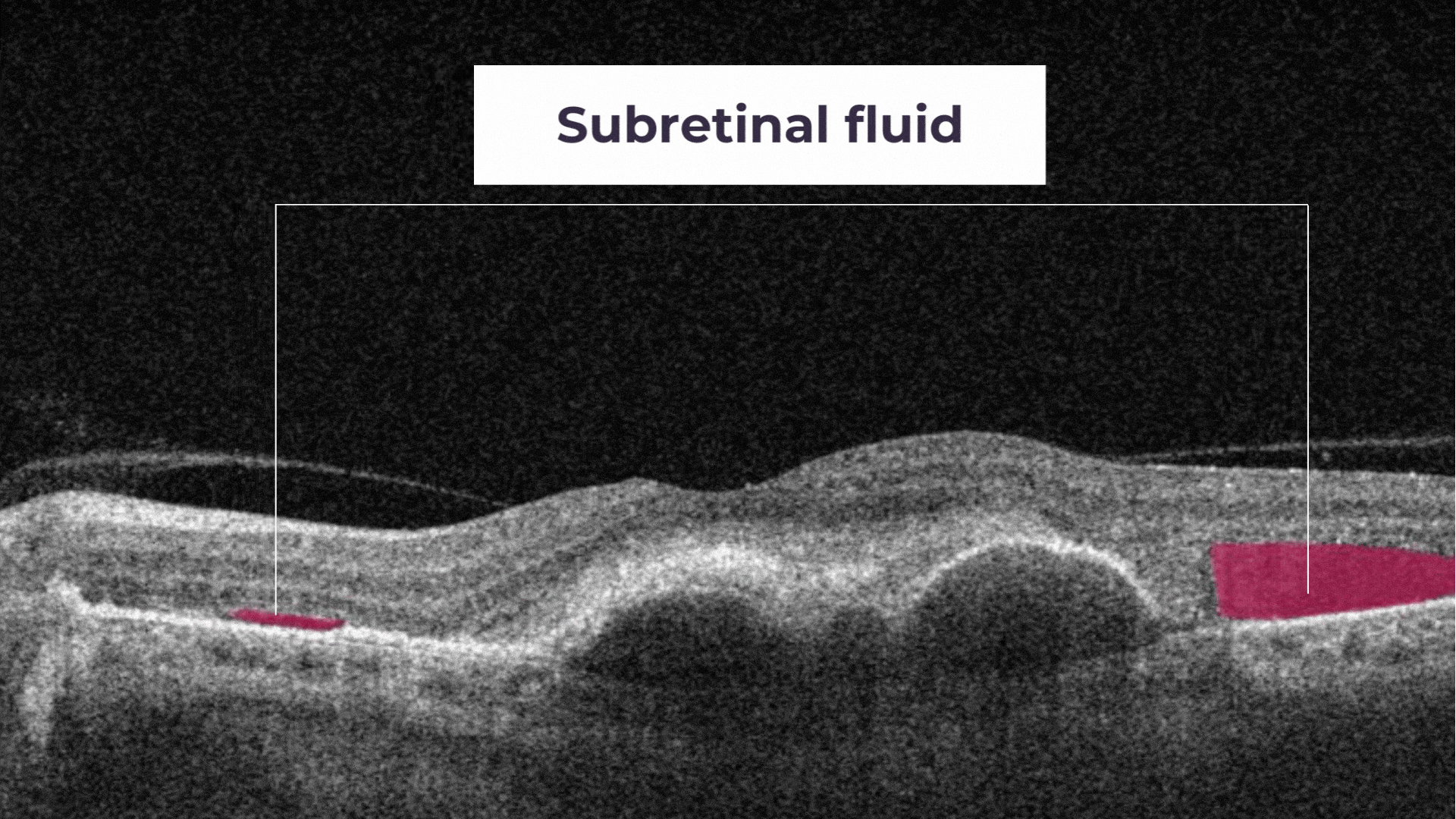
Subretinal Fluid corresponds to the accumulation of a clear or lipid-rich exudate (serous fluid) in the subretinal space.
-


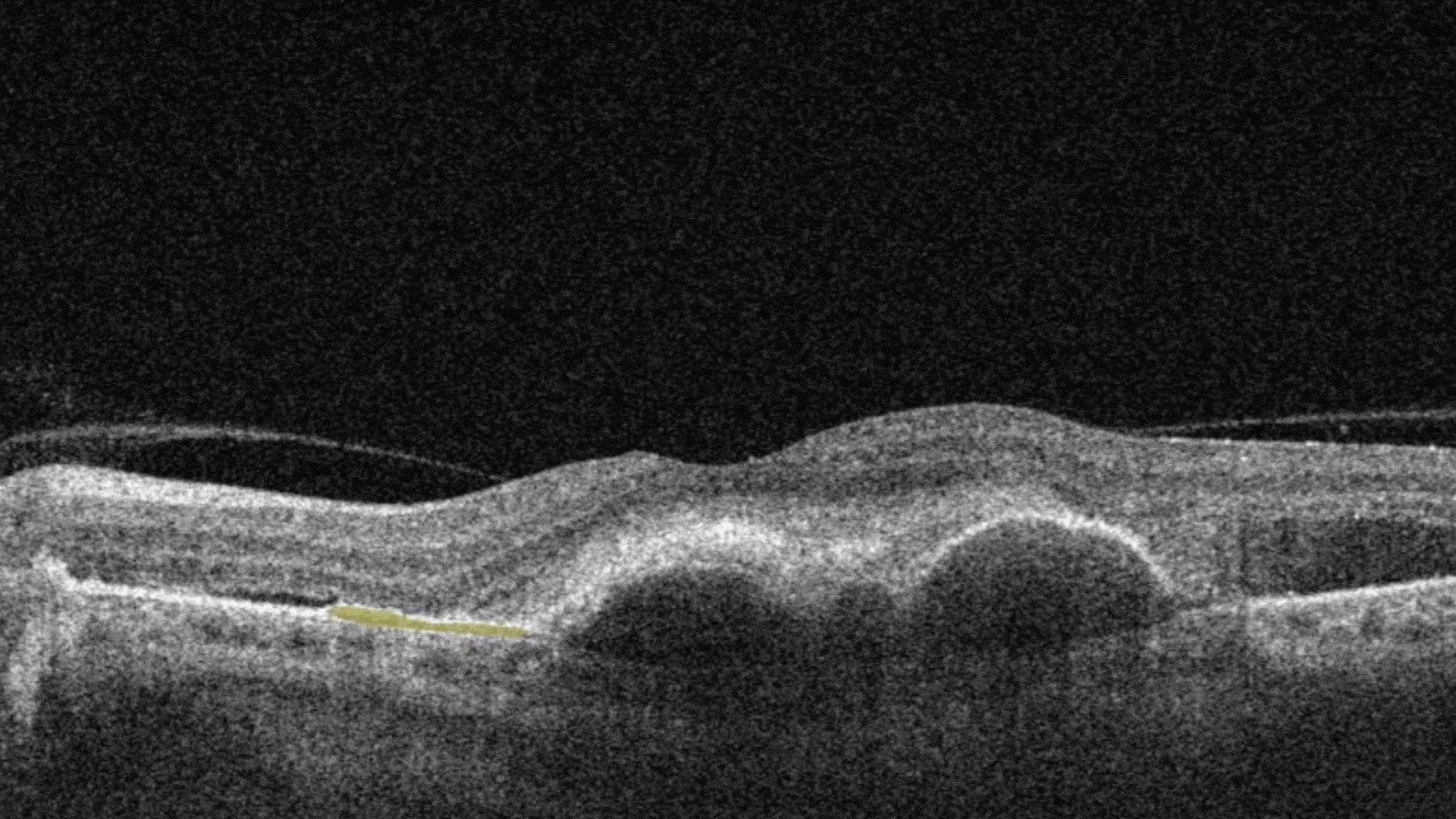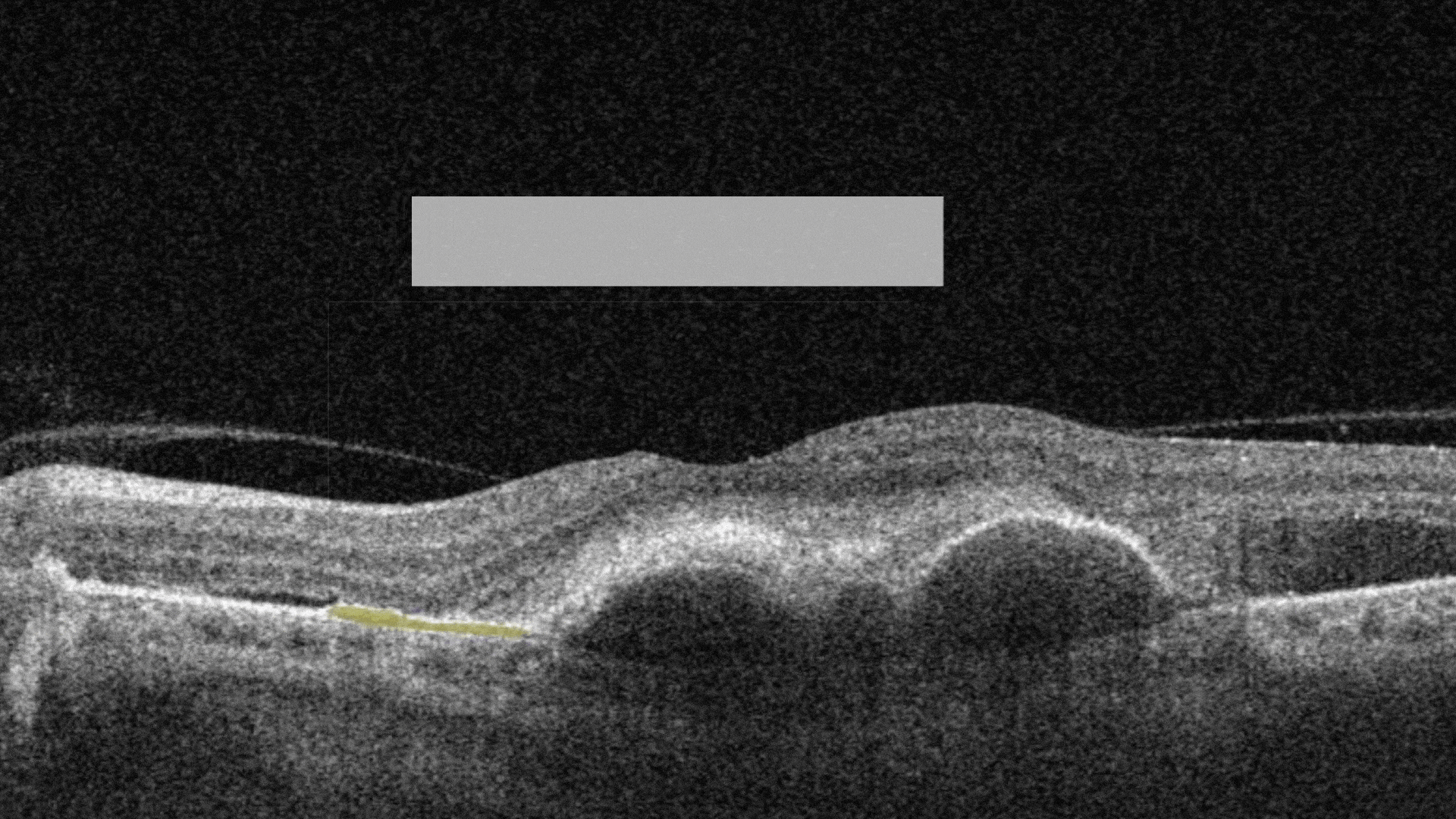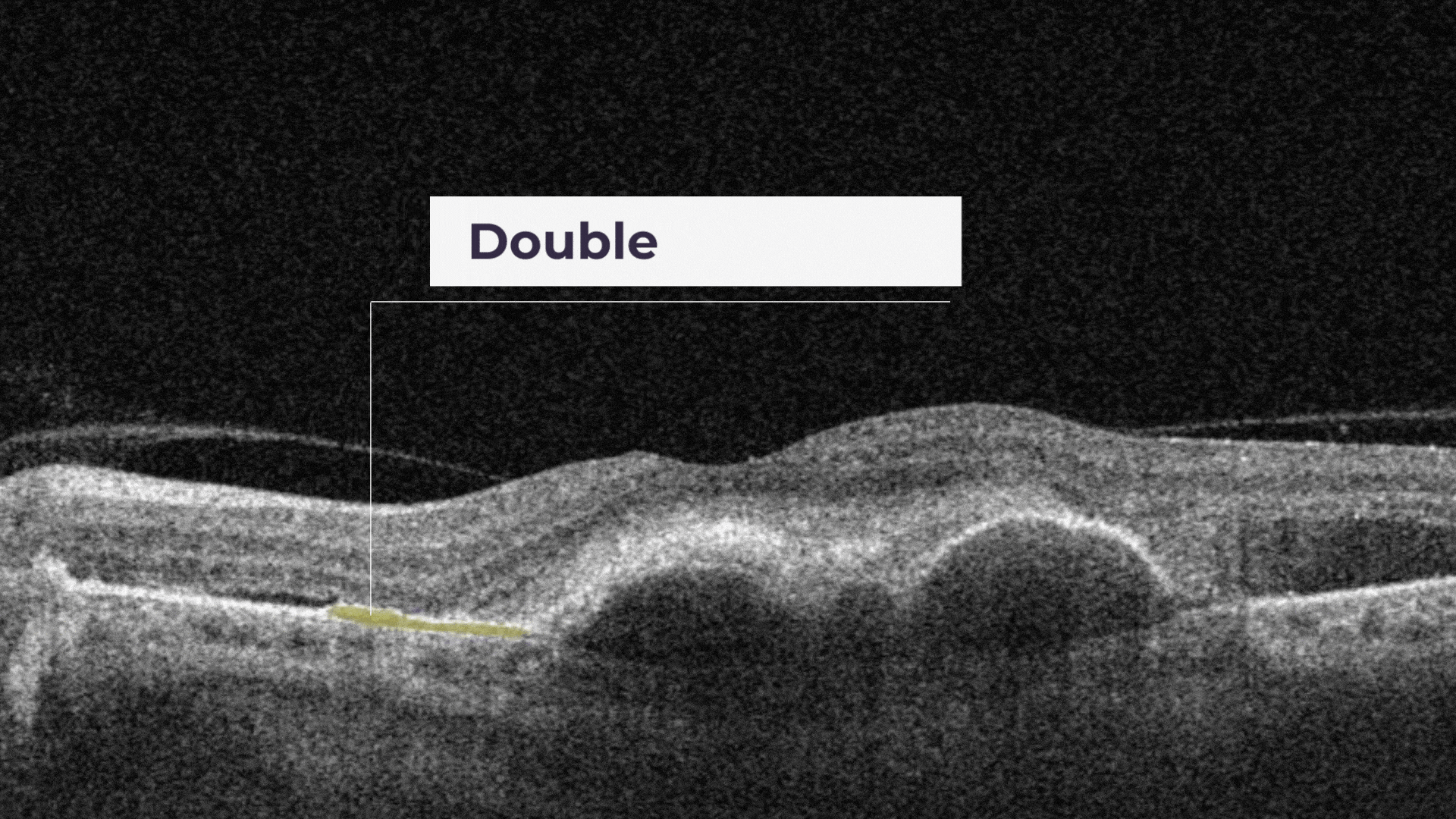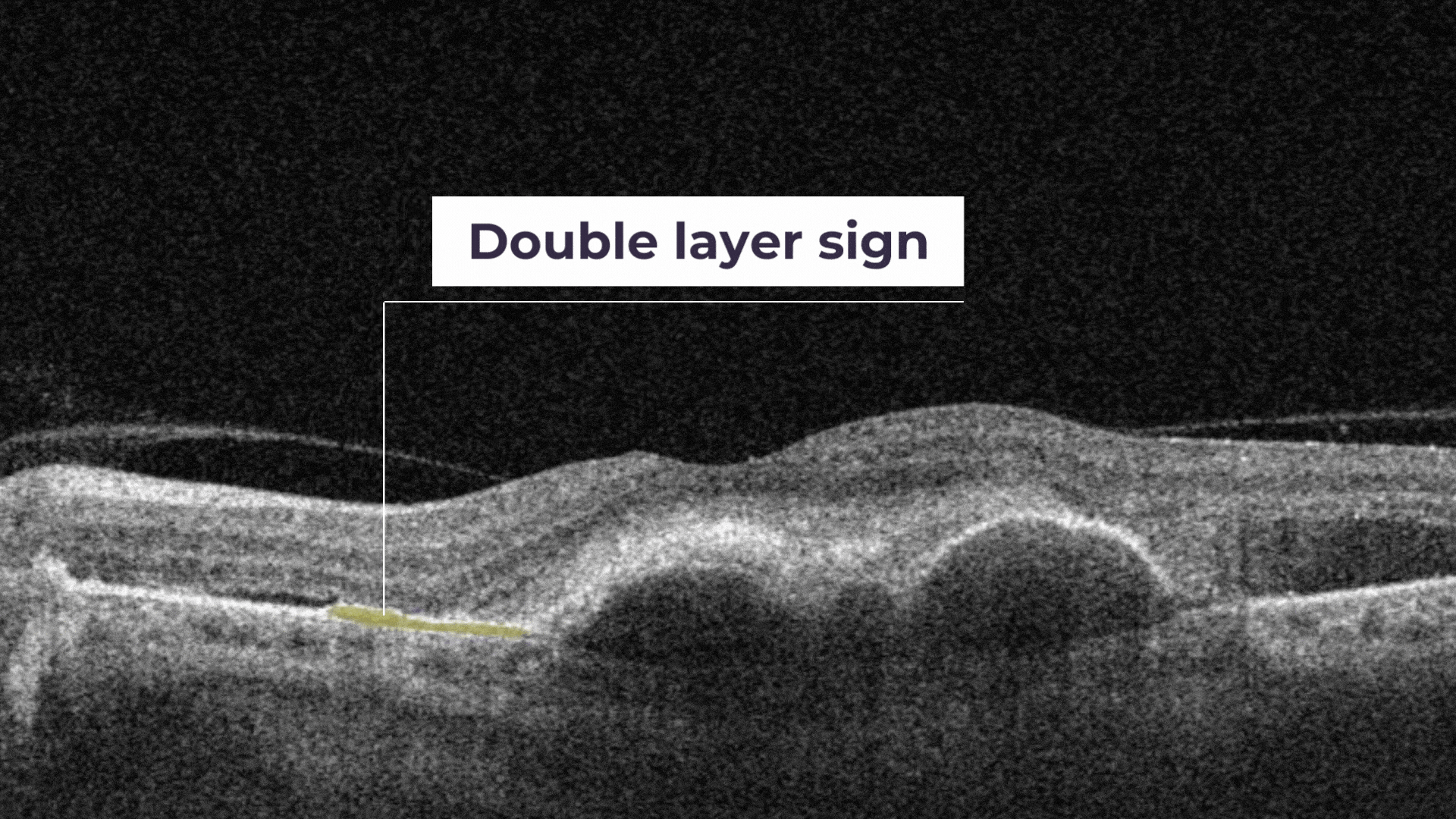
Double layer sign is a biomarker that is produced due to the shallow irregular pigment epithelial detachment.
-


RPE Disruption is the disruption of the Retinal Pigment Epithelium layer.
See how it works in a Demo
Demo Account
AI for OCT scan analysis offers every ophthalmologist a chance to unleash the full potential of this diagnostic tool.
OCT is the most effective method of retina diagnosis yet it requires years of learning and practice to truly master it. AI-powered OCT workflow becomes a solid and reliable diagnostic decision-making support tool for optometrists and dispensing opticians.
- Altris AI detects 70+ pathologies and biomarkers
- Altris AI assesses early risk of glaucoma
- Altris AI enables quantitative progression analysis of biomarkers
- Altris AI provides the chance to build customisable reports